Abstract
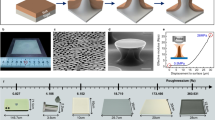
In this communication, we have introduced bioinspired polymeric dry adhesive structures made by using low-expertise yet robust over-etching fabrication process and chemical treatment method. The structure of gecko-foot in nature has been adopted into various applications for its remarkable smart adhesion performance. Although a lot of methods have been proposed to fabricate the gecko-inspired dry adhesion systems, they have faced on problem of structural failure of wide-tip on the top of the micro structures. To solve the problem, we have focused on developing proper wide-tip shape of the polymeric dry adhesive structures. Through the controlled over-etching process and C4F8 deposition method, we have made wide-tip microstructures without any structural failure. As a result, we develop the robust dry adhesive structures with highly reproducible and accurate wide-tip arrays for strong potential applications such as in green-environmental industries.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MEMS:
-
Microelectromechanical systems
- SOI:
-
Silicon on insulator
- C4F8 :
-
Octafluorocyclobutane
- PDMS:
-
Polydimethylsiloxane
References
Autumn, K., Liang, Y. A., Hsieh, S. T., Zesch, W., Chan, W. P., et al., “Adhesive Force of a Single Gecko Foot-Hair,” Nature, Vol. 405, No. 6787, pp. 681–685, 2000.
Arzt, E., Gorb, S., and Spolenak, R., “From Micro to Nano Contacts in Biological Attachment Devices,” Proc. of the National Academy of Sciences, Vol. 100, No. 19, pp. 10603–10606, 2003.
Kwak, M. K., Jeong, H. E., and Suh, K. Y., “Rational Design and Enhanced Biocompatibility of a Dry Adhesive Medical Skin Patch,” Advanced Materials, Vol. 23, No. 34, pp. 3949–3953, 2011.
Jeong, H. E. and Suh, K. Y., “Nanohairs and Nanotubes: Efficient Structural Elements for Gecko-Inspired Artificial Dry Adhesives,” Nano Today, Vol. 4, No. 4, pp. 335–346, 2009.
Kwak, J.-S. and Kim, T.-W., “A Review of Adhesion and Friction Models for Gecko Feet,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., Vol. 11, No. 1, pp. 171–186, 2010.
Del Campo, A., Greiner, C., Alvarez, I., and Arzt, E., “Patterned Surfaces with Pillars with Controlled 3D Tip Geometry Mimicking Bioattachment Devices,” Advanced Materials, Vol. 19, No. 15, pp. 1973–1977, 2007.
Pang, C., Kwak, M. K., Lee, C., Jeong, H. E., Bae, W.-G., et al., “Nano Meets Beetles from Wing to Tiptoe: Versatile Tools for Smart and Reversible Adhesions,” Nano Today, Vol. 7, No. 6, pp. 496–513, 2012.
Cho, K.-J., Koh, J.-S., Kim, S., Chu, W.-S., Hong, Y., et al., “Review of Manufacturing Processes for Soft Biomimetic Robots,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., Vol. 10, No. 3, pp. 171–181, 2009.
Chu, B., Jung, K., Han, C.-S., and Hong, D., “A Survey of Climbing Robots: Locomotion and Adhesion,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., Vol. 11, No. 4, pp. 633–647, 2010.
Kwak, M. K., Jeong, H. E., Bae, W. G., Jung, H. S., and Suh, K. Y., “Anisotropic Adhesion Properties of Triangular-Tip-Shaped Micropillars,” Small, Vol. 7, No. 16, pp. 2296–2300, 2011.
Bae, W. G., Kim, D., Kwak, M. K., Ha, L., Kang, S. M., et al., “Enhanced Skin Adhesive Patch with Modulus-Tunable Composite Micropillars,” Advanced Healthcare Materials, Vol. 2, No. 1, pp. 109–113, 2013.
Kim, S. and Sitti, M., “Biologically Inspired Polymer Microfibers with Spatulate Tips as Repeatable Fibrillar Adhesives,” Applied Physics Letters, Vol. 89, No. 26, Paper No. 261911, 2006.
Federle, W., “Why are So Many Adhesive Pads Hairy?” Journal of Experimental Biology, Vol. 209, No. 14, pp. 2611–2621, 2006.
Heepe, L., Kovalev, A. E., Filippov, A. E., and Gorb, S. N., “Adhesion Failure at 180 000 Frames Per Second: Direct Observation of the Detachment Process of a Mushroom-Shaped Adhesive,” Physical Review Letters, Vol. 111, No. 10, Paper No. 104301, 2013.
Yi, H., Hwang, I., Sung, M., Lee, D., Kim, J.-H., et al., “Bio-Inspired Adhesive Systems for Next-Generation Green Manufacturing,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf.-Green Tech., Vol. 1, No. 4, pp. 347–351, 2014.
Kang, S. M., Kim, S. M., Kim, H. N., Kwak, M. K., Tahk, D. H., et al., “Robust Superomniphobic Surfaces with Mushroom-Like Micropillar Arrays,” Soft Matter, Vol. 8, No. 33, pp. 8563–8568, 2012.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, S.M. Bioinspired design and fabrication of green-environmental dry adhesive with robust wide-tip shape. Int. J. of Precis. Eng. and Manuf.-Green Tech. 3, 189–192 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40684-016-0025-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40684-016-0025-3