Abstract
Background:
Many children develop a sensitization to peanut in early infancy, even before peanut is introduced in their diet. Sensitization is particularly common in young children with eczema. There have been scant data available to date on the sensitization pattern for specific peanut allergens in this patient group. The aim of this study was to investigate the allergen profile of infants and young children with peanut sensitization and eczema.
Methods:
Sera from 53 children aged ≤ 20 months with eczema and sensitization to peanut but who had not yet consumed products containing peanuts were included in the analysis. Sera were analyzed using microarray immunoassay (ImmunoCAP ISAC).
Results:
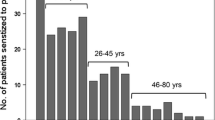
In total, 63 % of peanut-sensitized children showed specific immunoglobulin E (sIgE) against at least one peanut allergen on the microarray. Specific IgE to the 7S globulin Ara h 1 was detected in 40 % of the children, to the 2S albumin Ara h 2 in 30 % and to the 11S globulin Ara h 3 in 23 %. Only one child had sIgE to Arah 8, the homologoue of Bet-v-1. Data on clinical relevance were available for 24 of 53 children: 14 of 24 patients had objective allergic reactions to peanut, while 10 children were peanut-tolerant. The seed storage protein Ara h 2 was not detected on microarray in 43 % (6 of 14) of children with peanut allergy. Two of these six children were mono-sensitized to Ara h 1 and two to Ara h 3, while in three children none of these seed storage proteins was detected.
Discussion:
It could be shown that infants and young children with eczema and sensitization to peanut recognize predominantly seed storage proteins from peanut, even before the introduction of peanut into their diet. Sensitization to pollen-related food allergens seems to be rare at this age. At this age not only Ara h 2, but also Ara h 1 seems to be related to clinical relevance.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AD:
-
Atopic dermatitis
- DBPCFC:
-
Double-blind placebo-controlled food challenge
- FEIA:
-
Fluorescence enzyme immunoassay
- ISU:
-
Standardized units
- ISAC:
-
Immuno solid-phase allergen chip
- ns:
-
Not specified
- kU/l:
-
Kilounits/liter
- LTP:
-
Lipid transfer protein
- OFC:
-
Open food challenge
- sIgE:
-
Specific immunoglobulin E
References
Sicherer SH, Sampson HA. Food allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2010; 125:116–25
Sicherer SH. Clinical update on peanut allergy. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 2002;88:350–61
Grundy J, Matthews S, Bateman B, Dean T, Arshad SH. Rising prevalence of allergy to peanut in children: Data from 2 sequential cohorts. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2002;110:784–9
Hourihane JO, Aiken R, Briggs R, Gudgeon LA, Grimshaw KE, DunnGalvin A et al. The impact of government advice to pregnant mothers regarding peanut avoidance on the prevalence of peanut allergy in United Kingdom children at school entry. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2007;119:1197–202
Sicherer SH, Muñoz-Furlong A, Godbold JH, Sampson HA. US prevalence of self-reported peanut, tree nut, and sesame allergy: 11-year follow-up. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2010;125:1322–6
Moneret-Vautrin DA, Rance F, Kanny G, Olsewski A, Gueant JL, Dutau G et al. Food allergy to peanuts in France — evaluation of 142 observations. Clin Exp Allergy 1998; 28: 1113–9
Sicherer SH, Furlong TJ, Muñoz-Furlong A, Burks AW, S ampson HA. A voluntary registry for peanut and tree nut allergy: Characteristics of the first 5149 registrants. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2001;108:128–32
Burks AW. Peanut allergy. Lancet 2008;371:1538–46
Nicolaou N, P oorafshar M, Murray C, Simpson A, Winell H, Kerry G et al. Allergy or tolerance in children sensitized to peanut: Prevalence and differentiation using component-resolved diagnostics. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2010;125:191–7.e13
Vereda A,Hage M van, Ahlstedt S, Ibañez MD, Cuesta-Herranz J, Odijk J van et al. Peanut allergy: clinical and immunologic differences among patients from 3 different geographic regions. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2011;127:603–7
Mittag D, Akkerdaas J, Ballmer-Weber BK, Vogel L, Wensing M, Becker WM et al. Ara h 8, a Bet v 1-homologous allergen from peanut, is a major allergen in patients with combined birch pollen and peanut allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2004;114:1410–7
Asarnoj A, Movérare R, Östblom E, Poorafshar M, Lilja G, Hedlin G et al. IgE to peanut allergen components: relation to peanut symptoms and pollen sensitization in 8-yearolds. Allergy 2010;65:1189–95
Maleki SJ, Chung SY, Champagne ET, Raufman JP. The effects of roasting on the allergenic properties of peanut proteins. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2000;106:763–8
Lehmann K, Schweimer K, Reese G, Randow S, Suhr M, Becker WM et al. Structure and stability of 2S albumin-type peanut allergens: implications for the severity of peanut allergic reactions. Biochem J 2006;395:463–72
Beyer K, Morrow E, Li XM, Bardina L, Bannon GA, Burks AW et al. Effects of cooking methods on peanut allergenicity. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2001;107:1077–81
Codreanu F, Collignon O, Roitel O, Thouvenot B, Sauvage C, Vilain A et al. A novel immunoassay using recombinant allergens simplifies peanut allergy diagnosis. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 2011;154:216–26
Bernard H, Paty E, Mondoulet L, Burks AW, Bannon GA, Wal JM et al. Serological characteristics of peanut allergy in children. Allergy 2003;58:1285–92
Koppelman S, Wensing M, Ertmann M, Knulst A, Knol E. Relevance of Ara h1, Ara h2 and Ara h3 in peanut-allergic patients, as determined by immunoglobulin E Western blotting, basophil-histamine release and intracutaneous testing: Ara h2 is the most important peanut allergen. Clin Exp Allergy 2004;34:583–90
Flinterman AE, Hoffen E van, Hartog Jager den CF, Koppelman S, Pasmans SG, Hoekstra MO et al. Children with peanut allergy recognize predominantly Ara h2 and Ara h6, which remains stable over time. Clin Exp Allergy 2007;37:1221–8
Niggemann B, Schmitz R, Schlaud M. The high prevalence of peanut sensitization in childhood is due to cross-reactivity to pollen. Allergy 2011;66:980–1
Vadas P, Wai Y, Burks W, Perelman B. Detection of peanut allergens in breast milk of lactating women. JAMA 2001; 285: 1746–8
Sicherer SH, Wood RA, Stablein D, Lindblad R, Burks AW, Liu AH et al. Maternal consumption of peanut during pregnancy is associated with peanut sensitization in atopic infants. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2010;126:1191–7
DesRoches A, Infante-Rivard C, Paradis L, Paradis J, Haddad E. Peanut allergy: is maternal transmission of antigens during pregnancy and breastfeeding a risk factor? J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol 2010;20:289–94
Leon MP de, Drew AC, Glaspole IN, Suphioglu C, O’Hehir RE, Rolland JM. IgE cross-reactivity between the major peanut allergen Ara h 2 and tree nut allergens. Mol Immunol 2007; 44:463–71
Leon MP de, Glaspole IN, Drew AC, Rolland JM, O’Hehir RE, Suphioglu C. Immunological analysis of allergenic cross-reactivity between peanut and tree nuts. Clin Exp Allergy 2003;33:1273–80
Brough HA, Santos AF, Makinson K, Penagos M, Stephens AC, Douiri A et al. Peanut protein in household dust is related to household peanut consumption and is biologically active. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2013;132:630–8
Fox AT, Sasieni P, Du Toit G, Syed H, Lack G. Household peanut consumption as a risk factor for the development of peanut allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2009;123: 417–23;
Lack G, Fox D, Northstone K, Golding J; Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children Study Team. Factors associated with the development of peanut allergy in childhood. N Engl J Med 2003;348:977–85
Trendelenburg V, Ahrens B, Wehrmann AK, Kalb B, Niggemann B, Beyer K. Peanut allergen in house dust of eating area and bed — a risk factor for peanut sensitization? Allergy 2013;68:1460–2
Verweij MM, Hagendorens MM, De Knop KJ, Bridts CH, De Clerck LS, Stevens WJ et al. Young infants with atopic dermatitis can display sensitization to Cor a 9, an 11S leguminlike seed-storage protein from hazelnut (Corylus avellana). Pediatr Allergy Immunol 2011;22:196–201
De Knop KJ,Verweij MM, Grimmelikhuijsen M, Philipse E, Hagendorens MM, Bridts CH et al. Age-related sensitization profiles for hazelnut (Corylus avellana) in a birch-endemic region. Pediatr Allergy Immunol\ 2011;22:e139–49
Wohrl S, Vigl K, Zehetmayer S, Hiller R, Jarisch R, Prinz M et al. The performance of a component-based allergen-microarray in clinical practice. Allergy 2006;61:633–9
Krause S, R eese G, Randow S, Zennaro D, Quaratino D, Palazzo P et al. Lipid transfer protein (Ara h 9) as a new peanut allergen relevant for a Mediterranean allergic population. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2009;124:771–8.e5
Flinterman AE, Knol EF, Lencer DA, Bardina L, Hartog Jager CF den, Lin J et al. Peanut epitopes for IgE and IgG4 in peanut-sensitized children in relation to severity of peanut allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2008;121: 737–43.e10
Shreffler WG, Beyer K, Chu T-HT, Burks AW, Sampson HA. Microarray immunoassay: association of clinical history, in vitro IgE function, and heterogeneity of allergenic peanut epitopes. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2004;113:776–82
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Conflict of interest
The authors Valérie Trendelenburg, Alexander Rohrbach, Gabriele Schulz and Veronika Schwarz state that there are no conflicts of interest. Kirsten Beyer has received consulting or speaker’s fees from Danone, MedaPharma, ALK, Novartis, Unilever, Allergopharma, MedUpdate, HAL, Hipp, Mead Johnson, ECARF Institute, Infectopharm and funding from the European Union, German Research Foundation, ThermoFisher, Danone, DST, FAAN and the Foundation for the Treatment of peanut allergy.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by a grant from the German Research Foundation (DFG-BE 3991/1–1).
Cite this as Trendelenburg V, Rohrbach A, Schulz G, Schwarz V, Beyer K. Molecular sIgE profiles in infants and young children with peanut sensitization and dermatitis. Allergo J Int 2014; 23: 152–7 DOI 10.1007/s40629-014-0018-0
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Trendelenburg, V., Rohrbach, A., Schulz, G. et al. Molecular sIgE profile in infants and young children with peanut sensitization and eczema. Allergo J Int 23, 152–157 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40629-014-0018-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40629-014-0018-0