Abstract
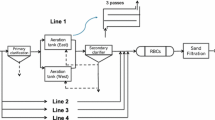
Wastewater treatment plants are one of the major routes transporting emerging contaminants (ECs) to the water environment. Mathematical modelling is an essential tool to assess the fate of ECs through wastewater treatment. In the context of this study, a plant-wide mathematical model was developed and calibrated. According to the results, the dominant removal mechanisms have been identified for each target compound, thus confirming previously published data on their physicochemical properties. Solids retention time is an important operating parameter which highly influences the removal rate of most biodegradable ECs, while the performance of primary sedimentation, with regard to solids removal, influences the fate of both soluble and particulate fraction of ECs. Furthermore, the increase of solids capture rate in sludge thickening and dewatering units is associated with a decrease in ECs removal rate and their content in biomass. The hourly fluctuations in the inflow loads of ECs result in a variation of effluent ECs concentration with the same periodicity but with a significantly lower range.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abegglen C, Joss A, McArdell CS, Fink G, Schlüsener MP, Ternes TA, Siegrist H (2009) The fate of selected micropollutants in a single-house MBR. Water Res 43(7):2036–2046. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2009.02.005
Almeida B, Oehmen A, Marques R, Brito D, Carvalho G, Crespo MB (2013) Modelling the biodegradation of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) by activated sludge and a pure culture. Bioresour Technol 133:31–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.01.035
Alvarino T, Suarez S, Lema JM, Omil F (2014) Understanding the removal mechanisms of PPCPs and the influence of main technological parameters in anaerobic UASB and aerobic CAS reactors. J Hazard Mater 278:506–513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.06.031
Alvarino T, Suarez S, Katsou E, Vazquez-Padin J, Lema JM, Omil F (2015) Removal of PPCPs from the sludge supernatant in a one stage nitritation/anammox process. Water Res 68:701–709. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2014.10.055
Alvarino T, Suarez S, Lema J, Omil F (2018) Understanding the sorption and biotransformation of organic micropollutants in innovative biological wastewater treatment technologies. Sci Total Environ 615:297–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.09.278
Archer E, Petrie B, Kasprzyk-Hordern B, Wolfaardt GM (2017) The fate of pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs), endocrine disrupting contaminants (EDCs), metabolites and illicit drugs in a WWTW and environmental waters. Chemosphere 174:437–446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.01.101
Baalbaki Z, Torfs E, Yargeau V, Vanrolleghem PA (2017) Predicting the fate of micropollutants during wastewater treatment: calibration and sensitivity analysis. Sci Total Environ 601–602:874–885. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.05.072
Barber LB, Loyo-Rosales JE, Rice CP, Minarik TA, Oskouie AK (2015) Endocrine disrupting alkylphenolic chemicals and other contaminants in wastewater treatment plant effluents, urban streams, and fish in the Great Lakes and upper Mississippi River regions. Sci Total Environ 517:195–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.02.035
Batstone DJ, Keller J, Angelidaki I, Kalyuzhnyi SV, Pavlostathis SG, Rozzi A, Sanders WTM, Siegrist H, Vavilin VA (2002). Anaerobic digestion model no. 1, IWA STR no. 13. IWA publishing, London, UK
Behera SK, Kim HW, Oh JE, Park HS (2011) Occurrence and removal of antibiotics, hormones and several other pharmaceuticals in wastewater treatment plants of the largest industrial city of Korea. Sci Total Environ 409(20):4351–4360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.07.015
Bernhard M, Muller J, Knepper TP (2006) Biodegradation of persistent polar pollutants in wastewater: comparison of an optimised lab-scale membrane bioreactor and activated sludge treatment. Water Res 40(18):3419–3428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2006.07.011
Boix C, Ibáñez M, Fabregat-Safont D, Morales E, Pastor L, Sancho JV, Sánchez-Ramírez JE, Hernández F (2016) Behaviour of emerging contaminants in sewage sludge after anaerobic digestion. Chemosphere 163:296–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.07.098
Campos JM, Queiroz SC, Roston DM (2019) Removal of the endocrine disruptors ethinyl estradiol, bisphenol a, and levonorgestrel by subsurface constructed wetlands. Sci Total Environ 693:133514. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.07.320
Caracciolo AB, Topp E, Grenni P (2015) Pharmaceuticals in the environment: biodegradation and effects on natural microbial communities. A review J Pharm Biomed Anal 106:25–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2014.11.040
Carballa M, Omil F, Lema JM (2005) Removal of cosmetic ingredients and pharmaceuticals in sewage primary treatment. Water Res 39(19):4790–4796. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2005.09.018
Carballa M, Omil F, Ternes T, Lema JM (2007) Fate of pharmaceutical and personal care products (PPCPs) during anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge. Water Res 41(10):2139–2150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2007.02.012
Clara M, Kreuzinger N, Strenn B, Gans O, Kroiss H (2005a) The solids retention time—a suitable design parameter to evaluate the capacity of wastewater treatment plants to remove micropollutants. Water Res 39(1):97–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2004.08.036
Clara M, Strenn B, Gans O, Martinez E, Kreuzinger N, Kroiss H (2005b) Removal of selected pharmaceuticals, fragrances and endocrine disrupting compounds in a membrane bioreactor and conventional wastewater treatment plants. Water Res 39:4797–4807. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2005.09.015
Collado N, Buttiglieri G, Ferrando-Climent L, Rodriguez-Mozaz S, Barceló D, Comas J, Rodriguez-Roda I (2012) Removal of ibuprofen and its transformation products: experimental and simulation studies. Sci Total Environ 433:296–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.06.060
Copp JB, Jeppsson U, Rosen C (2003). ASM1 to ADM1 transformation (Towards an ASM1 - ADM1 State Variable Interface for Plant-Wide Wastewater Treatment Modeling. Proc. Water Environment Federation Conference WEFTEC, Los Angeles, California
Dionisi D, Bertin L, Bornoroni L, Capodicasa S, Papini MP, Fava F (2006) Removal of organic xenobiotics in activated sludges under aerobic conditions and anaerobic digestion of the adsorbed species. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 81(9):1496–1505. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.1561
Fauser P, Vikelsøe J, Sørensen PB, Carlsen L (2003) Phthalates, nonylphenols and LAS in an alternately operated wastewater treatment plant—fate modelling based on measured concentrations in wastewater and sludge. Water Res 37:1288–1295. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(02)00482-7
Fernandez-Fontaina E, Pinho I, Carballa M, Omil F, Lema JM (2013) Biodegradation kinetic constants and sorption coefficients of micropollutants in membrane bioreactors. Biodegradation 24(2):165–177. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-012-9568-3
Fernandez-Fontaina E, Carballa M, Omil F, Lema JM (2014) Modelling cometabolic biotransformation of organic micropollutants in nitrifying reactors. Water Res 65:371–383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2014.07.048
Gogoi A, Mazumder P, Tyagi VK, Chaminda GT, An AK, Kumar M (2018) Occurrence and fate of emerging contaminants in water environment: a review. Groundw Sustain Dev 6:169–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2017.12.009
Gonzalez-Gil L, Papa M, Feretti D, Ceretti E, Mazzoleni G, Steimberg N, Pedrazzani R, Bertanza G, Lema JM, Carballa M (2016) Is anaerobic digestion effective for the removal of organic micropollutants and biological activities from sewage sludge? Water Res 102:211–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.06.025
Gonzalez-Gil L, Mauricio-Iglesias M, Carballa M, Lema JM (2018) Why are organic micropollutants not fully biotransformed? A mechanistic modelling approach to anaerobic systems. Water Res 142:115–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.05.032
Grandclément C, Seyssiecq I, Piram A, Wong-Wah-Chung P, Vanot G, Tiliacos N, Roche N, Doumenq P (2017) From the conventional biological wastewater treatment to hybrid processes, the evaluation of organic micropollutant removal: a review. Water Res 111:297–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.01.005
Gurung K, Ncibi MC, Sillanpää M (2019) Removal and fate of emerging organic micropollutants (EOMs) in municipal wastewater by a pilot-scale membrane bioreactor (MBR) treatment under varying solid retention times. Sci Total Environ 667:671–680. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.02.308
Hatoum R, Potier O, Roques-Carmes T, Lemaitre C, Hamieh T, Toufaily J, Horn H, Borowska E (2019) Elimination of micropollutants in activated sludge reactors with a special focus on the effect of biomass concentration. Water 11(11):2217. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112217
Heidler J, Halden RU (2007) Mass balance assessment of triclosan removal during conventional sewage treatment. Chemosphere 66:362–369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.04.066
Henze H, Grady Jr CPL, Gujer W, Marais G, Matsuo T (1987). Activated sludge model no. 1. IWA STR no. 1. IWA publishing, London, UK
Hyland KC, Dickenson ER, Drewes JE, Higgins CP (2012) Sorption of ionized and neutral emerging trace organic compounds onto activated sludge from different wastewater treatment configurations. Water Res 46(6):1958–1968. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2012.01.012
Inyang M, Flowers R, McAvoy D, Dickenson E (2016) Biotransformation of trace organic compounds by activated sludge from a biological nutrient removal treatment system. Bioresour Technol 216:778–784. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.05.124
Jeppsson U, Pons MN, Nopens I, Alex J, Copp JB, Gernaey KV, Rosen C, Steyer JP, Vanrolleghem PA (2007) Benchmark simulation model no. 2: general protocol and exploratory case studies. Water Sci Technol 56(8):67–78. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2007.604
Jones OAH, Voulvoulis N, Lester JN (2002) Aquatic environmental assessment of the top 25 English prescription pharmaceuticals. Water Res 36(20):5013–5022. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(02)00227-0
Joss A, Zabczynski S, Göbel A, Hoffman B, Löffler D, McArdell CS, Ternes TA, Thomsen A, Siegrist H (2006) Biological degradation of pharmaceuticals in municipal wastewater treatment: proposing a classification scheme. Water Res 40(8):1686–1696. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2006.02.014
Kimura K, Hara H, Watanabe Y (2007) Elimination of selected acidic pharmaceuticals from municipal wastewater by an activated sludge system and membrane bioreactors. Environ Sci Technol 41:3708–3714. https://doi.org/10.1021/es061684z
Kosma CI, Lambropoulou DA, Albanis TA (2014) Investigation of PPCPs in wastewater treatment plants in Greece: occurrence, removal and environmental risk assessment. Sci Total Environ 466-467:421–438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.07.044
Koumaki E, Mamais D, Noutsopoulos C, Nika MC, Bletsou A, Thomaidis N, Eftaxias A, Stratogianni G (2015) Degradation of emerging contaminants from water under natural sunlight: the effect of season, pH, humic acids and nitrate and identification of photodegradation by-products. Chemosphere 138:675–681. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.07.033
Koumaki E, Mamais D, Noutsopoulos C (2017) Environmental fate of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in river water/sediment systems. J Hazard Mater 323:233–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.03.026
Koumaki E, Mamais D, Noutsopoulos C (2018) Assessment of the environmental fate of endocrine disrupting chemicals in rivers. Sci Total Environ 628-629:947–958. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.02.110
Kreuzinger N, Clara M, Strenn B, Kroiss H (2004) Relevance of the sludge retention time (SRT) as design criteria for wastewater treatment plants for the removal of endocrine disruptors and pharmaceuticals from wastewater. Water Sci Technol 50(5):149–156. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2004.0322
Kümmerer K (2009) The presence of pharmaceuticals in the environment due to human use–present knowledge and future challenges. J Environ Manag 90(8):2354–2366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2009.01.023
Lahti M, Oikari A (2011) Microbial transformation of pharmaceuticals naproxen, bisoprolol, and diclofenac in aerobic and anaerobic environments. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 61(2):202–210. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-010-9622-2
Lakshminarasimman N, Quiñones O, Vanderford BJ, Campo-Moreno P, Dickenson EV, McAvoy DC (2018) Biotransformation and sorption of trace organic compounds in biological nutrient removal treatment systems. Sci Total Environ 640:62–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.05.145
Lapworth DJ, Baran N, Stuart ME, Ward RS (2012) Emerging organic contaminants in groundwater: a review of sources, fate and occurrence. Environ Pollut 163(0):287–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2011.12.034
Lee KC, Rittmann BE, Shi J, McAvoy D (1998) Advanced steady-state model for the fate of hydrophobic and volatile compounds in activated sludge. Water Environ Res 70(6):1118–1131. https://doi.org/10.2175/106143098X123480
Li C, Cabassud C, Cuigui C (2014) Evaluation of membrane bioreactor on removal of pharmaceutical micropollutants: a review. Desalination Water Treat 55(4):845–858. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2014.926839
Lindblom E, Press-Kristensen K, Vanrolleghem PA, Mikkelsen PS, Henze M (2009) Dynamic experiments with high bisphenol-A concentrations modelled with an ASM model extended to include a separate XOC degrading microorganism. Water Res 43(13):3169–3176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2009.04.030
Lindholm-Lehto P, Ahkola HSJ, Knuutinen JS, Herve SH (2016) Widespread occurrence and seasonal variation of pharmaceuticals in surface waters and municipal wastewater treatment plants in Central Finland. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:7985–7997. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5997-y
Loos R, Gawlik BM, Locoro G, Rimaviciute E, Contini S, Bidoglio G (2009) EU-wide survey of polar organic persistent pollutants in European river waters. Environ Pollut 157(2):561–568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2008.09.020
Loos R, Locoro G, Comero S, Contini S, Schwesig D, Werres F, Balsaa P, Gans O, Weiss S, Blaha L, Bolchi M (2010) Pan-European survey on the occurrence of selected polar organic persistent pollutants in ground water. Water Res 44(14):4115–4126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2010.05.032
Luo Y, Guo W, Ngo HH, Nghiem LD, Hai FI, Zhang J, Liang S, Wang XC (2014) A review on the occurrence of micropollutants in the aquatic environment and their fate and removal during wastewater treatment. Sci Total Environ 473:619–641. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.12.065
Maeng SK, Choi BG, Lee KT, Song KG (2013) Influences of solid retention time, nitrification and microbial activity on the attenuation of pharmaceuticals and estrogens in membrane bioreactors. Water Res 47:3151–3162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2013.03.014
Majewsky M, Gallé T, Yargeau V, Fischer K (2011) Active heterotrophic biomass and sludge retention time (SRT) as determining factors for biodegradation kinetics of pharmaceuticals in activated sludge. Bioresour Technol 102(16):7415–7421. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.05.032
Mannina G, Cosenza A, Viviani G (2017) Micropollutants throughout an integrated urban drainage model: sensitivity and uncertainty analysis. J Hydrol 554:397–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.09.026
Marco-Urrea E, Perez-Trujillo M, Blanquez P, Vicent T, Caminal G (2010) Biodegradation of the analgesic naproxen by Trametes versicolor and identification of intermediates using HPLC-DAD-MS and NMR. Bioresour Technol 101:2159–2166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2009.11.019
Martinez-Alcala I, Guillén-Navarro JM, Fernandez-Lopez C (2017) Pharmaceutical biological degradation, sorption and mass balance determination in a conventional activated-sludge wastewater treatment plant from Murcia, Spain. Chem Eng J 316:332–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.01.048
Mathias FT, Fockink DH, Disner GR, Prodocimo V, Ribas JLC, Ramos LP, Cestari MM, de Assis HCS (2018) Effects of low concentrations of ibuprofen on freshwater fish Rhamdia quelen. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 59:105–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2018.03.008
Mentor A, Brunström B, Mattsson A, Jönsson M (2019) Developmental exposure to a human relevant mixture of endocrine disruptors alters metabolism and adipogenesis in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Chemosphere 238:124584. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124584
Mohapatra DB, Brar SK, Tyagi R, Surampalli R (2011) Occurrence of bisphenol a in wastewater and wastewater sludge of CUQ treatment plant. J Xenobiot 1:9–16. https://doi.org/10.4081/xeno.2011.e3
Murdoch RW, Hay AG (2013) Genetic and chemical characterization of ibuprofen degradation by Sphingomonas Ibu-2. Microbiology 159:621–632. https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.062273-0
Nakada N, Tanishima T, Shinohara H, Kiri K, Takada H (2006) Pharmaceutical chemicals and endocrine disrupters in municipal wastewater in Tokyo and their removal during activated sludge treatment. Water Res 40:3297–3303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2006.06.039
Narumiya M, Nakada N, Yamashita N, Tanaka H (2013) Phase distribution and removal of pharmaceuticals and personal care products during anaerobic sludge digestion. J Hazard Mater 260:305–312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.05.032
Nie Υ, Qiang Ζ, Zhang Η, Ben W (2012) Fate and seasonal variation of endocrine-disrupting chemicals in a sewage treatment plant with a/a/O process. Sep Purif Technol 84:9–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2011.01.030
Nopens I, Batstone D, Copp JB, Jeppsson U, Volcke E, Alex J, Vanrolleghem PA (2009) An ASM/ADM model interface for dynamic plantwide simulation. Water Res 43(7):1913–1923. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2009.01.012
Noutsopoulos C, Koumaki E, Sarantopoulos V, Mamais D (2019) Analytical and mathematical assessment of emerging pollutants fate in a river system. J Hazard Mater 364:48–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.10.033
Papageorgiou M, Kosma C, Lambropoulou D (2016) Seasonal occurrence, removal, mass loading and environmental risk assessment of 55 pharmaceuticals and personal care products in a municipal wastewater treatment plant in Central Greece. Sci Total Environ 543:547–569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.11.047
Paterakis N, Chiu TY, Koh YKK, Lester JN, McAdam EJ, Scrimshaw MD, Soares A, Cartmell E (2012) The effectiveness of anaerobic digestion in removing estrogens and nonylphenol ethoxylates. J Hazard Mater 199:88–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.10.075
Petrie B, Barden R, Kasprzyk-Hordern B (2015) A review on emerging contaminants in wastewaters and the environment: current knowledge, understudied areas and recommendations for future monitoring. Water Res 72:3–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2014.08.053
Plósz BG, Langford KH, Thomas KV (2012) An activated sludge modeling framework for xenobiotic trace chemicals (ASM-X): assessment of diclofenac and carbamazepine. Biotechnol Bioeng 109(11):2757–2769. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.24553
Pomiès M, Choubert JM, Wisniewski C, Coquery M (2013) Modelling of micropollutant removal in biological wastewater treatments: a review. Sci Total Environ 443:733–748. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.11.037
Quintana JB, Weiss S, Reemtsma T (2005) Pathways and metabolites of microbial degradation of selected acidic pharmaceutical and their occurrence in municipal wastewater treated by a membrane bioreactor. Water Res 39:2654–2664. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2005.04.068
Radjenović J, Petrović M, Barceló D (2009) Fate and distribution of pharmaceuticals in wastewater and sewage sludge of the conventional activated sludge (CAS) and advanced membrane bioreactor (MBR) treatment. Water Res 43(3):831–841. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2008.11.043
Rangasamy B, Hemalatha D, Shobana C, Nataraj B, Ramesh M (2018) Developmental toxicity and biological responses of zebrafish (Danio rerio) exposed to anti-inflammatory drug ketoprofen. Chemosphere 213:423–433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.09.013
Salveson A, Rauch-Williams T, Dickenson E, Drewes J, Drury D, McAvoy D, Snyder S (2012) Trace organic compound removal during wastewater treatment–categorizing wastewater treatment processes by their efficacy in reduction of a suite of Indicator TOrC. Water Environment Research Foundation, Alexandria, VA
Samaras VG, Stasinakis AS, Mamais D, Thomaidis NS, Lekkas TD (2013) Fate of selected pharmaceuticals and synthetic endocrine disrupting compounds during wastewater treatment and sludge anaerobic digestion. J Hazard Mater 244:259–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.11.039
Samaras VG, Stasinakis AS, Thomaidis NS, Mamais D, Lekkas TD (2014) Fate of selected emerging micropollutants during mesophilic, thermophilic and temperature co-phased anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge. Bioresour Technol 162:365–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.03.154
Shon HK, Vigneswaran S, Kandasamy J, Cho J (2009). Water and wastewater treatment technologies, volume 1 encyclopedia of life support systems (EOLSS). Membrane Technology for Organic Removal in wastewater. United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization ISBN 978-1-84826-188-4
Singer H, Müller S, Tixier C, Pillonel L (2002) Triclosan: occurrence and fate of a widely used biocide in the aquatic environment: field measurements in wastewater treatment plants. Environ Sci Technol 36:4998–5004. https://doi.org/10.1021/es025750i
Sousa JCG, Ribeiro AR, Barbosa MO, Pereira MFR, Silva AMT (2018) A review on environmental monitoring of water organic pollutants identified by EU guidelines. J Hazard Mater 344:146–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.09.058
Stasinakis AS (2012) Review on the fate of emerging contaminants during sludge anaerobic digestion. Bioresour Technol 121:432–440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.06.074
Stasinakis AS, Gatidou G, Mamais D, Thomaidis NS, Lekkas TD (2008) Occurrence and fate of endocrine disrupters in Greek sewage treatment plants. Water Res 42:1796–1804. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2007.11.003
Stasinakis AS, Thomaidis NS, Arvaniti OS, Asimakopoulos AG, Samaras VG, Ajibola A, Mamais D, Lekkas TD (2013) Contribution of primary and secondary treatment on the removal of benzothiazoles, benzotriazoles, endocrine disruptors, pharmaceuticals and perfluorinated compounds in a sewage treatment plant. Sci Total Environ 463:1067–1075. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.06.087
Stevens-Garmon J, Drewes JE, Khan SJ, McDonald JA, Dickenson ER (2011) Sorption of emerging trace organic compounds onto wastewater sludge solids. Water Res 45(11):3417–3426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2011.03.056
Su L, Aga D, Chandran K, Khunjar WO (2015) Factors impacting biotransformation kinetics of trace organic compounds in lab-scale activated sludge systems performing nitrification and denitrification. J Hazard Mater 282:116–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.08.007
Suarez S, Lema JM, Omil F (2010) Removal of pharmaceutical and personal care products (PPCPs) under nitrifying and denitrifying conditions. Water Res 44(10):3214–3224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2010.02.040
Suarez S, Reif R, Lema JM, Omil F (2012) Mass balance of pharmaceutical and personal care products in a pilot-scale single-sludge system: influence of T, SRT and recirculation ratio. Chemosphere 89(2):164–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.05.094
Symsaris EC, Fotidis IA, Stasinakis AS, Angelidaki I (2015) Effects of triclosan, diclofenac, and nonylphenol on mesophilic and thermophilic methanogenic activity and on the methanogenic communities. J Hazard Mater 291:45–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.03.002
Ternes TA, Herrmann N, Bonerz M, Knacker T, Siegrist H, Joss A (2004) A rapid method to measure the solid–water distribution coefficient (Kd) for pharmaceuticals and musk fragrances in sewage sludge. Water Res 38(19):4075–4084. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2004.07.015
The PubChem Project (2017) USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information, Online PubChem Compound Database. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pccompound. Accessed 21 Apr 2020
Toxicology Data Network (TOXNET) (2017) U.S. National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health, Health & Human Services. http://toxnet.nlm.nih.gov/cgi-bin/sis/htmlgen?HSDB. Accessed 21 Apr 2020
Tran NH, Reinhard M, Gin KY (2018) Occurrence and fate of emerging contaminants in municipal wastewater treatment plants from different geographical regions-a review. Water Res 133:182–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.12.029
Urase T, Kikuta T (2005) Separate estimation of adsorption and degradation of pharmaceutical substances and estrogens in the activated sludge process. Water Res 39(7):1289–1300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2005.01.015
Verlicchi P, Al Aukidy M, Zambello E (2012) Occurrence of pharmaceutical compounds in urban wastewater: removal, mass load and environmental risk after a secondary treatment—a review. Sci Total Environ 429:123–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.04.028
Wanda EM, Nyoni H, Mamba BB, Msagati TA (2017) Occurrence of emerging micropollutants in water systems in Gauteng, Mpumalanga, and north west provinces, South Africa. Int J Environ Res Public Health 14(1):79. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14010079
Xue W, Wu C, Xiao K, Huang X, Zhou H, Tsuno H, Tanaka H (2010) Elimination and fate of selected micro-organic pollutants in a full-scale anaerobic/anoxic/aerobic process combined with membrane bioreactor for municipal wastewater reclamation. Water Res 44(20):5999–6010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2010.07.052
Yang Y, Ok YS, Kim KH, Kwon EE, Tsang YF (2017) Occurrences and removal of pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) in drinking water and water/sewage treatment plants: a review. Sci Total Environ 596:303–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.04.102
Zhang Y, Geißen SU, Gal C (2008) Carbamazepine and Diclofenac: removal in wastewater treatment plants and occurrence in water bodies. Chemosphere 73:1151–1161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.07.086
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest/Competing interests.
Not Applicable
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Article Highlights
• A plant-wide mathematical model was developed to study the fate of ECs through wastewater treatment.
• Low solids retention time and high primary sedimentation solids removal are associated with poor ECs removal.
•The high variation of ECs load in raw wastewater results in a lower range variation in their effluent concentrations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Noutsopoulos, C., Charalambous, V. & Koumaki, E. Evaluating the Fate of Emerging Contaminants in Wastewater Treatment Plants through Plant-Wide Mathematical Modelling. Environ. Process. 7, 1065–1094 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-020-00459-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-020-00459-y