Summary
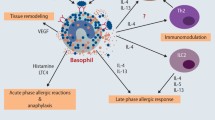
In recent years there has been growing evidence to suggest a major role for basophils in allergy despite being one of the rarest leukocytes. These blood-borne cells have clearly been observed to invade other tissues such as skin or lung affected by allergic inflammation. More recent studies have shown that basophil responses — typified by degranulation — correlate with the severity of allergic reactions in food allergy. However, despite studies suggesting major input in governing allergy symptoms their immunomodulatory roles are less clearly defined. While basophils are an important early source for pro-allergic Th2-type cytokines, interleukins 4 and 13 (IL-4 and IL-13), it is unclear whether they play a role in initiating allergic immunity or merely enhance existing allergy. In this regard, mouse models of allergy are more supportive of a key innate immune function of basophils in orchestrating Th2-type immunity and allergy, and potentially acting as antigen presenting cells. However, these important roles have not been observed in primary human basophils although there is clear evidence to suggest that they crucially promote group 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s) in atopic dermatitis. Shedding more light on these immunomodulatory roles of human basophils, and differentiating them from their rodent counterparts, will provide much needed greater understanding of this elusive cell type, especially in view of developing new therapeutic strategies against allergy.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- alpha-gal:
-
Galactose-alpha-1,3-galactose
- ATP:
-
Adenosine triphosphate
- BAT:
-
Basophil activation tests
- FcεRI:
-
Immunoglobulin E receptor
- HIF-1:
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1
- Ig:
-
Immunoglobulin
- IL:
-
Interleukin
- ILC2:
-
Group 2 innate lymphoid cell
- MHC:
-
Major histocompatibility complex
- PGD2:
-
Prostaglandin D2
- Th:
-
T helper
- VEGF:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor
References
Gurzeler U, Rabachini T, Dahinden CA, Salmanidis M, Brumatti G, Ekert PG et al. In vitro differentiation of near-limited numbers of functional mouse basophils using conditional Hoxb8. Allergy 2013;68:604–13
Gibbs BF, Nilsson GP. Basophils unlimited. Allergy. 2013;68:553–4
Schulman ES, MacGlashan DW Jr, Schleimer RP, Peters SP, Kagey-Sobotka A, Newball HH et al. Purified human basophils and mast cells: current concepts of mediator release. Eur J Respir Dis Suppl. 1983;128(Pt 1):53–61
Kleine-Tebbe J, Erdmann S, Knol EF, MacGlashan DW Jr, Poulsen LK, Gibbs BF. Diagnostic tests based on human basophils: potentials, pitfalls and perspectives. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2006;41:79–90
Santos AF, Du Toit G, Douiri A, Radulovic S, Stephens A, Turcanu V et al. Distinct parameters of the basophil activation test reflect the severity and threshold of allergic reactions to peanut. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015;135:179–86
Homšak M, Silar M, Berce V, Tomazin M, Skerbinjek-Kavalar M, Celesnik N et al. The relevance of basophil allergen sensitivity testing to distinguish between severe and mild peanut-allergic children. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2013;162:310–7
Schmid JM, Würtzen PA, Dahl R, Hoffmann HJ. Early improvement in basophil sensitivity predicts symptom relief with grass pollen immunotherapy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;134:741–4
Glaumann S, Nopp A, Johansson SG, Rudengren M, Borres MP, Nilsson C. Basophil allergen threshold sensitivity, CD-sens, IgE-sensitization and DBPCFC in peanut-sensitized children. Allergy. 2012;67:242–7
Dahlén B1, Nopp A, Johansson SG, Eduards M, Skedinger M, Adédoyin J. Basophil allergen threshold sensitivity, CD-sens, is a measure of allergen sensitivity in asthma. Clin Exp Allergy. 2011;41:1091–7
Commins SP, James HR, Stevens W, Pochan SL, Land MH, King C et al. Delayed clinical and ex vivo response to mammalian meat in patients with IgE to galactose-alpha-1,3-galactose. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;134:108–15
Lin H, Boesel KM, Griffith DT, Prussin C, Foster B, Romero FA et al. Omalizumab rapidly decreases nasal allergic response and FcepsilonRI on basophils. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004;113:297–302
Savage JH, Courneya JP, Sterba PM, Macglashan DW, Saini SS, Wood RA. Kinetics of mast cell, basophil, and oral food challenge responses in omalizumab-treated adults with peanut allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012;130:1123–9
Voskamp AL, Gillman A, Symons K, Sandrini A, Rolland JM, O’Hehir RE et al. Clinical efficacy and immunologic effects of omalizumab in allergic bronchopulmonaryaspergillosis. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2015;3:192–9
Reber LL, Marichal T, Mukai K, Kita Y, Tokuoka SM, Roers A et al. Selective ablation of mast cells or basophils reduces peanut-induced anaphylaxis in mice. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013;132:881–8
Tsujimura Y, Obata K, Mukai K, Shindou H, Yoshida M, Nishikado H et al. Basophils play a pivotal role in immunoglobulin-G-mediated but not immunoglobulin-E-mediated systemic anaphylaxis. Immunity. 2008;28:581–9
Kepley CL, Cambier JC, Morel PA, Lujan D, Ortega E, Wilson BS et al. Negative regulation of FcepsilonRIsignaling by FcgammaRIIcostimulation in human blood basophils. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2000;106:337–48
Bruhns P, Frémont S, Daëron M. Regulation of allergy by Fc receptors. Curr Opin Immunol. 2005;17:662–9
Falanga YT, Chaimowitz NS, Charles N, Finkelman FD, Pullen NA, Barbour S et al. Lyn but not Fyn kinase controls IgG-mediated systemic anaphylaxis. J Immunol. 2012;188:4360–8
Falcone FH, Knol EF, Gibbs BF. The role of basophils in the pathogenesis of allergic disease. ClinExp Allergy. 2011;41:939–47
McEuen AR, Buckley MG, Compton SJ, Walls AF. Development and characterization of a monoclonal antibody specific for human basophils and the identification of a unique secretory product of basophil activation. Lab Invest. 1999;79:27–38
Kepley CL, Craig SS, Schwartz LB. Identification and partial characterization of a unique marker for human basophils. J Immunol. 1995;154:6548–55
Koshino T, Teshima S, Fukushima N, Takaishi T, Hirai K, Miyamoto Y et al. Identification of basophils by immunohistochemistry in the airways of post-mortem cases of fatal asthma. Clin Exp Allergy. 1993;23:919–25
Kepley CL, McFeeley PJ, Oliver JM, Lipscomb MF. Immunohistochemical detection of human basophils in postmortem cases of fatal asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001;164:1053–8
Ono E, Taniguchi M, Higashi N, Mita H, Kajiwara K, Yamaguchi H et al. CD203c expression on human basophils is associated with asthma exacerbation. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2010;125:483–9
Gibbs BF. Human basophils as effectors and immunomodulators of allergic inflammation and innate immunity. Clin Exp Med. 2005;5:43–9
Nabe T, Matsuya K, Akamizu K, Fujita M, Nakagawa T, Shioe M et al. Roles of basophils and mast cells infiltrating the lung by multiple antigen challenges in asthmatic responses of mice. Br J Pharmacol. 2013;169:462–76
Nouri-Aria KT, Irani AM, Jacobson MR, O’brien F, Varga EM, Till SJ, et al. Basophil recruitment and IL-4 production during human allergen-induced late asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001;108:205–11
Schroeder JT, Lichtenstein LM, Roche EM, Xiao H, Liu MC. IL-4 production by human basophils found in the lung following segmental allergen challenge. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001;107:265–71
Gibbs BF, Haas H, Falcone FH, Albrecht C, Vollrath IB, Noll T et al. Purified human peripheral blood basophils release interleukin-13 and preformed interleukin-4 following immunological activation. Eur J Immunol. 1996;26:2493–8
Yanagihara Y, Kajiwara K, Basaki Y, Ikizawa K, Ebisawa M, Ra C et al. Cultured basophils but not cultured mast cells induce human IgE synthesis in B cells after immunologic stimulation. ClinExpImmunol. 1998;111:136–43
Ying S, Humbert M, Meng Q, Pfister R, Menz G, Gould HJ et al. Local expression of epsilon germline gene transcripts and RNA for the epsilon heavy chain of IgE in the bronchial mucosa in atopic and nonatopic asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001;107:686–92
Takhar P, Corrigan CJ, Smurthwaite L, O’Connor BJ, Durham SR, Lee TH et al. Class switch recombination to IgE in the bronchial mucosa of atopic and nonatopic patients with asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007;119:213–8.
Mukai K, Matsuoka K, Taya C, Suzuki H, Yokozeki H, Nishioka K et al. Basophils play a critical role in the development of IgE-mediated chronic allergic inflammation independently of T cells and mast cells. Immunity. 2005;23:191–202
Obata K, Mukai K, Tsujimura Y, Ishiwata K, Kawano Y, Minegishi Y et al. Basophils are essential initiators of a novel type of chronic allergic inflammation. Blood. 2007;110: 913–20
Ohnmacht C, Schwartz C, Panzer M, Schiedewitz I, Naumann R, Voehringer D. Basophils orchestrate chronic allergic dermatitis and protective immunity against helminths. Immunity. 2010;33:364–74
Sumbayev VV, Nicholas SA, Streatfield CL, Gibbs BF. Involvement of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 HiF(1alpha) in IgE-mediated primary human basophil responses. Eur J Immunol. 2009;39:3511–9
Sumbayev VV1, Yasinska I, Oniku AE, Streatfield CL, Gibbs BF. Involvement of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 in the inflammatory responses of human LAD2 mast cells and basophils. PLoS One. 2012;7:e34259
Gibbs BF1, Yasinska IM, Pchejetski D, Wyszynski RW, Sumbayev VV. Differential control of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 activity during pro-inflammatory reactions of human haematopoietic cells of myeloid lineage. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2012;44:1739–49
Motomura Y, Morita H, Moro K, Nakae S, Artis D, Endo TA et al. Basophil-derived interleukin-4 controls the function of natural helper cells, a member of ILC2s, in lung inflammation. Immunity. 2014;40:758–71
Kim BS, Wang K, Siracusa MC, Saenz SA, Brestoff JR, Monticelli LA et al. Basophils promote innate lymphoid cell responses in inflamed skin. J Immunol. 2014;193:3717–25
Suzukawa M, Iikura M, Koketsu R, Nagase H, Tamura C, Komiya A et al. An IL-1 cytokine member, IL-33, induces human basophil activation via its ST2 receptor. J Immunol. 2008;181:5981–9
Sharma M, Stephen-Victor E, Poncet P, Kaveri SV, Bayry J. Basophils are inept at promoting human Th17 responses. Hum Immunol. 2015;76:176–80
Sokol CL, Chu NQ, Yu S, Nish SA, Laufer TM, Medzhitov R. Basophils function as antigen-presenting cells for an allergen-induced T helper type 2 response. Nat Immunol. 2009;10:713–20
Perrigoue JG, Saenz SA, Siracusa MC, Allenspach EJ, Taylor BC, Giacomin PR et al. MHC class II-dependent basophil-CD4+ T cell interactions promote T(H)2 cytokine-dependent immunity. Nat Immunol. 2009;10:697–5
Yoshimoto T, Yasuda K, Tanaka H, Nakahira M, Imai Y, Fujimori Y et al. Basophils contribute to T(H)2-IgE responses in vivo via IL-4 production and presentation of peptide-MHC class II complexes to CD4+ T cells. Nat Immunol. 2009;10:706–12
Tang H, Cao W, Kasturi SP, Ravindran R, Nakaya HI, Kundu K et al. The T helper type 2 response to cysteine proteases requires dendritic cell-basophil cooperation via ROS-mediated signaling. Nat Immunol. 2010;11:608–17
Hammad H, Plantinga M, Deswarte K, Pouliot P, Willart MA, Kool M et al. Inflammatory dendritic cells - not basophils - are necessary and sufficient for induction of Th2 immunity to inhaled house dust mite allergen. J Exp Med. 2010;207:2097–111
Voskamp AL, Prickett SR, Mackay F, Rolland JM, O’Hehir RE. PLoS One. MHC class II expression in human basophils: induction and lack of functional significance. PLoS One. 2013;8:e81777
Falcone FH, Morroll S, Gibbs BF. Lack of protease activated receptor (PAR) expression in purified human basophils. Inflamm Res. 2005;54 Suppl 1:S13–4
Eckl-Dorna J, Ellinger A, Blatt K, Ghanim V, Steiner I, Pavelka M et al. Basophils are not the key antigen-presenting cells in allergic patients. Allergy. 2012;67:601–8
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Cite this as
Raap U, Sumbayev V V, Gibbs B F. The role of basophils in allergic inflammation. Allergo J Int 2015;24:152–7
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raap, U., Sumbayev, V.V. & Gibbs, B.F. The role of basophils in allergic inflammation. Allergo J Int 24, 152–157 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40629-015-0064-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40629-015-0064-2