Abstract
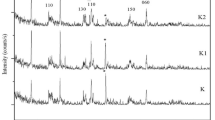
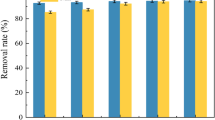
The removal of aqueous methylene blue (MB) dye using organically modified natural Na-kaolinite was optimized. Organo-kaolinite was synthesized by replacing exchangeable Na+ ions in Na-kaolinite with cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB), and the adsorption behaviour was systematically explored as an efficient adsorbent for the removal of dyes. Furthermore, the properties of the obtained samples were characterized by FTIR spectrophotometric analysis, which confirmed that CTAB cations had modified the kaolinite to possess a new functional group. Batch mode experiments were conducted to test the performance of the modified kaolinite in removing MB dye to optimize the following experimental conditions: adsorbent quantity, initial concentration, mixing speed, contact time and initial pH. The findings indicated that the MB adsorbent efficiency could reach up to 100% when the above conditions were set at 0.3 g/100 mL, 50 mg/L, 200 rpm, 60 min and pH = 12, respectively. The adsorption isotherms and kinetics of the organic-modified kaolinite for MB concurred with Freundlich adsorption equation and the pseudo-second-order kinetics, respectively. In accordance with the principles of environmental preservation and reuse of waste, granulated glass waste was used to optimize the adsorption efficiency of kaolinite. Furthermore, two tested reactive systems were used in two-dimensional (2D) domain experiments by mixing a 1:1 ratio of modified kaolinite:granulated glass waste. The COMSOL Multiphysics 3.5a software was utilized to determine the spread of MB within the permeable reactive barrier (PRB) for the 2D domain at equilibrium conditions.
Highlights
• Kaolinite was modified by cetyltrimethylammonium bromide to remove methylene blue.
• Organo-kaolinite was used in a two-dimensional permeable reactive barrier.
• The COMSOL Multiphysics model was used to simulate the permeable reactive barrier.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
Materials Availability
Not applicable.
References
Abd Ali ZT, Naji LA, Almuktar SAAAN, Faisal AAH, Abed SN, Scholz M, Naushad M, Ahamad T (2020) Predominant mechanisms for the removal of nickel metal ion from aqueous solution using cement kiln dust. J Water Process Eng 33:101033. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2019.101033
Ahmed DN, Faisal AAH, Jassam SH, Naji LA, Naushad M (2020a) Kinetic model for pH variation resulted from interaction of aqueous solution contaminated with nickel ions and cement kiln dust. J Chem 2020:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8732308
Ahmed DN, Naji LA, Faisal AAH, Al-Ansari N, Naushad M (2020b) Waste foundry sand/MgFe-layered double hydroxides composite material for efficient removal of Congo red dye from aqueous solution. Sci Rep 10:2042. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-58866-y
Alquzweeni SS, Faisal AAH (2020) Possibility of using granular iron slag by-product as permeable reactive barrier for remediation of simulated water contaminated with lead ions. Desalin Water Treat 178:211–219. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2020.24974
Alshammari M, Al Juboury MF, Naji LA, Faisal AAH, Zhu H, Al-Ansari N, Naushad M (2020) Synthesis of a novel composite sorbent coated with siderite nanoparticles and its application for remediation of water contaminated with congo red dye. Int J Environ Res 14:177–191. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41742-020-00245-6
Anirudhan TS, Ramachandran M (2015) Adsorptive removal of basic dyes from aqueous solutions by surfactant modified bentonite clay (organoclay): kinetic and competitive adsorption isotherm. Process Saf Environ Prot 95:215–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2015.03.003
Belachew N, Hinsene H (2020) Preparation of cationic surfactant-modified kaolin for enhanced adsorption of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution. Appl Water Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-019-1121-7
Buasri A, Yongbut P, Chaiyut N, Phattarasirichot K (2008) Adsorption equilibrium of zinc ions from aqueous solution by using modified clinoptilolite. Chiang Mai J Sci 35:56–62
Chen D, Chen J, Luan X, Ji H, Xia Z (2011) Characterization of anion–cationic surfactants modified montmorillonite and its application for the removal of methyl orange. Chem Eng J 171:1150–1158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.05.013
Ciardelli G, Corsi L, Marcucci M (2001) Membrane separation for wastewater reuse in the textile industry. Resour Conserv Recycl 31:189–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-3449(00)00079-3
COMSOL Multiphysics User's Manual (2008) COMSOL user forums. www.comsol.com/support/forums
Dhodapkar R, Rao NN, Pande SP, Kaul SN (2006) Removal of basic dyes from aqueous medium using a novel polymer: Jalshakti. Bioresour Technol 97:877–885
Faisal AAH (2016) Effect of pH on the performance of olive pips reactive barrier through the migration of copper-contaminated groundwater. Desalin Water Treat. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2014.999132
Faisal AAH, Naji LA (2019) Simulation of ammonia nitrogen removal from simulated wastewater by sorption onto waste foundry sand using artificial neural network. Assoc Arab Univ J Eng Sci 26:28–34. https://doi.org/10.33261/jaaru.2019.26.1.004
Faisal AAH, Al-Wakel SFA, Assi HA, Naji LA, Naushad M (2020a) Waterworks sludge-filter sand permeable reactive barrier for removal of toxic lead ions from contaminated groundwater. J Water Process Eng 33:101112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2019.101112
Faisal AAH, Ali IM, Naji LA, Madhloom HM, Al-Ansari N (2020b) Using different materials as permeable reactive barrier for remediation of groundwater contaminated with landfill’s leachate. Desalin WATER Treat 175:152–163. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2020.24890
Faisal AAH, Alquzweeni SS, Naji LA, Naushad M (2020c) Predominant mechanisms in the treatment of wastewater due to interaction of benzaldehyde and iron slag byproduct. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17:226. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17010226
Faisal AAH, Ibreesam MM, Al-Ansari N, Naji LA, Naushad M, Ahamad T (2020d) COMSOL multiphysics 3.5a package for simulating the cadmium transport in the sand bed-bentonite low permeable barrier. J King Saud Univ - Sci 32:1944–1952. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksus.2020.01.047
Faisal AAH, Jasim HK, Naji LA, Naushad M, Ahamad T (2020e) Cement kiln dust-sand permeable reactive barrier for remediation of groundwater contaminated with dissolved benzene. Sep Sci Technol 56(5):870–883. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2020.1746341
Faisal AAH, Nassir ZS, Naji LA, Naushad M, Ahamad T (2020f) A sustainable approach to utilize olive pips for the sorption of lead ions: numerical modeling with aid of artificial neural network. Sustain Chem Pharm 15:100220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scp.2020.100220
Faisal AAH, Nassir ZS, Naji LA, Naushad M, Ahamad T (2020g) A sustainable approach to utilize olive pips for the sorption of lead ions: Numerical modeling with aid of artificial neural network. Sustain Chem Pharm. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scp.2020.100220
Fetter CW (1999) Contaminant hydrogeology, 2nd edn. Prentice-Hall, New Jersey
Ge M, Du M, Zheng L, Wang B, Zhou X, Jia Z, Hu G, Jahangir Alam SM (2017) A maleic anhydride grafted sugarcane bagasse adsorbent and its performance on the removal of methylene blue from related wastewater. Mater Chem Phys. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2017.01.063
Ge M, Cao L, Du M, Hu G, Jahangir Alam SM (2018) Adsorptive characterization of a pure magadiite and an organic modified magadiite on removal of methylene blue from related aqueous solution. Mater Chem Phys. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2018.06.085
Hajjaji M, Kacim S, Alami A, El Bouadili A, El Mountassir M (2001) Chemical and mineralogical characterization of a clay taken from the Moroccan Meseta and a study of the interaction between its fine fraction and methylene blue. Appl Clay Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-1317(00)00041-7
Ho YS, McKay G (1999) Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem 34:451–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-9592(98)00112-5
Huang Z, Li Y, Chen W, Shi J, Zhang N, Wang X, Li Z, Gao L, Zhang Y (2017) Modified bentonite adsorption of organic pollutants of dye wastewater. Mater Chem Phys 202:266–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2017.09.028
Khebchareon M (2012) Crank-Nicolson finite-element for 2D groundwater flow, advection-dispersion and interphase mass transfer: I. Model development. Int J Numer Anal Model Ser B 3:109–125
Limousin G, Gaudet J-P, Charlet L, Szenknect S, Barthès V, Krimissa M (2007) Sorption isotherms: A review on physical bases, modeling and measurement. Appl Geochemistry 22:249–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2006.09.010
Markovska L, Meshko V, Noveski V (2001) Adsorption of basic dyes in a fixed bed column. Korean J Chem Eng 18:190–195. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02698458
Mierczynska-Vasilev A, Smith PA (2016) Surface modification influencing adsorption of red wine constituents: the role of functional groups. Appl Surf Sci 386:14–23
Mishra AK, Ohtsubo M, Li L, Higashi T (2011) Controlling factors of the swelling of various bentonites and their correlations with the hydraulic conductivity of soil-bentonite mixtures. Appl Clay Sci 52:78–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2011.01.033
Monvisade P, Siriphannon P (2009) Chitosan intercalated montmorillonite: preparation, characterization and cationic dye adsorption. Appl Clay Sci 42:427–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2008.04.013
Naji LA, Faisal AAH, Rashid HM, Naushad M, Ahamad T (2020a) Environmental remediation of synthetic leachate produced from sanitary landfills using low-cost composite sorbent. Environ Technol Innov 18:100680. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2020.100680
Naji LA, Faisal AAH, Rashid HM, Naushad M, Ahamad T (2020b) Environmental remediation of synthetic leachate produced from sanitary landfills using low-cost composite sorbent. Environ Technol Innov 175:100680. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2020.100680
Naji LA, Jassam SH, Yaseen MJ, Faisal AAH, Al-Ansari N (2020c) Modification of Langmuir model for simulating initial pH and temperature effects on sorption process. Sep Sci Technol 55:2729–2736. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2019.1655055
National Research Council and GSC. (1984) Groundwater contamination. National Academies Press .The National Academies Press, Washington, DC. https://doi.org/10.17226/1770
Rahi MA, Faisal AAH, Naji LA, Almuktar SA, Abed SN, Scholz M (2020) Biochemical performance modelling of non-vegetated and vegetated vertical subsurface-flow constructed wetlands treating municipal wastewater in hot and dry climate. J Water Process Eng 33:101003. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2019.101003
Reddy CV, Reddy IN, Harish VVN, Reddy KR, Shetti NP, Shim J, Aminabhavi TM (2020a) Efficient removal of toxic organic dyes and photoelectrochemical properties of iron-doped zirconia nanoparticles. Chemosphere 239:124766. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124766
Reddy CV, Reddy IN, Ravindranadh K, Reddy KR, Shetti NP, Kim D, Shim J, Aminabhavi TM (2020b) Copper-doped ZrO2 nanoparticles as high-performance catalysts for efficient removal of toxic organic pollutants and stable solar water oxidation. J Environ Manage 260:110088. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110088
Reddy M, Shetti N, Nayak D, Malode S, Muddapur U (2019) Electrochemical oxidation of food dye at nanosilica modified carbon electrode. Mater Today Proc 18:798–805. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2019.06.502
Saad N, Abd Ali ZT, Naji LA, Faisal AAAH, Al-Ansari N (2019) Development of Bi-Langmuir model on the sorption of cadmium onto waste foundry sand: effects of initial pH and temperature. Environ Eng Res 25:677–684. https://doi.org/10.4491/eer.2019.277
Sarma GK, Sen GS, Bhattacharyya KG (2019) Removal of hazardous basic dyes from aqueous solution by adsorption onto kaolinite and acid-treated kaolinite: kinetics, isotherm and mechanistic study. SN Appl Sci 1:211. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-019-0216-y
Shetti NP, Malode SJ, Malladi RS, Nargund SL, Shukla SS, Aminabhavi TM (2019) Electrochemical detection and degradation of textile dye Congo red at graphene oxide modified electrode. Microchem J 146:387–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2019.01.033
Shin WS (2008) Competitive sorption of anionic and cationic dyes onto cetylpyridinium-modified montmorillonite. J Environ Sci Heal Part A 43:1459–1470. https://doi.org/10.1080/10934520802232337
Simon FG, Meggyes T (2002) Removal of organic and inorganic pollutants from groundwater using permeable reactive barriers: part 1. Treatment processes for pollutants. L ContamReclam 8(2):103–116
Vijayaraghavan K, Padmesh TVN, Palanivelu K, Velan M (2006) Biosorption of nickel(II) ions onto Sargassumwightii: application of two-parameter and three-parameter isotherm models. J Hazard Mater. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.10.016
Wang L, Zhang J, Wang A (2008) Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution using chitosan-g-poly(acrylic acid)/montmorillonite superadsorbent nanocomposite. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem Eng Asp 322:47–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2008.02.019
Zha SX, Zhou Y, Jin X, Chen Z (2013) The removal of amoxicillin from wastewater using organobentonite. J Environ Manage 129:569–576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2013.08.03
Zhang Y, Zhao Y, Zhu Y, Wu H, Wang H, Lu W (2012) Adsorption of mixed cationic-nonionic surfactant and its effect on bentonite structure. J Environ Sci 24:1525–1532. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(11)60950-9
Zhu J, Cui Y, Nawaz Z, Wang Y, Wei F (2010) In situ Synthesis of SAPO-34 zeolites in kaolin microspheres for a fluidized methanol or dimethyl ether to olefins process. Chin J ChemEng 18:979–987. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1004-9541(09)60156-7
Acknowledgements
We would like to gratefully acknowledge the technical support of Laith A. Naji, Technical Instructors Training Institute, Middle Technical University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Not applicable.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alkizwini, R.S. The Use of an Organo-Kaolinite Sorbent in a Permeable Reactive Barrier for Remediating Groundwater Contaminated with Methylene Blue Dye: Experimental and Theoretical Investigation. Environ. Process. 8, 889–910 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-021-00515-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-021-00515-1