Abstract
Background
Eating disorders are characterized by high levels of anxiety, especially while eating. However, little is known about anxiety experienced during meals and specifically what other variables may impact such anxiety.
Objective
We sought to further quantify and understand the relationship between food anxiety, eating disorders, and related correlates (e.g., comorbid diagnoses, personality).
Methods
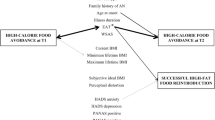
In the current study [N = 42 participants diagnosed with an eating disorder (n = 36 participants with anorexia nervosa)], we quantified anxiety before, during, and after a meal using data from a food exposure session in a partial hospital eating disorder center. We examined diagnostic, personality, and clinical factors as correlates of food anxiety.
Results
Participants were more likely to experience higher food anxiety if they had a current diagnosis of major depression, obsessive–compulsive disorder, or post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Concern over mistakes was the strongest and most consistent correlate of food anxiety regardless of time during the meal that anxiety was assessed. Other significant correlates were fear of positive evaluation, social appearance anxiety, BMI, and trust.
Conclusions
These findings show how diagnoses, perfectionism (concern over mistakes), and other correlates relate to anxiety during meals. Food exposure interventions may benefit from personalizations that address these factors.
Level of evidence
IV Evidence from a randomized control trial, but from the first session before effects of the design would be present.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen AE (1995) A standard test meal to assess treatment response in anorexia nervosa patients. ED 3(1):47–55. https://doi.org/10.1080/10640269508249145
American Psychiatric Association (2013) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 5th edn. American Psychiatric Association, Washington
Bardone-Cone AM, Wonderlich SA, Frost RO, Bulik CM, Mitchell JE, Uppala S, Simonich H (2007) Perfectionism and ED: current status and future directions. Clin Psychol Rev 27(3):384–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpr.2006.12.005
Bulik CM, Tozzi F, Anderson C, Mazzeo SE, Aggen S, Sullivan PF (2003) The relation between ED and components of perfectionism. Am J Psychiatry 160(2):366–368. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.160.2.366
Cardi V, Esposito M, Clarke A, Schifano S, Treasure J (2015) The impact of induced positive mood on symptomatic behaviour in ED. An experimental, AB/BA crossover design testing a multimodal presentation during a test-meal. Appetite 87:192–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2014.12.224
Cardi V, Leppanen J, Mataix-Cols D, Campbell IC, Treasure J (2018) A case series to investigate food-related fear learning and extinction using in vivo food exposure in anorexia nervosa: a clinical application of the inhibitory learning framework. Eur Eating Disord Rev. https://doi.org/10.1002/erv.2639 (Epub ahead of print)
Donnellan MB, Oswald FL, Baird BM, Lucas RE (2006) The mini-IPIP scales: tiny-yet-effective measures of the Big Five factors of personality. Psychol Assess 18(2):192–203. https://doi.org/10.1037/1040-3590.18.2.192
Fergus TA, Valentiner DP, McGrath PB, Stephenson K, Gier S, Jencius S (2009) The fear of positive evaluation scale: psychometric properties in a clinical sample. J Anxiety Disord 23(8):1177–1183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.janxdis.2009.07.024
Frost RO, Marten P, Lahart C, Rosenblate R (1990) The dimensions of perfectionism. Cogn Ther Res 14(5):449–468
Garner DM, Olmstead MP, Polivy J (1983) Development and validation of a multidimensional eating disorder inventory for anorexia nervosa and bulimia. Int J ED 2(2):15–34. https://doi.org/10.1002/1098-108X(198321)2:2%3C15::AID-EAT2260020203%3E3.0.CO;2-6
Gianini L, Liu Y, Wang Y, Attia E, Walsh BT, Steinglass J (2015) Abnormal eating behavior in video-recorded meals in anorexia nervosa. Eat Behav 19:28–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eatbeh.2015.06.005
Gomes-Schwartz B (1978) Effective ingredients in psychotherapy: prediction of outcome from process variables. J Consult Clin Psychol 46(5):1023–1035. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-006X.46.5.1023
Goodwin RD, Fitzgibbon ML (2002) Social anxiety as a barrier to treatment for ED. Int J ED 32(1):103–106. https://doi.org/10.1002/eat.10051
Halmi KA, Sunday SR, Strober M, Kaplan A, Woodside DB, Fichter M et al (2000) Perfectionism in anorexia nervosa: variation by clinical subtype, obsessionality, and pathological eating behavior. Am J Psychiatry 157(11):1799–1805. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.157.11.1799
Handley AK, Egan SJ, Kane RT, Rees CS (2015) A randomised controlled trial of group cognitive behavioural therapy for perfectionism. Behav Res Ther 68:37–47
Hart TA, Flora DB, Palyo SA, Fresco DM, Holle C, Heimberg RG (2008) Development and examination of the social appearance anxiety scale. Assessment 15(1):48–59. https://doi.org/10.1177/1073191107306673
Heimberg RC, Brozovich FA, Rapee RM (2010) A cognitive behavioral model of social anxiety disorder: Update and extension. In: Hofmann SG, DiBartolo PM (eds) Social anxiety: clinical, developmental, and social perspectives. Academic Press, Cambridge, pp 395–422
Johnson JA, Briggs SR, Hogan R (1997) Handbook of personality psychology. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Kaplan DM (1995) A validity study of the subjective unit of discomfort (SUD) score. Meas Eval Counsel Dev 27(4):195–199
Kaye WH, Bulik CM, Thornton L, Brbarich N, Masters K et al (2004) Comorbidity of anxiety disorders with anorexia and bulimia nervosa. Am J Psychiatry 161:2215–2221
Klump KL, Bulik CM, Kaye WH, Treasure J, Tyson E (2009) Academy for ED position paper: ED are serious mental illnesses. Int J ED 42:97–103. https://doi.org/10.1002/eat.20589
Koskina A, Van den Eynde F, Meisel S, Campbell IC, Schmidt U (2011) Social appearance anxiety and bulimia nervosa. Eat Weight Disord 16(2):e142–e145
Koskina A, Campbell IC, Schmidy U (2013) Exposure therapy in ED revisited. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 37:193–208
Leary MR (1983) A brief version of the fear of negative evaluation scale. Pers Soc Psychol Bull 9(3):371–375. https://doi.org/10.1177/0146167283093007
Lecrubier Y, Sheehan D, Weiller E, Amorim P, Bonora I, Sheehan KH, Dunbar GC (1997) The Mini International Neuropsychiatric Interview (MINI). A short diagnostic structured interview: reliability and validity according to the CIDI. Eur Psychiatry 12(5):224–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-9338(97)83296-8
Levinson CA, Brosof LC, Vanzhula IA, Bumberry L, Zerwas S, Bulik CM (2017) Perfectionism group treatment for ED in an inpatient, partial hospitalization, and outpatient setting. Eur ED Rev 25(6):579–585. https://doi.org/10.1002/erv.2557
Levinson CA, Byrne M (2015) The fear of food measure: a novel measure for use in exposure therapy for ED. Int J ED 48(3):271–283. https://doi.org/10.1002/eat.22344
Levinson CA, Rodebaugh TL (2011) Validation of the social appearance anxiety scale: factor, convergent, and divergent validity. Assessment 18(3):350–356. https://doi.org/10.1177/1073191111404808
Levinson CA, Rodebaugh TL (2012) Social anxiety and eating disorder comorbidity: the role of negative social evaluation fears. Eat Behav 13(1):27–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eatbeh.2011.11.006
Levinson CA, Rodebaugh TL (2014) Negative social-evaluative fears produce social anxiety, food intake, and body dissatisfaction. Clin Psychol Sci 3(5):744–757
Levinson CA, Rodebaugh TL, Fewell L, Kass AE, Riley EN, Stark L et al (2015) D-cycloserine facilitation of exposure therapy improves weight regain in patients with anorexia nervosa: a pilot randomized controlled trial. J Clin Psychiatry 76(6):e787–e793
Levinson CA, Rodebaugh TL, White EK, Menatti AR, Weeks JW, Iacovino JM, Warren CS (2013) Social appearance anxiety, perfectionism, and fear of negative evaluation: Distinct or shared risk factors for social anxiety and ED? Appetite 67:125–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2013.04.002
MacLaren VV, Best LA (2009) Female students’ disordered eating and the Big Five personality facets. Eat Behav 10(3):192–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eatbeh.2009.04.001
Mattick RP, Clarke JC (1998) Development and validation of measures of social phobia scrutiny fear and social interaction anxiety. Behav Res Ther 36(4):455–470
Menzel JE, Reilly EE, Luo TJ, Kaye WH (2019) Conceptualizing the role of disgust in avoidant/restrictive food intake disorder: Implications for the etiology and treatment of selective eating. Int J Eat Disord. https://doi.org/10.1002/eat.23006 (Epub ahead of print)
Murray SB, Loeb Kl, Le Grange D (2016) Dissecting the core fear in anorexia nervosa: can we optimize treatment mechanisms? JAMA Psychiatry 73:891–892
Murray SB, Treanor M, Liao B, Loeb KL, Griffiths S, Le Grange D (2016) Extinction theory and anorexia nervosa: deepening therapeutic mechanisms. Behav Res Ther 87:1–10
Pallister E, Waller G (2008) Anxiety in the ED: understanding the overlap. Clin Psychol Rev 28(3):366–386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpr.2007.07.001
Pla-Sanjuanelo J, Ferrer-García M, Vilalta-Abella F, Riva G, Dakanalis A, Ribas-Sabaté J et al (2017) Testing virtual reality-based cue-exposure software: which cue-elicited responses best discriminate between patients with eating disorders and healthy controls? Eating Weight Disord Stud Anorexia Bulimia Obes. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40519-017-0419-4 (Epub ahead of print)
Rosenthal R, Cooper H, Hedges LV (1994) Parametric measures of effect size. Handb Res Synth 621:231–244
Sassaroli S, Lauro LJR, Ruggiero GM, Mauri MC, Vinai P, Frost R (2008) Perfectionism in depression, obsessive–compulsive disorder and eating disorders. Behav Res Ther 46(6):757–765. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brat.2008.02.007
Shafran R, Lee M, Payne E, Fairburn CG (2006) The impact of manipulating personal standards on eating attitudes and behaviour. Behav Res Ther 44(6):897–906. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brat.2005.08.009
Steinglass J, Albano AM, Simpson HB, Carpenter K, Schebendach J, Attia E (2012) Fear of food as a treatment target: exposure and response prevention for anorexia nervosa in an open series. Int J ED 45(4):615–621. https://doi.org/10.1002/eat.20936
Steinglass JE, Albano AM, Simpson HB, Wang Y, Zou J, Attia E, Walsh BT (2014) Confronting fear using exposure and response prevention for anorexia nervosa: a randomized controlled pilot study. Int J ED 47(2):174–180. https://doi.org/10.1002/eat.22214
Steinglass JE, Sysko R, Glasofer D, Albano AM, Simpson HB, Walsh BT (2011) Rationale for the application of exposure and response prevention to the treatment of anorexia nervosa. Int J ED 44(2):134–141. https://doi.org/10.1002/eat.20784
Steinglass JE, Sysko R, Mayer L, Berner LA, Schebendach J, Wang Y et al (2010) Pre-meal anxiety and food intake in anorexia nervosa. Appetite 55(2):214–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2010.05.090
Steinglass J, Sysko R, Schebendach J, Broft A, Strober M, Walsh BT (2007) The application of exposure therapy and d-cycloserine to the treatment of anorexia nervosa: a preliminary trial. J Psychiatric Pract 13(4):238–245. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.pra.0000281484.89075.a8
Strober M, Freeman R, Lampert C, Diamond J (2007) The association of anxiety disorders and obsessive compulsive personality disorder with anorexia nervosa: evidence from a family study with discussion of nosological and neurodevelopmental implications. Int J ED 40:S46–S51
Watson D, Friend R (1969) Measurement of social-evaluative anxiety. J Consult Clin Psychol 33(4):448–457. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0027806
Weeks JW, Heimberg RG, Rodebaugh TL (2008) The fear of positive evaluation scale: assessing a proposed cognitive component of social anxiety. J Anxiety Disord 22(1):44–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.janxdis.2007.08.002
White HJ, Haycraft E, Wallis DJ, Arcelus J, Leung N, Meyer C (2015) Development of the Mealtime Emotions Measure for Adolescents (MEM-A): gender differences in emotional responses to family mealtimes and eating psychopathology. Appetite 85:76–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2014.11.011
Wolpe J (1988) Subjective anxiety scale. Dict Behav Assess Tech 455–457
Yilmaz Z, Gottfredson NC, Zerwas SC, Bulik CM, Micali N (2018) Developmental premorbid body mass index trajectories of adolescents with eating disorders in a longitudinal population cohort. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaac.2018.11.008 (Epub ahead of print)
Funding
This research was supported by NIMH F31-MH096433 to Cheri A. Levinson. The funding source had no role in the collection, analysis and interpretation of data; in the writing of the report; and in the decision to submit the article for publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The Washington University IRB approved all procedures in this study and all the procedures performed in the current study were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendment.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained for experimentation with human subjects.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of topical collection on Personality and eating and weight disorders.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Levinson, C.A., Sala, M., Murray, S. et al. Diagnostic, clinical, and personality correlates of food anxiety during a food exposure in patients diagnosed with an eating disorder. Eat Weight Disord 24, 1079–1088 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40519-019-00669-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40519-019-00669-w