Abstract
Purpose
Patients with advanced progressive metastatic medullary thyroid cancer (MTC), show poor prognosis and few available systemic therapeutic options. After the loss of clinical benefit with other tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI), we evaluated the use of lenvatinib as salvage therapy.
Methods
Ten patients who experienced the loss of clinical benefit after treatment with at least one previous TKI, were treated with lenvatinib. We assessed patient’s response immediately before, at the first (first-EV) and last (last-EV) evaluation, after the beginning of treatment.
Results
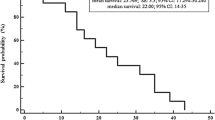
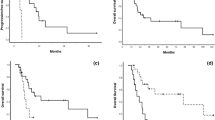
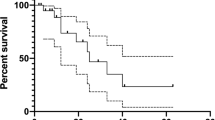
At first-EV, one patient died, while all the remaining 9 showed a stable disease (SD) in the target lesions. At last-EV, SD was still observed in seven patients, while partial response (PR) and progressive disease (PD), in one patient each. Conversely, analyzing all target and non-target lesions, at first-EV, we observed PR in one patient and SD in eight patients. At last-EV, PR was shown in two patients and SD was shown in seven. Bone metastases showed stable disease control at both first-EV and last-EV in only approximately 60% of cases. Tumor markers (CTN and CEA) decreased at first-EV, while they increased at last-EV. Seven patients experienced at least one dose reduction during treatment with lenvatinib.
Conclusions
In this real-life clinical experience, lenvatinib showed interesting results as salvage therapy in patients with advanced progressive metastatic MTC patients. Its usefulness could be effective in patients without any other available treatment, because previously used or unsuitable, especially with negative RET status with no access to the new highly selective targeted therapies.





Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
05 June 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-021-01592-7
References
Wells SA Jr, Asa SL, Dralle H, Elisei R, Evans DB, Gagel RF, Lee N, Machens A, Moley JF, Pacini F, Raue F, Frank-Raue K, Robinson B, Rosenthal MS, Santoro M, Schlumberger M, Shah M, Waguespack SG (2015) Revised American Thyroid Association guidelines for the management of medullary thyroid carcinoma. Thyroid: Off J Am Thyroid Assoc 25(6):567–610. https://doi.org/10.1089/thy.2014.0335
Modigliani E, Cohen R, Campos JM, Conte-Devolx B, Maes B, Boneu A, Schlumberger M, Bigorgne JC, Dumontier P, Leclerc L, Corcuff B, Guilhem I (1998) Prognostic factors for survival and for biochemical cure in medullary thyroid carcinoma: results in 899 patients. The GETC Study Group. Groupe d’etude des tumeurs a calcitonine. Clin Endocrinol 48(3):265–273
Kuo EJ, Sho S, Li N, Zanocco KA, Yeh MW, Livhits MJ (2018) Risk factors associated with reoperation and disease-specific mortality in patients with medullary thyroid carcinoma. JAMA Surg 153(1):52–59. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamasurg.2017.3555
Ceolin L, Duval M, Benini AF, Ferreira CV, Maia AL (2019) Medullary thyroid carcinoma beyond surgery: advances, challenges, and perspectives. Endocr Relat Cancer 26(9):R499–R518. https://doi.org/10.1530/ERC-18-0574
Schlumberger MJ, Elisei R, Bastholt L, Wirth LJ, Martins RG, Locati LD, Jarzab B, Pacini F, Daumerie C, Droz JP, Eschenberg MJ, Sun YN, Juan T, Stepan DE, Sherman SI (2009) Phase II study of safety and efficacy of motesanib in patients with progressive or symptomatic, advanced or metastatic medullary thyroid cancer. J Clin Oncol: Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol 27(23):3794–3801. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2008.18.7815
Schlumberger M, Jarzab B, Cabanillas ME, Robinson B, Pacini F, Ball DW, McCaffrey J, Newbold K, Allison R, Martins RG, Licitra LF, Shah MH, Bodenner D, Elisei R, Burmeister L, Funahashi Y, Ren M, O’Brien JP, Sherman SI (2016) A phase II trial of the multitargeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor lenvatinib (E7080) in advanced medullary thyroid cancer. Clin Cancer Res: Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res 22(1):44–53. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-1127
Nakazawa Y, Kawano S, Matsui J, Funahashi Y, Tohyama O, Muto H, Nakagawa T, Matsushima T (2015) Multitargeting strategy using lenvatinib and golvatinib: maximizing anti-angiogenesis activity in a preclinical cancer model. Cancer Sci 106(2):201–207. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.12581
Schlumberger M, Tahara M, Wirth LJ, Robinson B, Brose MS, Elisei R, Habra MA, Newbold K, Shah MH, Hoff AO, Gianoukakis AG, Kiyota N, Taylor MH, Kim SB, Krzyzanowska MK, Dutcus CE, de las Hera B, Zhu J, Sherman SI (2015) Lenvatinib versus placebo in radioiodine-refractory thyroid cancer. New England J Med 372(7):621–630. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1406470
Wells SA Jr, Robinson BG, Gagel RF, Dralle H, Fagin JA, Santoro M, Baudin E, Elisei R, Jarzab B, Vasselli JR, Read J, Langmuir P, Ryan AJ, Schlumberger MJ (2012) Vandetanib in patients with locally advanced or metastatic medullary thyroid cancer: a randomized, double-blind phase III trial. J Clin Oncol: Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol 30(2):134–141. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2011.35.5040
Elisei R, Schlumberger MJ, Muller SP, Schoffski P, Brose MS, Shah MH, Licitra L, Jarzab B, Medvedev V, Kreissl MC, Niederle B, Cohen EE, Wirth LJ, Ali H, Hessel C, Yaron Y, Ball D, Nelkin B, Sherman SI (2013) Cabozantinib in progressive medullary thyroid cancer. J Clin Oncol: Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol 31(29):3639–3646. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2012.48.4659
Valerio L, Bottici V, Matrone A, Piaggi P, Viola D, Cappagli V, Agate L, Molinaro E, Ciampi R, Tacito A, Ramone T, Romei C, Elisei R (2020) Medullary thyroid cancer treated with vandetanib: predictors of a longer and durable response. Endocr Relat Cancer 27(2):97–110. https://doi.org/10.1530/ERC-19-0259
Koehler VF, Adam P, Frank-Raue K, Raue F, Berg E, Hoster E, Allelein S, Schott M, Kroiss M, Spitzweg C (2020) Real-world efficacy and safety of cabozantinib and vandetanib in advanced medullary thyroid cancer. Thyroid. https://doi.org/10.1089/thy.2020.0206
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J, Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R, Dancey J, Arbuck S, Gwyther S, Mooney M, Rubinstein L, Shankar L, Dodd L, Kaplan R, Lacombe D, Verweij J (2009) New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer 45(2):228–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2008.10.026
Elisei R, Lorusso L, Piaggi P, Torregrossa L, Pellegrini G, Molinaro E, Agate L, Bottici V, Pani F, Cacciato Insilla A, Casella F, Ciampi R, Tognetti I, Materazzi G, Basolo F, Romei C (2015) Elevated level of serum carbohydrate antigen 19.9 as predictor of mortality in patients with advanced medullary thyroid cancer. Eur J Endocrinol Eur Federation Endocrine Soc 173(3):297–304. https://doi.org/10.1530/EJE-15-0304
(CTEP) CTEP (2017) Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE).v.5.0 [5x7] Cancer Ther Eval Progr
Bergers G, Hanahan D (2008) Modes of resistance to anti-angiogenic therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 8(8):592–603. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc2442
Matrone A, Valerio L, Pieruzzi L, Giani C, Cappagli V, Lorusso L, Agate L, Puleo L, Viola D, Bottici V, Del Re M, Molinaro E, Danesi R, Elisei R (2017) Protein kinase inhibitors for the treatment of advanced and progressive radiorefractory thyroid tumors: From the clinical trials to the real life. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 31(3):319–334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.beem.2017.06.001
Takahashi S, Kiyota N, Yamazaki T, Chayahara N, Nakano K, Inagaki L, Toda K, Enokida T, Minami H, Imamura Y, Fukuda N, Sasaki T, Suzuki T, Ikezawa H, Dutcus CE, Tahara M (2019) A phase II study of the safety and efficacy of lenvatinib in patients with advanced thyroid cancer. Future Oncol 15(7):717–726. https://doi.org/10.2217/fon-2018-0557
Masaki C, Sugino K, Saito N, Saito Y, Tanaka T, Ogimi Y, Maeda T, Osaku T, Akaishi J, Hames KY, Tomoda C, Suzuki A, Matsuzu K, Uruno T, Ohkuwa K, Kitagawa W, Nagahama M, Takami H, Ito K (2017) Lenvatinib induces early tumor shrinkage in patients with advanced thyroid carcinoma. Endocr J 64(8):819–826. https://doi.org/10.1507/endocrj.EJ17-0104
Sato H, Saito Y, Inomoto C, Suzuki Y (2020) Effect of lenvatinib on a patient with medullary thyroid carcinoma liver metastasis caused by multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2A. Tokai J Exp Clin Med 45(1):18–23
Werner RA, Schmid JS, Muegge DO, Luckerath K, Higuchi T, Hanscheid H, Grelle I, Reiners C, Herrmann K, Buck AK, Lapa C (2015) Prognostic value of serum tumor markers in medullary thyroid cancer patients undergoing vandetanib treatment. Medicine (Baltimore) 94(45):e2016. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000002016
Laure Giraudet A, Al Ghulzan A, Auperin A, Leboulleux S, Chehboun A, Troalen F, Dromain C, Lumbroso J, Baudin E, Schlumberger M (2008) Progression of medullary thyroid carcinoma: assessment with calcitonin and carcinoembryonic antigen doubling times. Eur J Endocrinol Eur Federation Endocrine Soc 158(2):239–246. https://doi.org/10.1530/EJE-07-0667
Drilon AE, Subbiah V, Oxnard GR, Bauer TM, Velcheti V, Lakhani NJ, Besse B, Park K, Patel JD, Cabanillas ME, Johnson ML, Reckamp KL, Boni V, Loong HHF, Schlumberger M, Solomon B, Cruickshank S, Rothenberg SM, Shah MH, Wirth LJ (2018) A phase 1 study of LOXO-292, a potent and highly selective RET inhibitor, in patients with RET-altered cancers. J Clin Oncol 36(15_suppl):102–102. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2018.36.15_suppl.102
Taylor MH, Gainor JF, Hu MI-N, Zhu VW, Lopes G, Leboulleux S, Brose MS, Schuler MH, Bowles DW, Kim D-W, Baik CS, Garralda E, Lin C-C, Adkins D, Sarker D, Curigliano G, Zhang H, Clifford C, Turner CD, Subbiah V (2019) Activity and tolerability of BLU-667, a highly potent and selective RET inhibitor, in patients with advanced RET-altered thyroid cancers. J Clin Oncol 37(15_suppl):6018–6018. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2019.37.15_suppl.6018
Romei C, Casella F, Tacito A, Bottici V, Valerio L, Viola D, Cappagli V, Matrone A, Ciampi R, Piaggi P, Ugolini C, Torregrossa L, Basolo F, Materazzi G, Vitti P, Elisei R (2016) New insights in the molecular signature of advanced medullary thyroid cancer: evidence of a bad outcome of cases with double RET mutations. J Med Genet. https://doi.org/10.1136/jmedgenet-2016-103833
Funding
This study was supported by Grants to R.E. from Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro (AIRC, Investigator Grant 2018, project code 21790) and Agenzia Italiana del Farmaco (AIFA, project code AIFA-2016- 02365049).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors listed have made a substantial, direct and intellectual contribution to the work, and approved it for publication.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
RE is a consultant for EISAI but this study was not influenced by this activity. The other authors have nothing to disclose.
Ethical approval
The study was approved by the local Ethical Committee (CEAVNO—Comitato Etico Area Vasta Nord-Ovest) and, for the policy of the University Hospital.
Informed consent
All patients provided written informed consent to use their data for scientific purposes.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matrone, A., Prete, A., Nervo, A. et al. Lenvatinib as a salvage therapy for advanced metastatic medullary thyroid cancer. J Endocrinol Invest 44, 2139–2151 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-020-01491-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-020-01491-3