Abstract
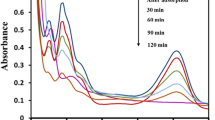
This work aims to prepare copper-substituted NdFeO3 (NdFe1 − xCuxO3, x = 0.05, 0.1, 0.15, and 0.20) photocatalysts via hydrothermal method and study their visible light-assisted Fenton catalytic activities for phenol degradation. The Cu-doped NdFeO3 photocatalysts were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), Inductively Coupled Plasma–Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS), N2 adsorption-desorption, Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), and UV-Vis absorption analysis. The results revealed that samples with lower Cu contents in NdFe1 − xCuxO3 exhibited higher photo-Fenton catalytic performances than pure and highly doped NdFeO3. Among them, NdFe0.85Cu0.15O3 showed the highest photo-Fenton catalytic activity for phenol degradation under visible light, reaching a removal rate of 98.4% when using 1 g/L catalyst in the presence of 10 mM H2O2 at pH 5. It has been demonstrated that Cu-NdFeO3-15 has good stability and reusability, and it also exhibits great potential for usage in photo-Fenton degradation of phenol under visible light irradiation.
Highlights
• Cu-doped NdFeO3 was studied as photocatalyst for photo-Fenton degradation of phenol
• Improved phenol removal rate was related to Cu-doped NdFeO3 structural and optical properties
• Cu-doped NdFeO3 potential applications were suggested by its good stability and reusability









Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Ahile UJ, Wuana RA, Itodo AU, Sha’Ato R, Dantas RF (2020) Stability of iron chelates during photo-Fenton process: the role of pH, hydroxyl radical attack and temperature. J Water Process Eng 36:101320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2020.101320
Ahmed Y, Yaakob Z, Akhtar P (2016) Degradation and mineralization of methylene blue using a heterogeneous photo-Fenton catalyst under visible and solar light irradiation. Catal Sci Technol 6(4):1222–1232. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CY01494H
Almasi A, Mahmoudi M, Mohammadi M, Dargahi A, Hamed B (2019) Optimizing biological treatment of petroleum industry wastewater in a facultative stabilization pond for simultaneous removal of carbon and phenol. Toxin Rev 40(2):189–197. https://doi.org/10.1080/15569543.2019.1573433
Alrozi R, Zubir NA, Bakar NFA, Ladewig BP, Motuzas J, Bakar NA, Wang DK, Costa JCD (2023) Functional role of B-site substitution on the reactivity of CaMFeO3 (M = cu, Mo, Co) perovskite catalysts in heterogeneous Fenton-like degradation of organic pollutant. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 143:104675. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2023.104675
Amdouni W, Otoničar M, Gemeiner P, Butin V, Guiblin N, Maghraoui-Meherzi H, Dkhil B (2023) A General Synthetic Route to High‐Quality Perovskite Oxide Nanoparticles and their enhanced solar photocatalytic activity. Angew Chem 135(7):202215700. https://doi.org/10.1002/ange.20221570
Boruah PK, Sharma B, Karbhal I, Shelke MV, Manash RD (2017) Ammonia-modified graphene sheets decorated with magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles for the photocatalytic and photo-Fenton degradation of phenolic compounds under sunlight irradiation. J Hazard Mater 325:90–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.11.023
Brillas E, Garcia-Segura S (2020) Benchmarking recent advances and innovative technology approaches of Fenton, photo-Fenton, electro-Fenton, and related processes: a review on the relevance of phenol as model molecule. Sep Purif Technol 237:116337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2019.116337
Caronna T, Fontana F, Sora IN, Pelosato R (2009) Chemical synthesis and structural characterization of the substitution compound LaFe1 – xCuxO3 (x = 0–0.40). Mater Chem Phys 116(2–3):645–648. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2009.05.020
Chanda S, Saha S, Dutta A, Sinha TP (2013) Raman spectroscopy and dielectric properties of nanoceramic NdFeO3. Mater Res Bull 48(4):1688–1693. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2012.12.075
Demircivi P, Simsek EB (2019) Visible-light-enhanced photoactivity of perovskite-type W-doped BaTiO3 photocatalyst for photodegradation of tetracycline. J Alloys Compds 774:795–802. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.09.354
Dhiman M, Singhal S (2019) Effect of doping of different rare earth (europium, gadolinium, dysprosium and neodymium) metal ions on structural, optical and photocatalytic properties of LaFeO3 perovskites. J Rare Earths 37(12):1279–1287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jre.2018.12.015
Ethiraj AS, Uttam P, Varunkumar K, Chong KF, Ali GA (2020) Photocatalytic performance of a novel semiconductor nanocatalyst: copper doped nickel oxide for phenol degradation. Mater Chem Phys 242:122520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2019.122520
García-López E, Marcì G, Puleo F, Parola VL, Liotta LF (2015) La1 – xSrxCo1–yFeyO3–δ perovskites: Preparation, characterization and solar photocatalytic activity. Appl Catal B: Environ 178:218–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.09.014
Garcia-Muñoz P, Lefevre C, Robert D, Keller N (2019) Ti-substituted LaFeO3 perovskite as photoassisted CWPO catalyst for water treatment. Appl Catal B: Environ 248:120–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.02.030
Gholami P, Khataee A, Soltani RDC, Dinpazhoh L, Amit B (2020) Photocatalytic degradation of gemifloxacin antibiotic using Zn-Co-LDH@ biochar nanocomposite. J Hazard Mater 382:121070. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121070
Grabowska E (2016) Selected perovskite oxides: characterization, preparation and photocatalytic properties—A review. Appl Catal B: Environ 186:97–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.12.035
Guo L, Zhang K, Han X, Zhao Q, Wang D, Fu F, Liang Y (2020) Highly efficient visible-light-driven photo-Fenton catalytic performance over FeOOH/Bi2WO6 composite for organic pollutant degradation. J Alloys Compds 816:152560. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.152560
Hassandoost R, Ouran SR, Khataee A, Orooji Y, Joo SW (2019) Hierarchically structured ternary heterojunctions based on Ce3+/Ce4+ modified Fe3O4 nanoparticles anchored onto graphene oxide sheets as magnetic visible-light-active photocatalysts for decontamination of oxytetracycline. J Hazard Mater 376:200–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.05.035
Hu J, Li J, Cui J, An W, Liu L, Liang Y, Cui W (2020) Surface oxygen vacancies enriched FeOOH/Bi2MoO6 photocatalysis-fenton synergy degradation of organic pollutants. J Hazard Mater 384:121399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121399
Huang T, Zhu J, Ge S, Guo T, Jiang C, Xie L (2020) Synthesis of novel CdSe QDs/BiFeO3 composite catalysts and its application for the photo-Fenton catalytic degradation of phenol. J Environ Chem Eng 8(5):104384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104384
Hussain S, Aneggi E, Goi D (2021) Catalytic activity of metals in heterogeneous Fenton-like oxidation of wastewater contaminants: a review. Environ Chem Lett 19:2405–2424. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-021-01185-z
Jiang J, Gao J, Li T, Chen Y, Wu Q, Xie T, Lin Y, Dong S (2019) Visible-light-driven photo-Fenton reaction with α-Fe2O3/BiOI at near neutral pH: boosted photogenerated charge separation, optimum operating parameters and mechanism insight. J Colloid Interf Sci 554:531–543. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2019.07.038
Jing J, Pervez MN, Sun P, Cao C, Li B, Naddeo V, Jin W, Zhao Y (2021) Highly efficient removal of bisphenol A by a novel co-doped LaFeO3 perovskite/PMS system in salinity water. Sci Total Environ 801:149490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.149490
Khanh HP, Thu HNT, Bich THT, Mai TT, Trung HH (2020) A comparative study on Photocatalytic Performance of Perovskite materials synthesized from discarded Rare Earth Magnet with the one from pure Neodymium Salt. Chem Eng 78:295–300. https://doi.org/10.3303/CET2078050
Li X, Tang C, Ai M, Dong L, Xu Z (2010) Controllable synthesis of pure-phase rare-earth orthoferrites hollow spheres with a porous shell and their catalytic performance for the CO + NO reaction. Chem Mater 22(17):4879–4889. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm101419w
Li P, Li L, Xu M, Chen Q, He Y (2017) Enhanced photocatalytic property of BiFeO3/N-doped graphene composites and mechanism insight. Appl Surf Sci 396:879–887. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.11.052
Ma P, Yu Y, Xie J,Fu Z (2017) Ag3PO4/CuO composites utilizing the synergistic effect of photocatalysis and Fenton-like catalysis to dispose organic pollutants. Adv Pow Technol 28(11):2797–2804. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2017.08.004
Magdy M, Alalm MG, El-Etriby HK (2021) Comparative life cycle assessment of five chemical methods for removal of phenol and its transformation products. J Clean Prod 291:125923. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.125923
Mao J, Quan X, Wang J, Gao C, Chen S, Yu H (2018) Enhanced heterogeneous Fenton-like activity by Cu-doped BiFeO3 perovskite for degradation of organic pollutants. Front Environ Sci Eng 12:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-018-1060-9
Mohamed A, Yousef S, Nasser WS, Osman TA, Knebel A, Elvia PVS, Hashem T (2020) Rapid photocatalytic degradation of phenol from water using composite nanofibers under UV. Environ Sci Eur 32:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12302-020-00436-0
Nguyen TA, Pham TL, Mittova IY, Mittova VO, Nguyen TLT, Nguyen HV, Bui VX (2011) Co-doped NdFeO3 nanoparticles: synthesis, optical, and magnetic properties study. Nanomater 11(4):937. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11040937
Palanivel B, Shkir M, Alshahrani T, Mani A (2021) Novel NiFe2O4 deposited S-doped g-C3N4 nanorod: visible-light-driven heterojunction for photo-Fenton like tetracycline degradation. Diam Relat Mater 112:108148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diamond.2020.108148
Parrey IR (2021) Mechanism of photo-Fenton removal of methyl dye orange using perovskite lanthanum orthoferrite doped with copper metal. Bulg J Phys 48(3):268–275
Pena M, Fierro J (2001) Chemical structures and performance of perovskite oxides. Chem Rev 101(7):1981–2018. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr980129f
Phan TTN, Nikoloski AN, Bahri PA, Li D (2018) Heterogeneous photo-Fenton degradation of organics using highly efficient Cu-doped LaFeO3 under visible light. J Ind Eng Chem 61:53–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2017.11.046
Phan TTN, Nikoloski AN, Bahri PA, Li D (2019) Enhanced removal of organic using LaFeO3-integrated modified natural zeolites via heterogeneous visible light photo-Fenton degradation. J Environ Manag 233:471–480. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.12.051
Phan TTN, Nguyen HL, Le VT, Phan CN, Pham TH (2021) Mesoporous LaFeO3: synergistic effect of adsorption and visible light photo-Fenton processes for phenol removal from refinery wastewater. J Chem 2021:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/5841066
Phan TTN, Phan TTN, Pham TH (2022) Hollow lanthanum ferrite perovskite for the enhanced adsorption-photo-Fenton catalytic activity of degradation of ibuprofen. J Porous Mater 30:775–786. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-022-01378-z
Prabagar JS, Tenzin T, Yadav S, Kumar KMA, Shivaraju HP (2023) Facile synthesis of NdFeO3 perovskite for photocatalytic degradation of organic dye and antibiotic. Mater Today 75:15–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2022.10.230
Shet AV, Shetty K (2016) Photocatalytic degradation of phenol using Ag core-TiO2 shell (Ag@TiO2) nanoparticles under UV light irradiation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:20055–20064. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5579-z
Simsek EB, Tuna O, Balta Z (2020) Construction of stable perovskite-type LaFeO3 particles on polymeric resin with boosted photocatalytic Fenton-like decaffeination under solar irradiation. Sep Purif Technol 237:116384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2019.116384
Singh S, Singh A, Yadav BC, Dwivedi PK (2013) Fabrication of nanobeads structured perovskite type neodymium iron oxide film: its structural, optical, electrical and LPG sensing investigations. Sens Act B: Chem 177:730–739. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2012.11.096
Soltani T, Lee BK (2017) Enhanced formation of sulfate radicals by metal-doped BiFeO3 under visible light for improving photo-Fenton catalytic degradation of 2-chlorophenol. Chem Eng J 313:1258–1268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.11.016
Soltani T, Tayyebi A, Lee BK (2018) Efficient promotion of charge separation with reduced graphene oxide (rGO) in BiVO4/rGO photoanode for greatly enhanced photoelectrochemical water splitting. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 185:325–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2018.05.050
Tu YJ, You CF, Lo SC, Chan TS, Chung CH (2019) Recycling of neodymium enhanced by functionalized magnetic ferrite. Environ Technol 40(12):1592–1604. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2018.1426643
Wang H, Zhang L, Chen Z, Hu J, Li S, Wang Z, Liu J, Wang X (2014) Semiconductor heterojunction photocatalysts: design, construction, and photocatalytic performances. Chem Soc Rev 43(15):5234–5244. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CS00126E
Wang H, Zhang L, Hu C, Wang X, Lyu L, Sheng D (2018) Enhanced degradation of organic pollutants over Cu-doped LaAlO3 perovskite through heterogeneous Fenton-like reactions. Chem Eng J 332:572–581. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.09.058
Wang Z, Lai C, Qin L, Fu Y, He J, Huang D, Li B, Zhang M, Liu S, Li L, Zhang W, Yi H, Liu X, Zhou X (2020) ZIF-8-modified MnFe2O4 with high crystallinity and superior photo-Fenton catalytic activity by Zn-O-Fe structure for TC degradation. Chem Eng J 392:124851. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.124851
Wei X, Wu H, He G, Guan Y (2017) Efficient degradation of phenol using iron-montmorillonite as a Fenton catalyst: importance of visible light irradiation and intermediates. J Hazard Mater 321:408–416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.09.031
Wei G, Yang Y, Li Y, Zhang L, Xin Z, Li Z, Huang L (2020) A new catalytic composite of bentonite-based bismuth ferrites with good response to visible light for photo-Fenton reaction: application performance and catalytic mechanism. Appl Clay Sci 184:105399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2019.105399
Zamri MSFA, Sapawe N (2019) Kinetic study on photocatalytic degradation of phenol using green electrosynthesized TiO2 nanoparticles. Mater Today: Proc 19:1261–1266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2019.11.131
Zhong P, Yu Q, Zhao J, Xu S, Qiu X, Chen J (2019) Degradation of bisphenol A by Fe-Al layered double hydroxides: a new synergy of homo-and heterogeneous Fenton systems. J Colloid Interf Sci 552:122–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2019.05.040
Funding
This research is funded by Vietnam Ministry of Education and Training under grant number B2021-BKA-15.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Thi To Nga Phan performed the activity tests and wrote the manuscript. Thi Hai Nam Chu performed all characterizations. Both authors wrote and revised the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Phan, T.T.N., Chu, T.H.N. Enhanced Degradation of Phenol by Visible Light-Assisted Fenton Catalytic Activity of Copper-Substituted Neodymium Ferrite. Environ. Process. 10, 25 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-023-00639-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-023-00639-6