Abstract
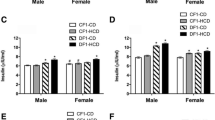
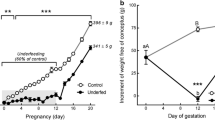
The effect of in-utero environment on fetal health and survival is long-lasting, and this is known as the fetal origin hypothesis. The oxidative stress state during gestation could play a pivotal role in fetal programming and development of diseases such as diabetes. In this study, we investigated the effect of intra-uterine obesity and malnutrition on oxidative stress markers in pancreatic and peripheral tissues of F1 offspring both prenatally and postnatally. Furthermore, the effect of postnatal diet on oxidative stress profile was evaluated. The results indicated that intra-uterine obesity and malnourishment significantly increased oxidative stress in F1 offspring. Moreover, the programming effect of obesity was more pronounced and protracted than malnutrition. The obesity-induced programming of offspring tissues was independent of high-caloric environment that the offspring endured; however, high-caloric diet potentiated its effect. In addition, pancreas and liver were the most affected tissues by fetal reprogramming both prenatally and postnatally. In conclusion, maternal obesity and malnutrition-induced oxidative stress could predispose offspring to insulin resistance and diabetes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- T2DM:
-
Type 2 diabetes mellitus
- GSH:
-
Glutathione
- GSSG:
-
Glutathione disulfide
- GST:
-
Glutathione S transferase
- GPx:
-
Glutathione peroxidase
- GR:
-
Glutathione reductase
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- RNS:
-
Reactive nitrogen species
- 8-oxo-dG:
-
8-Oxo-7,8-dihydro-2′-deoxyguanosine
- TBARS:
-
Thiobarbituric acid reactive substances
- CRL:
-
Crown-rump length
- CD:
-
Control diet
- HCD:
-
High-caloric diet
- CF1/CD:
-
F1 offspring of control mother under CD
- CF1/HCD:
-
F1 offspring of control mother under HCD
- OF1/CD:
-
F1 offspring of obese mother under CD
- OF1/HCD:
-
F1 offspring of obese mother under HCD
- MF1/CD:
-
F1 offspring of malnourished mother under CD
- MF1/HCD:
-
F1 offspring of malnourished mother under HCD
References
Barker DJ (1990) The fetal and infant origins of adult disease. BMJ 301:1111
Simmons RA (2012) Developmental origins of diabetes: the role of oxidative stress. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 26:701–708
Peuchant E, Brun J-L, Rigalleau V, Dubourg L, Thomas M-J, Daniel J-Y et al (2004) Oxidative and antioxidative status in pregnant women with either gestational or type 1 diabetes. Clin Biochem 37:293–298
Hracsko Z, Orvos H, Novak Z, Pal A, Varga IS (2008) Evaluation of oxidative stress markers in neonates with intra-uterine growth retardation. Redox Rep 13:11–16
Arikan S, Konuko\uglu D, Ar\ikan Ç, Akçay T, Davas I (2001) Lipid peroxidation and antioxidant status in maternal and cord blood. Gynecol Obstet Invest 51:145–149
Betteridge DJ (2000) What is oxidative stress? Metab Clin Exp 49:3–8
Valko M, Leibfritz D, Moncol J, Cronin MTD, Mazur M, Telser J (2007) Free radicals and antioxidants in normal physiological functions and human disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 39:44–84
Hashimoto K, Pinkas G, Evans L, Liu H, Al-Hasan Y, Thompson LP (2012) Protective effect of N-acetylcysteine on liver damage during chronic intrauterine hypoxia in fetal guinea pig. Reprod Sci 19:1001–1009
Stangenberg S, Nguyen LT, Chen H, Al-Odat I, Killingsworth MC, Gosnell ME et al (2015) Oxidative stress, mitochondrial perturbations and fetal programming of renal disease induced by maternal smoking. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 64:81–90
Wang X, Li H, De Leo D, Guo W, Koshkin V, Fantus IG et al (2004) Gene and protein kinase expression profiling of reactive oxygen species-associated lipotoxicity in the pancreatic $\beta$-cell line MIN6. Diabetes 53:129–140
Organization WH others (2015) Obesity and overweight Fact sheet N 311. 2014. Ref Type: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs311/en/
Goran MI, Ball GDC, Cruz ML (2003) Obesity and risk of type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease in children and adolescents. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88:1417–1427
Özcan U, Cao Q, Yilmaz E, Lee A-H, Iwakoshi NN, Özdelen E et al (2004) Endoplasmic reticulum stress links obesity, insulin action, and type 2 diabetes. Science 306:457–461
FAO, IFAD, WFP (2014) The State of Food Insecurity in the World 2014 strengthening the enabling environment for food security and nutrition. FAO, Rome, Italy
Pandey KB, Rizvi SI (2010) Markers of oxidative stress in erythrocytes and plasma during aging in humans. Oxid Med Cell Longev 3:2–12
Strange RC, Spiteri MA, Ramachandran S, Fryer AA (2001) Glutathione-S-transferase family of enzymes. Mutat Res 482:21–26
Zelko IN, Mariani TJ, Folz RJ (2002) Superoxide dismutase multigene family: a comparison of the CuZn-SOD (SOD1), Mn-SOD (SOD2), and EC-SOD (SOD3) gene structures, evolution, and expression. Free Radic Biol Med 33:337–349
Richter C (1995) Oxidative damage to mitochondrial DNA and its relationship to ageing. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 27:647–653
Armstrong D, Browne R (1994) The analysis of free radicals, lipid peroxides, antioxidant enzymes and compounds related to oxidative stress as applied to the clinical chemistry laboratory. Adv Exp Med Biol 366:43–58
Trevisan M, Browne R, Ram M, Muti P, Freudenheim J, Carosella AM et al (2001) Correlates of markers of oxidative status in the general population. Am J Epidemiol 154:348–356
Ademuyiwa O, Odusoga OL, Adebawo OO, Ugbaja R (2007) Endogenous antioxidant defences in plasma and erythrocytes of pregnant women during different trimesters of pregnancy. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 86:1175–1182
Malti N, Merzouk H, Merzouk S, Loukidi B, Karaouzene N, Malti A et al (2014) Oxidative stress and maternal obesity: feto-placental unit interaction. Placenta 35:411–416
Franco MCP, Akamine EH, Rebouças N, Carvalho MHC, Tostes RCA, Nigro D et al (2007) Long-term effects of intrauterine malnutrition on vascular function in female offspring: implications of oxidative stress. Life Sci 80:709–715
Kamel MA, Helmy MH, Hanafi MY, Mahmoud SA, Elfetooh HA, Badr MS (2014) Maternal obesity and malnutrition in rats differentially affect glucose sensing in the muscles and adipose tissues in the offspring. Int J Biochem Res Rev 4:440–469
Kamel MA (2012) Prenatal effects of different intra-uterine milieus on fetal glucose sensing mechanisms during gestation in rats. J Diabet Metab 3:181
Amoli MM, Moosavizadeh R, Larijani B (2005) Optimizing conditions for rat pancreatic islets isolation. Cytotechnology 48:75–78
Griffith OW (1980) Determination of glutathione and glutathione disulfide using glutathione reductase and 2-vinylpyridine. Anal Biochem 106:207–212
Smith IK, Vierheller TL, Thorne CA (1988) Assay of glutathione reductase in crude tissue homogenates using 5,5′-dithiobis(2-nitrobenzoic acid). Anal Biochem 175:408–413
Habig WH, Pabst MJ, Jakoby WB (1976) Glutathione S-transferase AA from rat liver. Arch Biochem Biophys 175:710–716
Flohé L, Günzler WA (1984) Assays of glutathione peroxidase. Methods Enzymol 105:114
Marklund S, Marklund G (1974) Involvement of the superoxide anion radical in the autoxidation of pyrogallol and a convenient assay for superoxide dismutase. Eur J Biochem 47:469–474
Draper H, Hadley M (1989) Malondialdehyde determination as index of lipid peroxidation. Methods Enzymol 186:421–431
Barker D (2004) The developmental origins of adult disease. J Am Coll Nutr 23:588S–595S
Woodall S, Johnston B, Breier B, Gluckman P (1996) Chronic maternal undernutrition in the rat leads to delayed postnatal growth and elevated blood pressure of offspring. Pediatr Res 40:438–443
Tonkiss J, Shumsky JS, Shultz PL, Almeida SS, Galler JR (1995) Prenatal cocaine but not prenatal malnutrition affects foster mother-pup interactions in rats. Neurotoxicol Teratol 17:601–608
Codoner-Franch P, Tavárez-Alonso S, Murria-Estal R, Tortajada-Girbes M, Simo-Jorda R, Alonso-Iglesias E (2012) Elevated advanced oxidation protein products (AOPPs) indicate metabolic risk in severely obese children. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 22:237–243
Jain A, Jadhav AA, Varma M (2013) Relation of oxidative stress, zinc and alkaline phosphatase in protein energy malnutrition. Arch Physiol Biochem 119:15–21
Farley D, Tejero ME, Comuzzie AG, Higgins PB, Cox L, Werner SL et al (2009) Feto-placental adaptations to maternal obesity in the baboon. Placenta 30:752–760
Qanungo S, Mukherjea M (2000) Ontogenic profile of some antioxidants and lipid peroxidation in human placental and fetal tissues. Mol Cell Biochem 215:11–19
Lappas M, Mittion A, Permezel M (2010) In response to oxidative stress, the expression of inflammatory cytokines and antioxidant enzymes are impaired in placenta, but not adipose tissue, of women with gestational diabetes. J Endocrinol 204:75–84
Vanderlelie J, Gude N, Perkins AV (2008) Antioxidant gene expression in preeclamptic placentae: a preliminary investigation. Placenta 29:519–522
Cadet J, Wagner JR (2013) DNA base damage by reactive oxygen species, oxidizing agents, and UV radiation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 5:a012559
Grankvist K, Marklund SL, Taljedal I-B (1981) CuZn-superoxide dismutase, Mn-superoxide dismutase, catalase and glutathione peroxidase in pancreatic islets and other tissues in the mouse. Biochem J 199:393–398
Reusens B, Theys N, Dumortier O, Goosse K, Remacle C (2011) Maternal malnutrition programs the endocrine pancreas in progeny. Am J Clin Nutr 94:1824S–1829S
Alfaradhi MZ, Fernandez-Twinn DS, Martin-Gronert MS, Musial B, Fowden A, Ozanne SE (2014) Oxidative stress and altered lipid homeostasis in the programming of offspring fatty liver by maternal obesity. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 307:R26–R34
Cannon MV, Buchner DA, Hester J, Miller H, Sehayek E, Nadeau JH et al (2014) Maternal nutrition induces pervasive gene expression changes but no detectable DNA methylation differences in the liver of adult offspring. PLoS One 9:e90335
Ruskovska T, Bernlohr DA (2013) Oxidative stress and protein carbonylation in adipose tissue: implications for insulin resistance and diabetes mellitus. J Proteomics 92:323–334
Yuzefovych LV, Musiyenko SI, Wilson GL, Rachek LI (2013) Mitochondrial DNA damage and dysfunction, and oxidative stress are associated with endoplasmic reticulum stress, protein degradation and apoptosis in high fat diet-induced insulin resistance mice. PLoS One 8(1):e54059
Heerwagen MJ, Miller MR, Barbour LA, Friedman JE (2010) Maternal obesity and fetal metabolic programming: a fertile epigenetic soil. Am J Physiol-Regul Integr Comp Physiol 299:R711–R722
Acknowledgments
This study is a part of project entitled “Intra-Uterine programming of adult diabetes: an experimental study” supported by Science and Technology Development Fund (STDF)—Egypt.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical statement
The Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee at the Medical Research Institute—Alexandria University—Alexandria—Egypt, has approved the animal protocol.
Informed consent
The study did not involve participation of humans and formal consent is not required.
Additional information
M. I. Saad and T. M. Abdelkhalek have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saad, M.I., Abdelkhalek, T.M., Haiba, M.M. et al. Maternal obesity and malnourishment exacerbate perinatal oxidative stress resulting in diabetogenic programming in F1 offspring. J Endocrinol Invest 39, 643–655 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-015-0413-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-015-0413-5