Abstract
Background
Hyperhomocysteinemia and vitamin B12 deficiency may be involved in the development of diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN). Metformin therapy may reduce vitamin B12 plasma levels, thus contributing to DPN.
Aim and methods
The purposes of this cross-sectional study were to assess (1) the potential associations of DPN with serum levels of homocysteine (tHcy), B-vitamins, and/or the common methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) C677T mutation; (2) the influence of chronic treatment with metformin on tHcy and B-vitamins concentrations and, finally, (3) to evaluate whether, by this influence, metformin is a risk factor for DPN in a group of type 2 diabetic outpatients.
Results
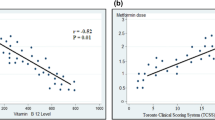
Our data showed that fasting tHcy, folate, and vitamin B12 levels and the MTHFR C677T genotype distribution were comparable between subjects with (n = 79, 30 %) and without DPN (n = 184, 70 %). Metformin-treated subjects (n = 124, 47 %) showed significantly lower levels of vitamin B12 (P < 0.001), but the prevalence of DPN was not different when compared to those not treated with this drug (33 vs. 27 %, P = NS). At univariate regression analysis, DPN was associated with age, duration of diabetes, HbA1c, creatinine levels, and the presence of coronary heart disease (CHD), and negatively with HDL-C concentrations (P < 0.05 all), but at multivariate regression analysis, high creatinine levels (P = 0.06), low HDL-C levels (P = 0.013), and a higher prevalence of CHD (P = 0.001) were the only variables independently associated with DPN in this population.
Conclusions
In conclusion, in these type 2 diabetic outpatients circulating levels of tHcy, folate, and the MTHFR C677T mutation are not associated with DPN, which was predicted by creatinine levels, CHD, and dyslipidemia. Metformin therapy is associated with a mild vitamin B12 level reduction, but not with DPN.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fedele D, Comi G, Coscelli C, Cucinotta D, Feldman EL, Ghirlanda G et al (1997) A multicenter study on the prevalence of diabetic neuropathy in Italy. Italian Diabetic Neuropathy Committee. Diabetes Care 20:836–843
American Diabetes Association (2014) Standards of medical care in diabetes 2014. Diabetes Care 37(Supplement):1
Russo GT, Cucinotta D (2003) Hyperhomocysteinemia and cardiovascular risk in diabetes mellitus. Ann Ist Super Sanita 39:153–163
Audelin MC, Genest J Jr (2001) Homocysteine and cardiovascular disease in diabetes mellitus. Atherosclerosis 159:497–511
Molina M, Gonzalez R, Folgado J, Real JT, Martínez-Hervás S, Priego A et al (2013) Correlation between plasma concentrations of homocysteine and diabetic polyneuropathy evaluated with the Semmes–Weinstein monofilament test in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Med Clin (Barc) 141:382–386
González R, Pedro T, Martinez-Hervas S, Civera M, Antonia Priego M, Catalá M et al (2012) Plasma homocysteine levels are independently associated with the severity of peripheral polyneuropathy in type 2 diabetic subjects. J Peripher Nerv Syst 17:191–196
Li JB, Cheng YZ, Shi M, Zhang HM, Dai Q, Zhang Y et al (2011) The relationship between plasma homocysteine levels and diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi 50:14–17
Stablerr SP, Estacio R, Jeffers BW, Cohen JA, Allen RH, Schrier RW (1999) Total homocysteine is associated with nephropathy in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Metabolism 48:1096–1101
Cohen JA, Jeffers BW, Stabler S, Schrier RW, Estascio R (2001) Increasing homocysteine levels and diabetic autonomic neuropathy. Auton Neurosci 87:268–273
Russo GT, Friso S, Jacques PF, Rogers G, Cucinotta D, Wilson PW et al (2003) Framingham Offspring Study Cohort. Age and gender affect the relation between methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase C677T genotype and fasting plasma homocysteine concentrations in the Framingham Offspring Study Cohort. J Nutr 133:3416–3421
Russo GT, Di Benedetto A, Giorda C, Alessi E, Crisafulli G, Ientile R et al (2004) Correlates of total homocysteine plasma concentration in type 2 diabetes. Eur J Clin Invest 34:197–204
Choi JH, Yates Z, Veysey M, Heo YR, Lucock M (2014) Contemporary issues surrounding folic acid fortification initiatives. Prev Nutr Food Sci 19:247–260
Moore E, Mander A, Ames D, Carne R, Sanders K, Watters D (2012) Cognitive impairment and vitamin B12: a review. Int Psychogeriatr 6:1–16
Jacobs AM, Cheng D (2011) Management of diabetic small-fiber neuropathy with combination l-methylfolate, methylcobalamin, and pyridoxal 5′-phosphate. Rev Neurol Dis 8:39–47
Walker MJ Jr, Morris LM, Cheng D (2010) Improvement of cutaneous sensitivity in diabetic peripheral neuropathy with combination l-methylfolate, methylcobalamin, and pyridoxal 5′-phosphate. Rev Neurol Dis 7:132–139
Farvid MS, Homayouni F, Amiri Z, Adelmanesh F (2011) Improving neuropathy scores in type 2 diabetic patients using micronutrients supplementation. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 93:86–94
Wile DJ, Toth C (2010) Association of metformin, elevated homocysteine, and methylmalonic acid levels and clinically worsened diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Diabetes Care 33:156–161
Xu Q, Pan J, Yu J, Liu X, Liu L, Zuo X et al (2013) A Meta-analysis of methylcobalamin alone and in combination with lipoic acid in patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 101:99–105
Yigit S, Karakus N, Inanir A (2013) Association of MTHFR gene C677T mutation with diabetic peripheral neuropathy and diabetic retinopathy. Mol Vis 19:1626–1630
Wu S, Han Y, Hu Q, Zhang XJ, Cui GC, Li ZZ, Guan YT (2014) Effects of common polymorphisms in the MTHFR and ACE genes on diabetic peripheral neuropathy progression: a meta-analysis. Mol Neurobiol (Epub ahead of print)
Buysschaert M, Dramais A-S, Wallemacq PE, Hermans M (2000) Hyperhomocysteinemia in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 23:1816–1822
Carlsen SM, Folling I, Grill V, Bjerve KS (1997) Metformin increases total serum homocysteine level in non-diabetic male patients with coronary heart disease. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 57:521
Aarsand AK, Carlsen SM (1998) Folate administration reduced circulating homocysteine levels in NIDDM patients on longterm metformin treatment. J Int Med 244:169
Beulens JW, Hart HE, Kuijs R, Kooijman-Buiting AM, Rutten GE (2015) Influence of duration and dose of metformin on cobalamin deficiency in type 2 diabetes patients using metformin. Acta Diabetol 52:47–53
Niafar M, Hai F, Porhomayon J, Nader ND (2015) The role of metformin on vitamin B12 deficiency: a meta-analysis review. Intern Emerg Med 10:93–102
Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, Cushman WC, Green LA, Izzo Joseph L et al (2003) The seventh report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of high blood pressure: the JNC 7 report. JAMA 289:2560–2572
Friedewald WT, Levy RI, Fredrickson DS (1972) Estimation of the concentration of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in plasma, without use of the preparative ultracentrifuge. Clin Chem 18:499–502
Dyck PJ, Albers JW, Andersen H, Arezzo JC, Biessels GJ, Bril V, Feldman EL, Litchy WJ, O’Brien PC, Russell JW, Toronto Expert Panel on Diabetic Neuropathy (2011) Diabetic polyneuropathies: update on research definition, diagnostic criteria and estimation of severity. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 27:620–628
Levey A, Bosch J, Breyer Lewis JB, Greene T, Rogers N, Roth D (1999) A more accurate method to estimate glomerular filtration rate from serum creatinine. Ann Intern Med 139:461–470
de Groot-Kamphuis DM, van Dijk PR, Groenier KH, Houweling ST, Bilo HJ, Kleefstra N (2013) Vitamin B12 deficiency and the lack of its consequences in type 2 diabetes patients using metformin. Neth J Med 71:386–390
Tucker KL, Mahnken B, Wilson PW, Jacques P, Selhub J (1996) Folic acid fortification of the food supply. Potential benefits and risks for the elderly population. JAMA 276:1879–1885 [Erratum in: JAMA 1997;277:714]
Liu Q, Li S, Quan H, Li J (2014) Vitamin B12 status in metformin treated patients: systematic review. PLoS One 9:e100379
Singh AK, Kumar A, Karmakar D, Jha RK (2013) Association of B12 deficiency and clinical neuropathy with metformin use in type 2 diabetes patients. J Postgrad Med 59:253–257
Sato Y, Ouchi K, Funase Y, Yamauchi K, Aizawa T (2013) Relationship between metformin use, vitamin B12 deficiency, hyperhomocysteinemia and vascular complications in patients with type 2 diabetes. Endocr J 60:1275–1280
Andrès E, Noel E, Goichot B (2002) Metformin-associated vitamin B12 deficiency. Arch Intern Med 162:2251–2252
Bauman WA, Shaw S, Jayatilleke E, Spungen AM, Herbert V (2000) Increased intake of calcium reverses vitamin B12 malabsorption induced by metformin. Diabetes Care 23:1227–1231
UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group (2002) Intensive blood glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33. Lancet 352:837–853
Wang DD, Bakhotmah BA, Hu FB, Alzahrani HA (2014) Prevalence and correlates of diabetic peripheral neuropathy in a Saudi Arabic population: a cross-sectional study. PLoS One 9:e106935
Hu Y, Liu F, Shen J, Zeng H, Li L, Zhao J et al (2014) Association between serum cystatin C and diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a cross-sectional study of a Chinese type 2 diabetic population. Eur J Endocrinol 171:641–648
Wiggin TD, Sullivan KA, Pop-Busui R, Amato A, Sima AA, Feldman EL (2009) Elevated triglycerides correlate with progression of diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes 58:1634–1640
Ansquer JC, Foucher C, Aubonnet P, Le Malicot K (2009) Fibrates and microvascular complications in diabetes–insight from the FIELD study. Curr Pharm Des 15:537–552
Vincent AM, Hinder LM, Pop-Busui R, Feldman EL (2009) Hyperlipidemia: a new therapeutic target for diabetic neuropathy. J Peripher Nerv Syst 14:257–267
Leiter LA (2005) The prevention of diabetic microvascular complications of diabetes: is there a role for lipid lowering? Diabetes Res Clin Pract 68(Suppl 2):S3–S14
Wiggin TD, Sullivan KA, Pop-Busui R, Amato A, Sima AA, Feldman EL (2009) Elevated triglycerides correlate with progression of diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes 58:1634–1640
Xie F, Fu H, Hou JF, Jiao K, Costigan M, Chen J (2013) High energy diets-induced metabolic and prediabetic painful polyneuropathy in rats. PLoS One 8:e57427
Obrosova IG, Ilnytska O, Lyzogubov VV, Pavlov IA, Mashtalir N, Nadler JL et al (2007) High-fat diet induced neuropathy of pre-diabetes and obesity: effects of “healthy” diet and aldose reductase inhibition. Diabetes 56:2598–2608
Baldereschi M, Inzitari M, Di Carlo A, Bovis F, Maggi S, Capurso A, ILSA Working Group et al (2013) Vascular factors predict polyneuropathy in a non-diabetic elderly population. Neurol Sci 34:955–962
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in this study were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Russo, G.T., Giandalia, A., Romeo, E.L. et al. Diabetic neuropathy is not associated with homocysteine, folate, vitamin B12 levels, and MTHFR C677T mutation in type 2 diabetic outpatients taking metformin. J Endocrinol Invest 39, 305–314 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-015-0365-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-015-0365-9