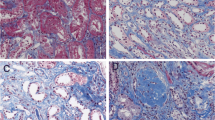
Abstract
Background
Non-invasive evaluation of renal fibrosis is still challenging. This study aimed to establish a nomogram based on shear wave elastography (SWE) and clinical features for the assessment of the severity of renal fibrosis in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD).
Methods
One hundred and sixty-two patients with CKD who underwent kidney biopsy and SWE examination were prospectively enrolled between April 2019 and December 2021. Patients were classified into mildly or moderately-severely impaired group based on pathology results. All patients were randomly divided into a training (n = 113) or validation cohort (n = 49). Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) algorithm was used for data dimensionality reduction and feature selection. Then, a diagnostic nomogram incorporating the selected features was constructed using multivariable logistic regression analysis. Nomogram performance was evaluated for discrimination, calibration, and clinical utility in training and validation cohorts.
Results
The established SWE nomogram, which integrated SWE value, hypertension, and estimated glomerular filtration rate, showed fine calibration and discrimination in both training (area under the receiver operator characteristic curve (AUC) = 0.94; 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.89–0.98) and validation cohorts (AUC = 0.84; 95% CI 0.71–0.96). Significant improvement in net reclassification and integrated discrimination indicated that the SWE value is a valuable biomarker to assess moderate-severe renal impairment. Furthermore, decision curve analysis revealed that the SWE nomogram has clinical value.
Conclusion
The proposed SWE nomogram showed favorable performance in determining individualized risk of moderate-severe renal pathological impairment in patients with CKD, which will help to facilitate clinical decision-making.
Graphical Abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lv J-C, Zhang L-X (2019) Prevalence and disease burden of chronic kidney disease. Renal fibrosis: mechanisms and therapies. Adv Exp Med Biol 75(6):868–878
Legrand K, Speyer E, Stengel B, Frimat L, Ngueyon Sime W, Massy ZA et al (2020) Perceived health and quality of life in patients with CKD, including those with kidney failure: findings from national surveys in France. Am J Kidney Dis 75(6):868–878
Humphreys BD (2018) Mechanisms of renal fibrosis. Annu Rev Physiol 10(80):309–326
Panizo S, Martinez-Arias L, Alonso-Montes C, Cannata P, Martin-Carro B, Fernandez-Martin JL et al (2021) Fibrosis in chronic kidney disease: pathogenesis and consequences. Int J Mol Sci 22(1):408
Mansour SG, Puthumana J, Coca SG, Gentry M, Parikh CR (2017) Biomarkers for the detection of renal fibrosis and prediction of renal outcomes: a systematic review. BMC Nephrol 18(1):72
Ruiz-Ortega M, Rayego-Mateos S, Lamas S, Ortiz A, Rodrigues-Diez RR (2020) Targeting the progression of chronic kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol 16(5):269–288
Hogan JJ, Mocanu M, Berns JS (2016) The native kidney biopsy: update and evidence for best practice. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 11(2):354–362
Halimi JM, Gatault P, Longuet H, Barbet C, Bisson A, Sautenet B et al (2020) Major bleeding and risk of death after percutaneous native kidney biopsies: a french nationwide cohort study. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 15(11):1587–1594
Dietrich CF, Bamber J, Berzigotti A, Bota S, Cantisani V, Castera L et al (2017) EFSUMB guidelines and recommendations on the clinical use of liver ultrasound elastography, update 2017 (long version). Ultraschall Med 38(4):e16–e47
Saftoiu A, Gilja OH, Sidhu PS, Dietrich CF, Cantisani V, Amy D et al (2019) The EFSUMB guidelines and recommendations for the clinical practice of elastography in non-hepatic applications: update 2018. Ultraschall Med 40(4):425–453
Hu Q, Wang XY, He HG, Wei HM, Kang LK, Qin GC (2014) Acoustic radiation force impulse imaging for non-invasive assessment of renal histopathology in chronic kidney disease. PLoS One 9(12):e115051
Moon SK, Kim SY, Cho JY, Kim SH (2015) Quantification of kidney fibrosis using ultrasonic shear wave elastography: experimental study with a rabbit model. J Ultrasound Med 34(5):869–877
Leong SS, Wong JHD, Md Shah MN, Vijayananthan A, Jalalonmuhali M, Chow TK et al (2019) Shear wave elastography accurately detects chronic changes in renal histopathology. Nephrology (Carlton) 26:38–45
Chen Z, Chen J, Chen H, Su Z (2022) Evaluation of renal fibrosis in patients with chronic kidney disease by shear wave elastography: a comparative analysis with pathological findings. Abdom Radiol (NY) 47(2):738–745
Park SY (2018) Nomogram: an analogue tool to deliver digital knowledge. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 155(4):1793
Wang G, Chen H, Xie X, Cao Q, Liao B, Jiang H et al (2020) 2D shear wave elastography combined with age and serum biomarkers prior to kasai surgery predicts native liver survival of biliary atresia infants. J Intern Med 288:570–580
Serenari M, Han KH, Ravaioli F, Kim SU, Cucchetti A, Han DH et al (2020) A nomogram based on liver stiffness predicts postoperative complications in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 52:e17
Ye J, Wang W, Feng S, Huang Y, Liao X, Kuang M et al (2020) Precise fibrosis staging with shear wave elastography in chronic hepatitis B depends on liver inflammation and steatosis. Hepatol Int 14(2):190–201
Stevens PE, Levin A (2013) Evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease: synopsis of the kidney disease: improving global outcomes 2012 clinical practice guideline. Ann Intern Med 158(11):825–830
Inker LA, Schmid CH, Tighiouart H, Eckfeldt JH, Feldman HI, Greene T et al (2012) Estimating glomerular filtration rate from serum creatinine and cystatin C. N Engl J Med 367(1):20–29
Wang K, Lu X, Zhou H, Gao Y, Zheng J, Tong M et al (2019) Deep learning Radiomics of shear wave elastography significantly improved diagnostic performance for assessing liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B: a prospective multicentre study. Gut 68(4):729–741
Sauerbrei W, Royston P, Binder H (2007) Selection of important variables and determination of functional form for continuous predictors in multivariable model building. Stat Med 26(30):5512–5528
Friedman JH, Hastie T, Tibshirani R (2010) Regularization paths for generalized linear models via coordinate descent. J Stat Softw. https://doi.org/10.18637/jss.v033.i01
Iasonos A, Schrag D, Raj GV, Panageas KS (2008) How to build and interpret a nomogram for cancer prognosis. J Clin Oncol 26(8):1364–1370
Akaike HT (1974) A new look at the statistical model identification. Automatic Control IEEE Trans 19(6):716–723
Kramer AA, Zimmerman JE (2007) Assessing the calibration of mortality benchmarks in critical care: The Hosmer-Lemeshow test revisited*. Crit Care Med 35(9):2052–2056
Pencina MJ, D’Agostino RB Sr, Steyerberg EW (2011) Extensions of net reclassification improvement calculations to measure usefulness of new biomarkers. Stat Med 30(1):11–21
Pencina MJ, D’Agostino RB Sr, Demler OV (2012) Novel metrics for evaluating improvement in discrimination: net reclassification and integrated discrimination improvement for normal variables and nested models. Stat Med 31(2):101–113
Vickers AJ, Cronin AM, Elkin EB, Gonen M (2008) Extensions to decision curve analysis, a novel method for evaluating diagnostic tests, prediction models and molecular markers. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak 26(8):53
Kerr KF, Brown MD, Zhu K, Janes H (2016) Assessing the clinical impact of risk prediction models with decision curves: guidance for correct interpretation and appropriate use. J Clin Oncol 34(21):2534–2540
Concato J, Peduzzi P, Holford TR, Feinstein AR (1995) Importance of events per independent variable in proportional hazards analysis. I. Background, goals, and general strategy. J Clin Epidemiol 48(12):1495–1501
Balachandran VP, Gonen M, Smith JJ, DeMatteo RP (2015) Nomograms in oncology: more than meets the eye. Lancet Oncol 16(4):e173–e180
El Nahas AM, Bello AK (2005) Chronic kidney disease: the global challenge. The Lancet 365(9456):331–340
Kalantar-Zadeh K, Li PK (2020) Strategies to prevent kidney disease and its progression. Nat Rev Nephrol 16(3):129–130
Klyuzhin IS, Fu JF, Hong A, Sacheli M, Shenkov N, Matarazzo M et al (2018) Data-driven, voxel-based analysis of brain PET images: Application of PCA and LASSO methods to visualize and quantify patterns of neurodegeneration. PLoS One 13(11):e0206607
Shiina T, Nightingale KR, Palmeri ML, Hall TJ, Bamber JC, Barr RG et al (2015) WFUMB guidelines and recommendations for clinical use of ultrasound elastography: Part 1: basic principles and terminology. Ultrasound Med Biol 41(5):1126–1147
Sigrist RMS, Liau J, Kaffas AE, Chammas MC, Willmann JK (2017) Ultrasound elastography: review of techniques and clinical applications. Theranostics 7(5):1303–1329
Woo KT, Choong HL, Wong KS, Tan HB, Chan CM (2012) The contribution of chronic kidney disease to the global burden of major noncommunicable diseases. Kidney Int 81(10):1044–1045
Yannoutsos A, Levy BI, Safar ME, Slama G, Blacher J (2014) Pathophysiology of hypertension: interactions between macro and microvascular alterations through endothelial dysfunction. J Hypertens 32(2):216–224
Chade AR (2017) Small vessels, big role: renal microcirculation and progression of renal injury. Hypertension 69(4):551–563
Kida Y (2020) Peritubular capillary rarefaction: an underappreciated regulator of CKD progression. Int J Mol Sci 21(21):8255
Genovese F, Manresa AA, Leeming DJ, Karsdal MA, Boor P (2014) The extracellular matrix in the kidney: a source of novel non-invasive biomarkers of kidney fibrosis? Fibrogen Tissue Repair 7(1):4 (2014/03/28)
Sangwaiya MJ, Sherman DI, Lomas DJ, Shorvon PJ (2014) Latest developments in the imaging of fibrotic liver disease. Acta Radiol 55(7):802–813
Bikbov B, Purcell CA, Levey AS, Smith M, Abdoli A, Abebe M et al (2020) Global, regional, and national burden of chronic kidney disease, 1990–2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. The Lancet 395(10225):709–733
Funding
The work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province [2018A0303130070]; National Natural Science Foundation of China [82072038].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: ZC, JC, HC, and ZS; Data curation: JC; Formal analysis: ZS; Funding acquisition: ZS; Investigation: ZS; Methodology: ZC, JC, HC; Project administration: ZS; Resources: ZS; Software: ZC; Supervision: ZS; Validation: ZS; Visualization: ZS; Writing-original draft: ZC; Writing-review and editing: ZS.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Review Board (or Ethics Committee) of Fifth Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University (protocol code K09-1; approval date: May 2019).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Z., Chen, J., Chen, H. et al. A nomogram based on shear wave elastography for assessment of renal fibrosis in patients with chronic kidney disease. J Nephrol 36, 719–729 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40620-022-01521-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40620-022-01521-8