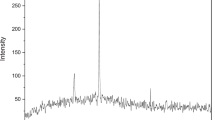
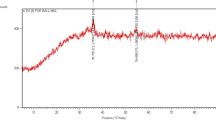
Abstract
The effect of aeration and ultrasonic irradiation on the performance of nano zero-valent iron (nZVI)-based Fenton reaction was investigated. The purpose of aeration was to create mixing in the system, and the mixing in the reactor was supplied only by using air bubbles without employing a mechanical mixer. The effect of four numerical variables, i.e., H2O2 amount, catalyst dose, aeration, and time, and one categorical one, i.e., ultrasonic (US) irradiation, was examined on the elimination of ciprofloxacin (CIP) from aqueous solution by response surface methodology. The accompanying the aeration and the US irradiation nZVI-based Fenton reaction could accelerate nZVI corrosion and formation of reactive intermediates, thus effectively oxidizing contaminants. A combined treatment of Fenton (nZVI/H2O2)/aeration/US resulted in higher antibiotic removal efficiency in comparison to conventional Fenton (nZVI/H2O2), Fenton (nZVI/H2O2)/aeration and Fenton (nZVI/H2O2)/US processes. A combined treatment of Fenton (nZVI/H2O2)/aeration/US achieved a 94% CIP removal within 60 min of an initial CIP concentration of 100 mg/L under neutral pH condition. Results demonstrated that ultrasonic-assisted nZVI/H2O2 process under aeration condition can be applied as an advisable choice for the treatment of organic wastewaters. Due to employing aeration instead of using mechanical stirring, this proposed process needs low energy consumption.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ammar HB (2016) Sono-Fenton process for metronidazole degradation in aqueous solution: effect of acoustic cavitation and peroxydisulfate anion. Ultrason Sonochem 33:164–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2016.04.035
Anju S, Yesodharan S, Yesodharan E (2012) Zinc oxide mediated sonophotocatalytic degradation of phenol in water. Chem Eng J 189:84–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.02.032
Ay F, Kargi F (2010) Advanced oxidation of amoxicillin by Fenton's reagent treatment. J Hazard Mater 179:622–627. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.03.048
Banerjee P, Chakrabarti S, Maitra S, Dutta BK (2012) Zinc oxide nano-particles–sonochemical synthesis, characterization and application for photo-remediation of heavy metal. Ultrason Sonochem 19:85–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2011.05.007
Bokare AD, Choi W (2014) Review of iron-free Fenton-like systems for activating H2O2 in advanced oxidation processes. J Hazard Mater 275:121–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.04.054
Bremner DH, Burgess AE, Houllemare D, Namkung K-C (2006) Phenol degradation using hydroxyl radicals generated from zero-valent iron and hydrogen peroxide. Appl Catal B Environ 63:15–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2005.09.005
Cao Z, Liu X, Xu J, Zhang J, Yang Y, Zhou J, Xu X, Lowry GV (2017) Removal of antibiotic florfenicol by sulfide-modified nanoscale zero-valent iron. Environ Sci Technol 51:11269–11277. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b02480
Chakma S, Moholkar VS (2013) Physical mechanism of sono-Fenton process. AICHE J 59:4303–4313. https://doi.org/10.1002/aic.14150
Chang SH, Chuang SH, Li HC, Liang HH, Huang LC (2009) Comparative study on the degradation of IC Remazol brilliant blue R and IC acid black 1 by Fenton oxidation and Fe0/air process and toxicity evaluation. J Hazard Mater 166:1279–1288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.12.042
Dai Y, Hu Y, Jiang B, Zou J, Tian G, Fu H (2016) Carbothermal synthesis of ordered mesoporous carbon-supported nano zero-valent iron with enhanced stability and activity for hexavalent chromium reduction. J Hazard Mater 309:249–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.04.013
Duesterberg CK, Mylon SE, Waite TD (2008) pH effects on iron-catalyzed oxidation using Fenton’s reagent. Environ Sci Technol 42:8522–8527. https://doi.org/10.1021/es801720d
Giri AS, Golder AK (2014) Ciprofloxacin degradation from aqueous solution by Fenton oxidation: reaction kinetics and degradation mechanisms. RSC Adv 4:6738–6745. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3RA45709E
Gogate PR (2008) Treatment of wastewater streams containing phenolic compounds using hybrid techniques based on cavitation: a review of the current status and the way forward. Ultrason Sonochem 15:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2007.04.007
González Labrada K, Alcorta Cuello DR, Saborit Sánchez I, García Batle M, Manero MH, Barthe L, Jáuregui-Haza UJ (2018) Optimization of ciprofloxacin degradation in wastewater by homogeneous sono-Fenton process at high frequency. J Environ Sci Health A 53:1139–1148. https://doi.org/10.1080/10934529.2018
Guan X, Sun Y, Qin H, Li J, Lo IM, He D, Dong H (2015) The limitations of applying zero-valent iron technology in contaminants sequestration and the corresponding countermeasures: the development in zero-valent iron technology in the last two decades (1994–2014). Water Res 75:224–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2015.02.034
Gupta A, Garg A (2018) Degradation of ciprofloxacin using Fenton's oxidation: effect of operating parameters, identification of oxidized by-products and toxicity assessment. Chemosphere 193:1181–1188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.11.046
Keenan CR, Sedlak DL (2008) Factors affecting the yield of oxidants from the reaction of nanoparticulate zero-valent iron and oxygen. Environ Sci Technol 42:1262–1267. https://doi.org/10.1021/es7025664
Khatri J, Nidheesh P, Singh TA, Kumar MS (2018) Advanced oxidation processes based on zero-valent aluminium for treating textile wastewater. Chem Eng J 348:67–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.04.074
Kidak R, Ince NH (2006) Ultrasonic destruction of phenol and substituted phenols: a review of current research. Ultrason Sonochem 13:195–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2005.11.004
Kim J, Martinez F, Metcalfe I (2007) The beneficial role of use of ultrasound in heterogeneous Fenton-like system over supported copper catalysts for degradation of p-chlorophenol. Catal Today 124:224–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2007.03.040
Leypold CF, Reiher M, Brehm G, Schmitt MO, Schneider S, Matousek P, Towrie M (2003) Tetracycline and derivatives—assignment of IR and Raman spectra via DFT calculations. Phys Chem Chem Phys 5:1149–1157. https://doi.org/10.1039/B210522E
Liu Y, He X, Fu Y, Dionysiou DD (2016) Degradation kinetics and mechanism of oxytetracycline by hydroxyl radical-based advanced oxidation processes. Chem Eng J 284:1317–1327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.09.034
Liu X, Cao Z, Yuan Z, Zhang J, Guo X, Yang Y, He F, Zhao Y, Xu J (2018) Insight into the kinetics and mechanism of removal of aqueous chlorinated nitroaromatic antibiotic chloramphenicol by nanoscale zero-valent iron. Chem Eng J 334:508–518. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.10.060
Martini J, Orge CA, Faria JL, Pereira MF, Soares OS (2018) Sulfamethoxazole degradation by combination of advanced oxidation processes. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering 6:4054–4060. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2018.05.047
Mason TJ (2007) Sonochemistry and the environment–providing a “green” link between chemistry, physics and engineering. Ultrason Sonochem 14:476–483. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2006.10.008
Noradoun CE, Cheng IF (2005) EDTA degradation induced by oxygen activation in a zerovalent iron/air/water system. Environ Sci Technol 39:7158–7163. https://doi.org/10.1021/es050137v
Noubactep C, Schöner A (2010) Metallic iron for environmental remediation: learning from electrocoagulation. J Hazard Mater 175:1075–1080. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.09.152
Schrebler R, Ballesteros LA, Gómez H, Greza P, Córdova R, Muñoz E, Schrebler R, Ramos-Barrado JR, Dalchiele EA (2014) Electrochemically grown self-organized hematite nanotube arrays for photoelectrochemical water splitting. J Electrochem Soc 161:H903–H908. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0481414jes
Segura Y, Martínez F, Melero JA (2013) Effective pharmaceutical wastewater degradation by Fenton oxidation with zero-valent iron. Appl Catal B Environ 136:64–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.01.036
Sharma S, Kapoor S, Christian R (2017) Effect of Fenton process on treatment of simulated textile wastewater: optimization using response surface methodology. Int J Environ Sci Technol 14:1665–1678. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-017-1253-y
Sivasankar T, Moholkar VS (2009a) Mechanistic approach to intensification of sonochemical degradation of phenol. Chem Eng J 149:57–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2008.10.004
Sivasankar T, Moholkar VS (2009b) Physical insights into the sonochemical degradation of recalcitrant organic pollutants with cavitation bubble dynamics. Ultrason Sonochem 16:769–781. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2009.02.009
Sun SP, Guo HQ, Ke Q, Sun JH, Shi SH, Zhang ML, Zhou Q (2009) Degradation of antibiotic ciprofloxacin hydrochloride by photo-Fenton oxidation process. Environ Eng Sci 2:753–759. https://doi.org/10.1089/ees.2008.0076
Tokumura M, Morito R, Shimizu A, Kawase Y (2009) Innovative water treatment system coupled with energy production using photo-Fenton reaction. Environ Sci Technol 60:2589–2597. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2009.582
Trovó A, Hassan A, Sillanpää M, Tang W (2016) Degradation of acid blue 161 by Fenton and photo-Fenton processes. Int J Environ Sci Technol 13:147–158. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-015-0854-6
Xu J, Sheng T, Hu Y, Baig SA, Lv X, Xu X (2013) Adsorption–dechlorination of 2, 4-dichlorophenol using two specified MWCNTs-stabilized Pd/Fe nanocomposites. Chem Eng J 219:162–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.01.010
Xu J, Liu X, Lowry GV, Cao Z, Zhao H, Zhou JL, Xu X (2016) Dechlorination mechanism of 2, 4-dichlorophenol by magnetic MWCNTs supported Pd/Fe nanohybrids: rapid adsorption, gradual dechlorination, and desorption of phenol. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:7333–7342. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b11859
Xu J, Cao Z, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Gao X, Ahmed MB, Zhang J, Yang Y, Zhou JL, Lowry GV (2019) Distributing sulfidized nanoscale zerovalent iron onto phosphorus-functionalized biochar for enhanced removal of antibiotic florfenicol. Chem Eng J 359:713–722. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.11.180
Yahya MS, Oturan N, El Kacemi K, El Karbane M, Aravindakumar CT, Oturan MA (2014) Oxidative degradation study on antimicrobial agent ciprofloxacin by electro-Fenton process: kinetics and oxidation products. Chemosphere 117:447–454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.08.016
Yang B, Zuo J, Tang X, Liu F, Yu X, Tang X, Jiang H, Gan L (2014) Effective ultrasound electrochemical degradation of methylene blue wastewater using a nanocoated electrode. Ultrason Sonochem 21:1310–1317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2014.01.008
Zhai J, Ma H, Liao J, Rahaman MH, Yang Z, Chen Z (2018) Comparison of Fenton, ultraviolet–Fenton and ultrasonic–Fenton processes on organics and colour removal from pre-treated natural gas produced water. Int J Environ Sci Technol 15:2411–2422. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-017-1604-8
Zhao H, Liu X, Cao Z, Zhan Y, Shi X, Yang Y, Zhou J, Xu J (2016) Adsorption behavior and mechanism of chloramphenicols, sulfonamides, and non-antibiotic pharmaceuticals on multi-walled carbon nanotubes. J Hazard Mater 310:235–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.02.045
Zou Y, Wang X, Khan A, Wang P, Liu Y, Alsaedi A, Hayat T, Wang X (2016) Environmental remediation and application of nanoscale zero-valent iron and its composites for the removal of heavy metal ions: a review. Environ Sci Technol 50:7290–7304. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b01897
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the Research Council of Kermanshah University of Medical Sciences (Grant Number: 96349) for their financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• Heterogeneous Fenton (nZVI/H2O2) is used for ciprofloxacin treatment.
• Aeration was used to supply mixing and reduction of operation cost.
• The combinative Fenton/US/aeration shows the highest efficiency.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pirsaheb, M., Moradi, S., Shahlaei, M. et al. Ultrasonic Enhanced Zero-Valent Iron-Based Fenton Reaction for Ciprofloxacin Removal under Aerobic Condition. Environ. Process. 7, 227–241 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-019-00415-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-019-00415-5