Abstract
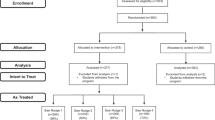
The current study evaluated the effects of a gamified package intervention on the accurate data entry of practicum experience hours by 15 behavior analysis graduate students at a small private university. The gamified intervention (Practicum Slayer) included feedback, added reinforcement in the form of points to access putative primary reinforcement, badges, and thematic enhancement. We compared this intervention to a feedback-only condition using a multiple-baseline design across classes. We collected weekly data on the percentage of students per class who entered data into the Behavior Analyst Certification Board (BACB) Fieldwork Tracker with 100% accuracy. The intervention was effective at increasing accurate data entry for all classes, and 93.33% (14 of 15) of participants reached 100% accuracy in their data entry by the end of the study. Social validity data indicated that participants received the gamification package with moderate positivity. We discuss limitations of the study and areas for future research.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baer, D. M., Wolf, M. M., & Risley, T. R. (1968). Some current dimensions of applied behavior analysis. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 1, 91–97. https://doi.org/10.1901/jaba.1968.1-91.
Behavior Analyst Certification Board. (2018). BCBA/BCaBA experience standards: Monthly system. Retrieved from https://www.bacb.com/wp-content/uploads/BACB_Experience-Standards_190730.pdf.
Chapman, J. R., & Rich, P. J. (2018). Does educational gamification improve students’ motivation? If so, which game elements work best? Journal of Education for Business, 7, 315–322. https://doi.org/10.1080/08832323.2018.1490687.
Deterding, S., Dixon, D., Khaled, R., & Nacke, L. (2011). From game design elements to gamefulness: Defining “gamification.” Proceedings of the 15th International Academic MindTrek Conference: Envisioning Future Media Environments, 9–15.
Dichev, D., & Dicheva, D. (2017). Gamifying education: What is known, what is believed, and what remains uncertain: A critical review. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education, 14(9). https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-017-0042-5.
Haaranen, L., Ihantola, P., Hakulinen, L., & Korhonen, A. (2014). How (not) to introduce badges to online exercises. Proceedings of the 45th ACM Technical Symposium on Computer Science Education, 33–38. https://doi.org/10.1145/2538862.2538921.
Hamari, J., Koivisto, J., & Sarsa, H. (2014). Does gamification work? A literature review of empirical studies on gamification. Proceedings of the Annual Hawaii International Conference on Systems Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1109/HICSS.2014.377.
Huang, B., Hew, K. F., & Lo, C. K. (2018). Investigating the effects of gamification-enhanced flipped learning on undergraduate students’ behavioral and cognitive engagement. Interactive Learning Environments, 27, 1106–1126. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2018.1495653.
Johnson, D., Deterding, S., Kuhn, K., Staneva, A., Stoyanov, S., & Hides, L. (2016). Gamification for health and wellbeing: A systematic review of the literature. Internet Intervention, 6, 89–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.invent.2016.10.002.
Lister, M. (2015). Gamification: The effect on student motivation and performance at the post-secondary level. Issues and Trends in Educational Technology, 3(2), 1–22. Retrieved from https://www.learntechlib.org/p/171075/.
Meyer, K. A. (2008). Do rewards shape online discussions? Journal of Interactive Online Learning, 7(2), 126–138. Retrieved from http://www.ncolr.org/jiol/issues/pdf/7.2.3.pdf.
Morford, Z. H., Witts, B. N., Killingsworth, K. J., & Alavosius, M. P. (2014). Gamification: The intersection between behavior analysis and game design technologies. The Behavior Analyst, 37, 25–40. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40614-014-0006-1.
Sailer, M., Hense, J. U., Mayr, S. K., & Mandi, H. (2017). How gamification motivates: An experimental study of the effects of specific game design elements on psychological need satisfaction. Computers in Human Behavior, 69, 371–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2016.12.033.
Skinner, B. F. (1984). The shame of the American education. American Psychologist, 39, 947–954. https://doi.org/10.1037/0003-066X.39.9.947.
Waldvogel, J. M., & Dixon, M. R. (2008). Exploring the utility of preference assessment in organizational behavior management. Journal of Organizational Behavior Management, 28, 76–87. https://doi.org/10.1080/01608060802006831.
Funding
The authors did not receive any funding for this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare they do not have any conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval
This research was completed with human subjects and approved through a university-affiliated institutional review board.
Informed Consent
All participants gave their informed consent before participation in the study and were debriefed following the conclusion of the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Research Highlights
• Many practitioners also supervise BACB candidates completing their practicum or fieldwork experience.
• This research highlights the need for additional systems for assisting practicum or fieldwork students in entering their data according to BACB guidelines.
• Supervisors may find the gamification model helpful in incentivizing correct data entry for their practicum or fieldwork students.
• Supervisors may find the table useful as a checklist for the required components of practicum/fieldwork data entry.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Parry-Cruwys, D., MacDonald, J. Using Gamification to Promote Accurate Data Entry of Practicum Experience Hours in Graduate Students. Behav Analysis Practice 14, 1–10 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40617-020-00421-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40617-020-00421-2