Abstract
Mesozoic and Cenozoic magma activity in the Wolong Lake mining area of Huaibei is frequent, and the degree of magma intrusion into coal seams remarkable. On the one hand, magma intrusion affects the utilization of coal resources; on the other hand, the macro and trace elements in coal are redistributed to form new mineral types. This study uses the Wolong Lake magma intrusion coal seam as a research object. The mineral paragenesis for igneous rock, coke, and thermally-altered coal in an igneous intrusion zone is studied using SEM, XRD, and Raman spectroscopy. During igneous intrusion, the temperature and pressure of igneous rock metamorphose ambient low-rank coal to high-rank coal and coke. The response mechanism of minerals and trace elements to magmatic intrusion is discussed. The results are: ① SEM analysis shows that ankerite and pyrite are formed from magma intrusion. Both minerals are strongly developed in the magma-coal contact zone, and less well developed in thermally-altered coal. ② XRD analysis shows that igneous intrusion strongly influences the types and content of minerals in coke and thermally-altered coal. In addition to the increase amounts of ankerite and pyrite, chlorite, serpentine, and muscovite, and other secondary minerals, are generated following igneous intrusion. ③ Raman analysis suggests that thermally-altered coal possesses the characteristics of both pyrite and coke. Coke from the magma-coal boundary zone possesses the typical characteristics of pyrite. Igneous rock contains a mineral similar to pyrite, confirmed by both having similar Raman peaks. The scattering intensity of Ag indicates that the formation pressure of pyrite increases from thermally-altered coal via the boundary between the coke zone and the igneous rock.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
The intrusion of coal beds by igneous fluids is a common phenomenon in coal-bearing strata around the world (Kisch and Taylor 1966; Finkelman et al. 1998; Stewart et al. 2005). Igneous intrusion not only disrupts the continuity and integrity of coal beds, but also severely affects the industrial values of coal and the geochemical parameters of organic and inorganic constituents in coal. These include the upgrade of the organic maturity and rank of coal, the reorganization of coal molecular and pore structure, the modification of methane-generation capacity, the transformation of minerals, and the enrichment and depletion of specific elements (Kwiecinska et al. 1992; Golab and Carr 2004; Stewart et al. 2005; Yao et al. 2011; Dai et al. 2012; Yang et al. 2012; Wu et al. 2014; Rahman and Rimmer 2014; Chen et al. 2014; Wang et al. 2015). The transformation of original minerals in coal in response to abrupt increases in the heat and pressure of intruded magma is of special interest, as it relates to the industrial utilization of coal and enrichment of hazardous trace elements. Additionally, new minerals might be formed at the boundary of the magma-coal contact zone after intrusion due to the precipitation of elements from hydrothermal and igneous fluids. For example, by studying a Cretaceous bituminous coal seam intruded by a felsic porphyry dike, Finkelman et al. (1998) observed significant enrichment of carbonates (dolomite, calcite, ankerite, and siderite) and pyrite in the coke at the magma-coal contact zone. Similar observations are also reported in early studies, such as by Kisch and Taylor (1966), Podwysocki and Dutcher (1971), and Kwiecinska et al. (1992), and in recent studies, such as by Prachiti et al. (2011), Singh et al. (2012), Chen et al. (2014), Rahman and Rimmer (2014), Wang et al. (2015), and Neupane et al. (2017).
Chinese coal deposits have been suffered from multiple-stage igneous intrusion from the Late Paleozoic to the Early Cenozoic (Yang et al. 1982). The Permo-Carboniferous coal deposits in the east of China, such as those in Hebei and Anhui Province are extensively intruded by Middle-Late Mesozoic magmatic activity (Dai and Ren 2007; Zheng et al. 2007, 2008; Jiang et al. 2011; Tan et al. 2011; Yang et al. 2012; Yan et al. 2013; Wu et al. 2013; Chen et al. 2014; Wang et al. 2015). However, there are still ongoing debates on the radiation radius of the thermal aureole of igneous intrusion and the variation in petrological and mineralogical parameters with heat and pressure gradients. Wolonghu Coal Mine in Huaibei Coalfield, Anhui Province, is a typical coal mine that has an abundance of igneous rocks in lower coal seams (Jiang et al. 2011; Yan et al. 2013). With the help of SEM, XRD, and Raman spectroscopy, this paper investigates the paragenesis of minerals at a magma-coal contact zone to understand the response of minerals to igneous intrusion.
2 Geological setting
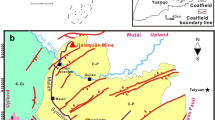
Huaibei Coalfield is located in the southeastern North China Plate, near the famous Tanlu fault zone. The Wolonghu Coal Mine in the northwestern Huaibei coalfield is located at the intersection of the western Fengxian-Guoyang fracture and the southern Subei fracture (Fig. 1a). Strata exposed in the mine include the Carboniferous Taiyuan Formation, the Permian Shanxi Formation, the Lower Shihezi Formation, the Upper Shihezi Formation, the Shiqianfeng Formation, and the Upper Tertiary and Quaternary. The coal seams in the mine were developed from the Upper Carboniferous to the Permian. The Upper Carboniferous strata primarily comprise bioclastic limestone, medium-fine grained clastic rocks, and non-mineable, thin coal seams. All mineable coal seams are produced in the Permian strata, and they can be divided into the Shanxi Formation, Lower Shihezi Formation, and Upper Shihezi Formation from bottom to top. Among them, the Shanxi Formation contains No. 10 and 11 coal seams, the Lower Shihezi Formation contains Nos. 4, 5, 6, 7, and 8 coal seams, and the Upper Shihezi Formation contains Nos. 1, 2, and 3 coal seams (Fig. 2).
Location of Wolonghu Coal Mine (a) showing the distribution of igneous rocks (b) and sampling points in No. 8 coal seam (c). (1–granodiorite (No. 3 pluton); 2–fine-grained sand (roof); 3–mudstone (floor); 4–No. 8 coal seam; 5regional fractures; 6–fault; 7–depth contour map of coal seam; 8–main shaft; 9–sampling transect; 10–sampling number. ① Xiayi-Gushi fracture; ② Fengxian-Guoyang fracture; ③ Guzhen-Changfeng fracture; ④ Lingbi-Wudian fracture; ⑤ Tancheng-Lujiang fracture; ⑥ Subei fracture; ⑦ Guangwu–Guzhen fracture; ⑧ Taihe-Wuhe fracture)
Wolonghu Coal Mine is severely affected by cretaceous yanshanian magmatism (Jiang et al. 2011; Yan et al. 2013). The magma, thought to derive from the southern Subei fracture zone, has intruded into the coal seams along the F2 (west) and F7 (east) controlling faults (Fig. 1b). Intrusive rocks are thicker in the southern part of the mine compared with the northern part. Intrusive magma engulfed most of the No. 10 coal seam, leaving randomly scattered high-rank coal and coke. In the No. 8 coal seam, igneous rocks (called No. 3 pluton) are in the form of sill and are intercalated into the middle of the coal seam (Fig. 1c). The No. 3 pluton is a set of granite diorite rocks; its phenocryst mainly consists of anorthite and hornblende, with a strong retrograde metamorphism, while its matrix consists of fine-grained quartz, plagioclase, sericite, chlorite, and epidote.
3 Sample description and analytical methods
A total of 9 samples were collected from the magmatic-intruded No. 8 coal seam (Fig. 1c), including three igneous rocks (R-1, R-2, R-3), three cokes (T-1, T-2, T-3), and three thermally-metamorphosed coal benches (C-1, C-2, C-3).
The ash, volatilization, and moisture in the sample were determined by referring to Chinese National Standard GB/T211–2001. The carbon, hydrogen, and nitrogen elements were tested using an elemental analyzer (model Vario EL cube). The total sulfur content was determined using a WS-S101 automatic sulfur meter. Using Chinese National Standard GB/T215–2003, the sulfate sulfur, sulfide sulfur, and organic sulfur in the samples were determined.
One portion of a sample was polished into a block to be examined using polarization microscopy, cold-field emission scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and Raman spectroscopy, while another portion was crushed into 200 meshes for X-ray diffraction (XRD). The SEM (S-4800) operating parameters were: resolution: 2.0 nm; magnification: 20× and 800,000×; beam current: 1 pA–2 nA; and acceleration voltage: 0.5–30 kV. The Raman spectrometer (In Via-Reflex with the 532 nm excitation line of Ar+) operating parameters were: output power: 25 mW; resolution: 1 cm−1; and spectral scanning range: 100–1800 cm−1. The XRD (XD-3) operating parameters were: maximum power 3 kW; repeatability of angle measurement: ≤ 0.0016°; scanning range: 30°–160°; and accuracy of angle measurement: ≤ 0.0052°(2θ).
Jade software was used to characterize different wave types (peak types). SPSS (IBM, 21.0) software was used for analysis of the experimental data, analysis including one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) statistical analysis and correlation analysis. All figures were drawn by using Origin 2017 software.
4 Results and discussion
4.1 Coal quality characteristics of magmatic altered coal
The data on coal chemistry for the No. 8 coal samples of Wolonghu Coal Mine are shown in Table 1. The weighted average of volatile matter yield (8.06%) and ash yield (19.67%) suggest that the coals possess extra low volatile and medium ash contents, according to Chinese National Standards GB/T 15224–2004. The total sulfur content in the coal ranges from 0.3% to 0.49%, with a weighted average of 0.4%, indicating an ultra-low sulfur content. The sulfur is mainly derived from coal-forming plants. Moreover, the pyrite sulfur increased with increasing levels of coal metamorphism, but the organic sulfur content decreased. This indicates that the pyrite in magmatic hydrothermal entered the coal through cracks; meanwhile the high temperature of the intrusive rocks caused some organic sulfur to evaporate.
4.2 Morphological characteristics of intrusive rocks and pyrites
Macroscopically, there is a clear boundary between intruded granodiorite (gray) and metamorphosed coke (dark gray). The polarizing microscope highlighted the presence of pyrites and iron dolomites in the granodiorite, coke, and altered coals. Abundant ankerite and quartz are seen in the granodiorite, with small amounts of euhedral-to-subhedral pyrite distributed in a carbonated feldspar periphery (Fig. 3, R-1). An irregular pyrite chain, as well as self-non euhedral quartz and feldspar are distributed in the magma-coal boundary zone (Fig. 3, T-1). In the thermally altered coal, pyrite is affected by the structure of natural coke and quartz grains, and is distributed in cracks and voids in the coal matrix (Fig. 3, C-1). SEM observation shows ankerite to coexist with pyrite, indicating that pyrite formation might relate to the carbonation of ankerite. The coexistence of chlorite and pyroxene suggests that chlorite was possibly the alteration product of pyroxene under the influence of hydrothermal fluids.
SEM observation shows that abundant ankerite, in the form of plates and sheets, is distributed in the intruded granodiorite (Fig. 4, R-1a), and that the edge of the ankerite developed with semi-euhedral and euhedral pyrite (Fig. 4, R-1b). Additionally, irregular and thread-like coke is admixed into the granodiorite (Fig. 4, R-1c). Along the magma-coal boundary, ankerite is present in irregular short columns and granulated shapes (Fig. 4, T-1a), with distinct quartz and pyrite bands distributed at both sides of the ankerite (Fig. 4, T-1b). The crystal of semi-euhedral and euhedral pyrite in the magma-coal boundary was not well developed. Subhedral to allotriomorphic quartz with a flocculent growth edge was also seen, presumably precipitated from late-stage hydrothermal fluids. The natural coke in the magma-coal boundary has an irregular vortex structure (Fig. 4, T-1c). In the thermally-altered coal, ankerite is present in regular long columns and needle-like shapes (Fig. 4, C-1a), while pyrite with undeveloped crystal exhibits plastic deformation characteristics (Fig. 4, C-1b). Both of minerals fill the matrix grids of the thermally-altered coal (Fig. 4, C-1c).
The abundant ankerite in the magma-coal contact zone implies that it was mainly formed during magma intrusion, while the ankerite distributed between the quartz and pyrite veins, indicates that it formed after the quartz. In the thermally-altered coal, the ankerite and pyrite filling the coal matrix were possibly deposited from Fe-rich fluids. Previous studies show that carbonates, including dolomite, calcite, ankerite, and siderite, are commonly present in the veins and vesicles of coke, with their relative proportions varying with distance from the intrusion rock (Kisch and Taylor 1966; Padwysocki and Dutcher 1971; Kwiecinska et al. 1992; Finkelman et al. 1998). In the present study, the primary carbonate is ankerite, and no other carbonates were observed. Pyrite, marcasite, and ankerite are commonly the products of Fe-S rich fluids, and marcasite is commonly thought to form at low temperatures. Thus, it is speculated that a low-temperature Fe-S fluid system might develop, surrounding igneous rock.
From thermally-altered coal via coke to intrusion rock, the crystal form of pyrite becomes more regular, its crystallization rate slows down, and its crystalline environment becomes stable. At the same time, the structure of ankerite changes from long columns to short columns, and then to plate, indicating a gradual increase in the crystallization temperature of ankerite. Igneous intrusion significantly alters the original minerals in coal, and possibly forms new minerals from magmatic or hydrothermal fluids.
4.3 Mineral characteristics of rock-coal alteration zone XRD
The XRD result (Table 2) shows different mineral combinations among the intruded granodiorite, coke, and thermally-altered coal. Kaolinite and quartz are the primary minerals in thermally-altered coal. The minerals in the granodiorite have multiple origins. First, the quartz and feldspar (anorthositic and albite) are formed from siliceous magma. Second, kaolinite may be produced by hydrothermal fluids, and ankerite is possibly the product of the reaction between CO2 and magma/hydrothermal fluids during igneous intrusion. Third, clinochlore and amesite are possibly formed from the transformation of pyroxene by low-temperature hydrothermal fluids. In addition, the granodiorite also contains trace amounts of muscovite and other minerals. Significant amounts of ankerite and pyrite, and small amounts of muscovite, chlorite, and other trace minerals, are observed in the coke. It can be concluded that igneous intrusion led to a significant increase in the content of several minerals (pyrite and ankerite) and generated several secondary minerals.
4.4 Pyrite crystal structure
Raman spectroscopy was used to study the minerals in granodiorite, coke, and thermally-altered coal, according to the peak-type combination (M), Raman shift (Δν), and scattering intensity (I) (Table 3). Earlier studies show that peaks in the regions of 327–350 cm−1, 378–390 cm−1, and 431–440 cm−1 are related to the deformation vibration and stretching vibration of pyrite; and the 1360 cm−1 and 1600 cm−1 peaks are related to microcrystalline vibration and the inner plane C–C stretching vibration of graphite (Jia and Zhu 1997; An et al. 2014). Figure 5 shows five obvious scattering ranges (342.3–344.4 cm−1, 378.7–380.4 cm−1, 431.6–432.2 cm−1, 1360 cm−1, and 1600 cm−1) for thermally-altered coal, linked to the characteristics of pyrite and graphite. However, there are only three scattering peaks (346.9–349.3 cm−1, 384.8–385.6 cm−1, 436.7–440 cm−1) in coke and two strong scattering peaks (327.6–328.8 cm−1, 389–390.1 cm−1) in granodiorite (Table 3 and Fig. 5). This suggests that pyrite is contained in the coke, and that the minerals in granodiorite have a component similar to pyrite.
The Raman shifts (Δν) in Table 2 show that both thermally-altered coal and coke display typical pyrite characteristics (Jia and Zhu 1997). However, the Raman shift of granodiorite suggests the existence of pyrite-like minerals (possibly marcasite). The Raman scattering intensity of pyrite is negatively correlated with system symmetry and iron-sulfur bonds. The scattering intensities of Eg and Ag in both thermally-altered coal and coke are higher than those of Tg. However, the scattering intensities of Eg, Ag and Tg in thermally-altered coal are higher than those of coke. The scattering intensities of Eg and Ag are comparatively lower in granodiorite. The scattering intensity of Eg is barely affected by pressure, but decreases with increasing temperature. From the scattering intensities, it can be inferred that the thermally-altered coal and coke exhibit pyrite characteristics, while granodiorite exhibits marcasite characteristics. The scattering intensity of Ag is less affected by temperature, but shifts to high-frequencies with increasing pressure. The scattering intensities of Eg and Ag show that formation pressure and temperature increase from thermally-altered coal to igneous rock.
5 Conclusions
-
(1)
Mineral paragenesis is different for igneous rock, coke, and thermally-altered coal. Both temperature and pressure decrease from igneous rock, to coke, than to thermally-altered coal during igneous intrusion. Ankerite and pyrite are initiated by igneous intrusion, and are strongly developed in the magma-coke contact zone.
-
(2)
The degree of coal alteration decreases with increasing distance between igneous rocks and coal beds. After igneous intrusion, the number of mineral types in thermally-altered coal increase, accompanied by the appearance of chlorite, serpentine, muscovite, and other secondary minerals.
-
(3)
Raman analysis shows that the thermally-altered coal possesses pyrite and graphite characteristics; igneous rock contains minerals similar to pyrite (likely marcasite) based on their similar Raman peaks. The scattering intensity of Ag indicates that the formation pressure of pyrite increases from thermally-altered coal to igneous rock.
References
An YF, Zhong LL, Jiang DP (2014) Micro-Raman spectral characteristics and implication of FeS2 from Augen Granites in West of Guangdong. Spectrosc Spectr Anal 34:2439–2443
Chen J, Liu GJ, Li H, Wu B (2014) Mineralogical and geochemical responses of coal to igneous intrusion in the Pansan Coal Mine of the Huainan coalfield, Anhui, China. Int J Coal Geol 124:11–35
Dai SF, Ren D, Chou CL, Finkelman RB, Seredin VV, Zhou YP (2012) Geochemistry of trace elements in Chinese coals: a review of abundances, genetic types, impacts on human health, and industrial utilization. Int J Coal Geol 94:3–21
Finkelman RB, Bostick NH, Dulong FT, Senftle FE, Thorpe AN (1998) Influence of an igneous intrusion on the inorganic geochemistry of a bituminous coal from Pitkin County, Colorado. Int J Coal Geol 36:223–241
Golab AN, Carr PF (2004) Changes in geochemistry and mineralogy of thermally altered coal, Upper Hunter Valley, Australia. Int J Coal Geol 57:197–210
Jia J, Zhu Z (1997) Raman spectral characteristics of gold-bearing pyrite and discussion about their prospecting significance. Earth Sci 6:575–578
Jiang JY, Cheng YP, Wang L, Li W, Wang L (2011) Petrographic and geochemical effects of sill intrusions on coal and their implications for gas outbursts in the Wolonghu Mine, Huaibei Coalfield, China. Int J Coal Geol 88:55–66
Kisch HJ, Taylor GH (1966) Metamorphism and alteration near an intrusive-coal contact. Econ Geol 61:343–361
Kwiecinska BK, Hamburg G, Vleeskens JM (1992) Formation temperatures of natural coke in the lower Silesian coal basin, Poland. Evidence from pyrite and clays by SEM-EDX. Int J Coal Geol 21:217–235
Neupane B, Ju YW, Silwal BJ, Singh PK, Huang C (2017) Structural investigations of Eocene coals from foreland basin of central Nepal Himalaya. Energy Explor Exploit 35:713–733
Padwysocki MH, Dutcher RR (1971) Coal dikes that intrude lamprophyre sills; purgatoire river valley, Colorado. Econ Geol 66:267–280
Prachiti PK, Manikyamba C, Singh PK, Balaram V, Lakshminarayana G, Raju K, Singh MP, Kalpana MS, Arora M (2011) Geochemical systematics and precious metal content of the sedimentary horizons of Lower Gondwanas from the Sattupalli coal field, Godavari Valley, India. Int J Coal Geol 88:83–100
Rahman MW, Rimmer SM (2014) Effects of rapid thermal alteration on coal: geochemical and petrographic signatures in the Springfield (No. 5) Coal, Illinois Basin. Int J Coal Geol 131:214–226
Singh PK, Singh MP, Prachiti PK, Kalpana MS, Manikyamba C, Lakshminarayana G, Singh AK, Naik AS (2012) Petrographic characteristics and carbon isotopic composition of Permian coal: implications on depositional environment of Sattupalli coalfield, Godavari Valley, India. Int J Coal Geol 90–91:34–42
Stewart AK, Massey M, Padgett PL, Rimmer SM, Hower JC (2005) Influence of a basic intrusion on the vitrinite reflectance and chemistry of the Springfield (No. 5) coal, Harrisburg, Illinois. Int J Coal Geol 63:58–67
Tan JQ, Ju YW, Yuan WM, Hou QL, Pan JN, Fan JJ (2011) Thermochronological and structural evolution of the Huaibei coalfield in eastern China: constrains from zircon fission-track data. Radiat Meas 46:183–189
Wang XB, Jiang YF, Zhou GQ, Wang PP, Wang RX, Zhao L, Chou CL (2015) Behavior of minerals and trace elements during natural coking: a case study of an intruded bituminous coal in the Shuoli Mine, Anhui Province, China. Energy Fuels 29:4100–4113
Wu D, Liu GJ, Sun RY, Fan X (2013) Investigation of structural characteristics of thermally metamorphosed coal by FTIR spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction. Energy Fuels 27:5823–5830
Wu D, Liu GJ, Sun RY, Chen SC (2014) Influences of magmatic intrusion on the macromolecular and pore structures of coal: evidences from Raman spectroscopy and atomic force microscopy. Fuel 119:191–201
Yan ZC, Liu GJ, Sun RY, Wu D, Wu B, Zhou CC (2013) Mercury distribution in coals influenced by magmatic intrusions, and surface waters from the Huaibei Coal Mining District, Anhui, China. Appl Geochem 33:298–305
Yang Q, Ren DY, Pan ZG (1982) Preliminary investigation on the metamorphism of Chinese coals. Int J Coal Geol 2:31–48
Yang M, Liu GJ, Sun RY, Chou CL, Zheng LG (2012) Characterization of intrusive rocks and REE geochemistry of coals from the Zhuji Coal Mine, Huainan Coalfield, Anhui, China. Int J Coal Geol 94:283–295
Yao YB, Liu DM, Huang WH (2011) Influences of igneous intrusions on coal rank, coal quality and adsorption capacity in Hongyang, Handan and Huaibei coalfields, North China. Int J Coal Geol 88:135–146
Zheng LG, Liu GJ, Chou CL, Qi CC, Zhang Y (2007) Geochemistry of Rare Earth elements in Permian coals from the Huaibei Coalfield, Anhui Province, China. J Asian Earth Sci 31:167–176
Zheng LG, Liu GJ, Qi CC, Zhang Y, Wong MH (2008) The use of sequential extraction to determine the distribution and modes of occurrence of mercury in Permian Huaibei Coal, Anhui, Province, China. Int J Coal Geol 73:139–155
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41373108 and 41702176), Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province (No. 1608085QD79), the Scientific and Technological Project of Huaibei Mining Industry (Group) Co. Ltd. (HK-2018-1), and the Scientific and Technological Project of Anhui Traffic and Aviation Engineering (Group) Co. Ltd. We acknowledge the editors and reviewers for polishing the language and providing in-depth discussion.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, X., Zheng, L., Jiang, Y. et al. Transformation of minerals at the boundary of magma-coal contact zone: case study from Wolonghu Coal Mine, Huaibei Coalfield, China. Int J Coal Sci Technol 8, 168–175 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40789-020-00373-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40789-020-00373-6