Abstract
Background
Sevoflurane is one of the most commonly used volatile anesthetics and it has been shown to induce widespread apoptotic neurodegeneration in aged rat. Calpain is also activated during apoptosis in several types of cells. We hypothesized that calpain resulted in apoptosis under long time sevoflurane exposure, and it might play a role in the sevoflurane-induced memory impairment in aged rats.
Methods
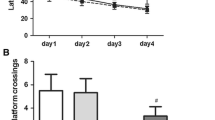
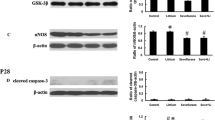
Seventy-two 18-month-old male Sprague–Dawley rats were randomly divided into three groups (n = 24): Control group rats were exposed to simply humid 50 % O2 balanced by N2 for 3 h; While M group rats received calpain inhibitor 10 mg/kg via the tail vein intravenously at 30 min before the animals inhaled 3 % sevoflurane for 3 h, subsequently received MDL 28170 3.33 mg/kg/h for 3 h. Sev group rats were only exposed to 3 % sevoflurane for 3 h without calpain inhibitor. Morris Water Maze was used to test the ability of learning and memory. Cytosolic calcium concentration was measured by using flow cytometry. Annexin-V labeled with a fluorophore or biotin can identify apoptotic cells by binding to PS. The expression of calpain in the hippocampus of rats was tested by Western blots.
Results
The results showed that the M group had a shorter latency and had a larger number of times crossing over the previous platform site than that of the Sev group. Compared with Sev group, apoptosis rate and 76/80 kDa ratio of μ-calpain were significantly decreased in M group on the 1st day.
Conclusions
Sevoflurane might induce apoptosis through increasing [Ca2+]c and the activity of μ-calpain, which might be identified at least partially the molecular mechanism by which sevoflurane induces apoptosis.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parikh SS, Chung F (1995) Postoperative delirium in the elderly. Anesth Analg 80:1223–1232
Vacas S, Degos V, Feng X et al (2013) The neuroinflammatory response of postoperative cognitive decline. Br Med Bull 106:161–178
McLay RN, Freeman SM, Harlan RE et al (1997) Aging in the hippocampus: interrelated actions of neurotrophins and glucocorticoids. Neurosci Behav Rev 21:615–629
Liu XS, Xue QS, Zeng QW et al (2010) Sevoflurane impairs memory consolidation in rats, possibly through inhibiting phosphorylation of glycogen synthase kinase-3beta in the hippocampus. Neurobiol Learn Mem 94:461–467
Culley DJ, Xie Z, Crosby G (2007) General anesthetic-induced neurotoxicity: an emerging problem for the young and old? Curr Opin Anaesthesiol 20:408–413
Hudson AE, Hemmings HC Jr (2011) Are anaesthetics toxic to the brain? Br J Anaesth 107:30–37
Perouansky M (2008) General anesthetics and long-term neurotoxicity. Handb Exp Pharmacol 182:143–157
Alkire MT, Gruver R, Miller J et al (2008) Neuroimaging analysis of an anesthetic gas that blocks human emotional memory. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:1722–1727
Wiklund A, Granon S, Faure P et al (2009) Object memory in young and aged mice after sevoflurane anaesthesia. NeuroReport 20:1419–1423
Vanags DM, PormAres MI, Coppola S et al (1996) Protease involvement in fodrin cleavage and phosphatidyl- serine exposure in apoptosis. J Biol Chem 271:31075–31085
Zimmerman UJP, Schlaepfer WW (1991) Two stage autolysis of the catalytic subunit initiates activation of calpain. Biochim Biophys Acta 1078:192–198
Neumar RW, Hagle SM, DeGracia DJ et al (1996) Brain μ-calpain autolysis during global cerebral ischemia. J Neurochem 66:421–424
Ostwald K, Hayashi M, Nakamura M et al (1994) Subcellular distribution of calpain and calpastatin immunoreactivity and fodrin proteolysis in rabbit hippocampus after hypoxia and glucocorticoid treatment. J Neurochem 63:1069–1076
Markgraf CG, Velayo NL, Johnson MP et al (1998) Six-hour window of opportunity for calpain inhibition in focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Stroke 29:152–158
Ishida A, Trescher WH, Lange MS et al (2001) Prolonged suppression of brain nitric oxide synthase activity by 7-nitroindazole protects against cerebral hypoxic–ischemic injury in neonatal rat. Brain Dev 23:349–354
Satomoto M, Satoh Y, Terui K et al (2009) Neonatal exposure to sevoflurane induces abnormal social behaviors and deficits in fear conditioning in mice. Anesthesiology 110:628–637
Gupta S (2001) Molecular steps of death receptor and mitochondrial pathways of apoptosis. Life Sci 69:2957–2964
Chen G, Gong M, Yan M et al (2013) Sevoflurane induces endoplasmic reticulum stress mediated apoptosis inhippocampal neurons of aging rats. PLoS One 8:e57870
Matus S, Glimcher LH, Hetz C (2011) Protein folding stress in neurodegenerative diseases: a glimpse into the ER. Curr Opin Cell Biol 23:239–252
Wang QJ, Li KZ, Yao SL (2008) Effect of inhalational anesthetics on cytotoxicity and intracellular calcium differently in rat pheochromocytoma cells (PC 12). J Huazhong Univ Sci Technol [Med Sci] 28:104–109
Nathb R, Raser KJ, Stafford D et al (1996) Nonerythroid alpha-spectrin breakdown by calpain and interleukin 1 betaconverting- enzyme-like protease(s) in apoptotic cells: contributory roles of both protease families in neuronal apoptosis. Biochem J 319:683–690
O’Hanlon GM, Humphreys PD, Goldman RS et al (2003) Calpain inhibitors protect against axonal degeneration in a model of anti-ganglioside antibody-mediated motor nerve terminal injury. Brain 126:2497–2509
Hong SC, Goto Y, Lanzino G et al (1994) Neuroprotection with a calpain inhibitor in a model of focal cerebral ischemia. Stroke 25:663–669
Hiramatsu K, Kassell NF, Lee KS (1993) Improved posthypoxic recovery of synaptic transmission in gerbil neocortical slices treated with a calpain inhibitor. Stroke 24:1725–1728
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by departments Funding (National Natural Science Foundation and Hebei Province Science and Technology Support Project) and institutions involved and grants from The third hospital, Hebei Medical University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Statement of human and animal rights
We solemnly declare there is no harm to animals of fundamental rights.
Informed consent
All institutional and national guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals were followed.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Song, X., Yuan, T. et al. Effects of calpain on sevoflurane-induced aged rats hippocampal neuronal apoptosis. Aging Clin Exp Res 28, 633–639 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40520-015-0466-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40520-015-0466-5