Abstract
The water flow in the dam spillway has a lot of energy. This energy can cause an increase in flow velocity, damaging the installations as well as erosion of the riverbed in downstream. The use of stepped spillways is one of the common methods to dissipate energy during the flow of spillway and reduce the dimensions of the stilling basin in the dams. One of the main parameters affecting the rate of energy loss in stepped spillways is the spillway geometry. In this study, the effect of using five different stairs with new and different geometries, in comparison with previous studies, was investigated in terms of energy dissipation. The simulation was performed by Flow 3D software and by the turbulence model (RNG) for discharges between 0.00213 and 0.0121 m3/s. The (RNG) and (k–ε) turbulence models were used for calibration, which (RNG) had better results. The simulation results were compared with the experimental model results where the RMSE error index for type A–E spillways, 0.035, 0.014, 0.021, 0.032, and 0.031, respectively. After this step, to improve the experimental model, barriers were placed on the type D spillway, which was the best experimental model for energy dissipation. Numerical simulation results show that adding these barriers increases the energy dissipation by 15%.


















Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Fractional area-volume obstacle representation.
Abbreviations
- \(\theta\) :
-
Stepped spillway slope in degrees
- B :
-
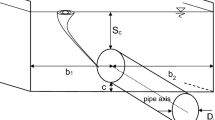
Channel width (m)
- E L :
-
Total energy loss: EL = E0–E1 (expressed in m)
- E 0 :
-
Energy at the inlet section (upstream section; m)
- E 1 :
-
Energy at the downstream section (m)
- EL/E0 :
-
Energy dissipation rate
- E1/yc :
-
Dimensionless residual energy
- y 0 :
-
Upstream clear water flow depth (m)
- y 1 :
-
Downstream clear water flow depth (m)
- y c :
-
Critical flow depth (m)
- yc/h :
-
Critical no dimensional depth
- H dam :
-
Dam height (crest height) (m)
- h :
-
Vertical step height (m)
- Q :
-
Water discharge (m3/s)
- q :
-
Water discharge per unit width (m2/s), q = Q/B
- v 1 :
-
Downstream flow velocity (m/s)
- v 0 :
-
Upstream average flow velocity (m/s)
- \({\text{Fr}}^{*}\) :
-
Froude number in the stepped spillway
References
Aminpour Y, Farhoudi J (2017) Similarity of local scour profiles downstream of stepped spillways. Int J Civ Eng 15(5):763–774
Bai Z, Wang Y, Zhang J (2017) Pressure distributions of stepped spillways with different horizontal face angles. Inst Civ Eng Water Manag 171(6):299–310
Carosi G, Chanson H (2008) Turbulence characteristics in skimming flows on stepped spillways. J Civ Eng 35(9):865–880
Chamani MR, Rajaratnam N (1999) Characteristics of skimming flow over stepped spillways. J Hydraul Eng ASCE 125(4):361–368
Chanson H (2001) The hydraulics of stepped chutes and spillways. Balkema, Lisse
Estrella S, Sánchez-Juny M, Bladé E, Dolz J (2015) Physical modeling of a stepped spillway without sidewalls. J Civ Eng 42(5):311–318
Felder S, Chanson H (2013) Aeration, flow instabilities, and residual Drain. J Struct Eng ASCE 139(10):880–887
Flow Science (2016) Incorporated: FLOW-3D UsersManual Version 11.04. Santa Fe, New Mexico
Gamal M et al (2018) Improving energy dissipation on stepped spillways using breakers. Ain Shams Eng J 9(4):1887–1896
Hekmatzadeh A, Papari S, Amiri SM (2018) Investigation of energy dissipation on various configurations of stepped spillways considering several RANS turbulence models. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Civ Eng 42(2):97–109
Li S, Jianmin Z, Weilin X (2017) Numerical investigation of air–water flow properties over steep flat and pooled stepped spillways. J Hydraul Res 56(1):1–14
Mero Sh, Mitchell S (2016) Investigation of energy dissipation and flow regime over various forms of stepped spillways. Water Environ J 31(1):127–137
Mohammad Rezapour Tabari M, Tavakoli Sh (2016) Effects of stepped spillway geometry on flow pattern and energy dissipation. Arab J Sci Eng 41:1215–1224
Rajaei SH, Khodashenas SH, Esmaili K (2019) Comparative evaluation of energy dissipation over short stepped gabion and rigid spillways. J Hydraul Res. https://doi.org/10.1080/00221686.2019.1572661
Shahheydari H, Jafari Nodoshan E, Barati R, Azhdary Moghadam M (2015) Discharge coefficient and energy dissipation over stepped spillway under skimming flow regime. KSCE J Civ Eng 19(4):1174–1182
Shen J, Wu J, Ma F (2019) Hydraulic characteristics of stepped spillway dropshafts. J Hydrodyn 62(5):868–874
Tabbara M, Chatila J, Awwad R (2005) Computational simulation of flow over stepped spillways. J Comput Struct 83(27):2215–2224
Torabi H, Parsaei A, Yonesi H, Mozafari E (2018) Energy dissipation on rough stepped spillways. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Civ Eng 9(2):5–18
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arjenaki, M.O., Sanayei, H.R.Z. Numerical investigation of energy dissipation rate in stepped spillways with lateral slopes using experimental model development approach. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 6, 605–616 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-020-00714-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-020-00714-z