Abstract
Purpose
We investigated whether perfectionism, body image, attachment style, and self-esteem are predictors of orthorexia nervosa.
Methods
A cohort of 220 participants completed a self-administered, online questionnaire consisting of five measures: ORTO-15, the Multidimensional Perfectionism Scale (MPS), the Multidimensional Body-Self Relations Questionnaire-Appearance Scale (MBSRQ-AS), the Relationship Scales Questionnaire (RSQ), and Rosenberg’s Self-Esteem Scale (RSES).
Results
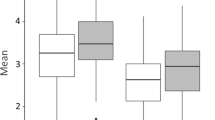
Correlation analysis revealed that higher orthorexic tendencies significantly correlated with higher scores for perfectionism (self-oriented, others-oriented and socially prescribed), appearance orientation, overweight preoccupation, self-classified weight, and fearful and dismissing attachment styles. Higher orthorexic tendencies also correlated with lower scores for body areas satisfaction and a secure attachment style. There was no significant correlation between orthorexia nervosa and self-esteem. Multiple linear regression analysis revealed that overweight preoccupation, appearance orientation and the presence of an eating disorder history were significant predictors of orthorexia nervosa with a history of an eating disorder being the strongest predictor.
Conclusions
Orthorexia nervosa shares similarities with anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa with regards to perfectionism, body image attitudes, and attachment style. In addition, a history of an eating disorder strongly predicts orthorexia nervosa. These findings suggest that these disorders might be on the same spectrum of disordered eating.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bratman S (1997) Orthorexia nervosa. Yoga J: 42–50. http://www.orthorexia.com/original-orthorexia-essay/. Accessed May 2015
Varga M, Dukay-Szabó S, Túry F, van Furth EF, van Furth Eric F (2013) Evidence and gaps in the literature on orthorexia nervosa. Eat Weight Disord 18(2):103–111. doi:10.1007/s40519-013-0026-y
Bratman S, Knight D (2000) Health food junkies. Orthorexia nervosa: overcoming the obsession with healthful eating. Brodways Books, New York
Donini LM, Marsili D, Graziani MP, Imbriale M, Cannella C (2004) Orthorexia nervosa: a preliminary study with a proposal for diagnosis and an attempt to measure the dimension of the phenomenon. Eat Weight Disord 9(2):151–157. doi:10.1007/BF03325060
Koven NS, Abry AW (2015) The clinical basis of orthorexia nervosa: emerging perspectives. Neuropsychiat Dis Treat 11:385–394. doi:10.2147/NDT.S61665
Segura-Garcia C, Ramacciotti C, Rania M, Aloi M, Caroleo M, Bruni A, Gazzarrini D, Sinopoli F, De Fazio P (2015) The prevalence of orthorexia nervosa among eating disorder patients after treatment. Eat Weight Disord 20(2):161–166. doi:10.1007/s40519-014-0171-y
Dunn TM, Gibbs J, Whitney N, Starosta A (2016) Prevalence of orthorexia nervosa is less than 1%: data from a US sample. Eat Weight Disord. doi:10.1007/s40519-016-0258-8
Brytek-Matera A (2012) Orthorexia nervosa–an eating disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder or disturbed eating habit. Arch Psychiatry Psychother 1:55–60. http://www.archivespp.pl/uploads/images/2012_14_1/BrytekMatera55__APP1_2012.pdf
Varga M, Thege BK, Dukay-Szabó S, Túry F, van Furth EF (2014) When eating healthy is not healthy: orthorexia nervosa and its measurement with the ORTO-15 in Hungary. BMC Psychiatry 14(1):59–70. doi:10.1186/1471-244X-14-59
Brown AJ, Parman KM, Rudat DA, Craighead LW (2012) Disordered eating, perfectionism, and food rules. Eat Behav 13(4):347. doi:10.1016/j.eatbeh.2012.05.011
Zachrisson HD, Skårderud F (2010) Feelings of insecurity: review of attachment and eating disorders. Eur Eat Disord Rev 18(2):97–106. doi:10.1002/erv.999
Bardone-Cone AM, Wonderlich SA, Frost RO, Bulik CM, Mitchell JE, Uppala S, Simonich H (2007) Perfectionism and eating disorders: current status and future directions. Clin Psychol Rev 27(3):384–405. doi:10.1016/j.cpr.2006.12.005
Mathieu J (2005) What is orthorexia? J Am Diet Assoc 105(10):1510–1512. doi:10.1016/j.jada.2005.08.021
Koven NS, Senbonmatsu R (2013) A neuropsychological evaluation of orthorexia nervosa. Open J Psychiat 3(2):214–222. doi:10.4236/ojpsych.2013.32019
Keel PK, Dorer DJ, Franko DL, Jackson SC, Herzog DB (2005) Postremission predictors of relapse in women with eating disorders. Am J Psychiat 162(12):2263–2268. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.162.12.2263
Brytek-Matera A, Donini LM, Krupa M, Poggiogalle E, Hay P (2015) Orthorexia nervosa and self-attitudinal aspects of body image in female and male university students. J Eat Disord 3(1):2. doi:10.1186/s40337-015-0038-2
Eriksson L, Baigi A, Marklund B, Lindgren EC (2008) Social physique anxiety and sociocultural attitudes toward appearance impact on orthorexia test in fitness participants. Scand J Med Sci in Sports 18(3):389–394. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0838.2007.00723.x
Ringer F, Crittenden PM (2007) Eating disorders and attachment: the effects of hidden family processes on eating disorders. Eur Eat Disord Rev 15(2):119–130. doi:10.1002/erv.761
Gual P, Pérez-Gaspar M, Martínez-González MA, Lahortiga F, Irala-Estévez JD, Cervera-Enguix S (2002) Self-esteem, personality, and eating disorders: baseline assessment of a prospective population-based cohort. Int J Eat Disord 31(3):261–273. doi:10.1002/eat.10040
Kinzl JF, Hauer K, Traweger C, Kiefer I (2006) Orthorexia nervosa in dieticians. Psychother Psychosom 75(6):395–396. doi:10.1159/000095447
Donini LM, Marsili D, Graziani MP, Imbriale M, Cannella C (2005) Orthorexia nervosa: validation of a diagnosis questionnaire. Eat Weight Disord 10(2):28–32. doi:10.1007/BF03327537
Hewit PL, Flett GL (2004) Multidimensional perfectionism scale: technical manual. Multi-Health Systems, Toronto
Cash TF (2000) The multidimensional body-self relations questionnaire user’s manual, 3rd edn. Old Dominion University, Norfolk
Griffin DW, Bartholomew K (1994) The metaphysics of measurement: the case of adult attachment. In: Bartholomew K, Perlman DP (eds) Advances in personal relationships: attachment processes in adult relationships, vol 5. Jessica Kingsley, London, pp 17–52
Rosenberg M (1979) Conceiving the self. Basic Books, New York
Hrabosky JI, Cash TF, Veale D, Neziroglu F, Soll EA, Garner DM, Strachan-Kinser M, Bakke B, Clauss LJ, Phillips KA (2009) Multidimensional body image comparisons among patients with eating disorders, body dysmorphic disorder, and clinical controls: a multisite study. Body Image 6(3):155–163. doi:10.1016/j.bodyim.2009.03.001
Jia H, Lubetkin EI (2005) The impact of obesity on health-related quality-of-life in the general adult US population. J Public Health 27(2):56–164. doi:10.1093/pubmed/fdi025
Segura-García C, Papaianni MC, Caglioti F, Procopio L, Nisticò CG, Bombardiere L, Ammendolia A, Rizza P, De Fazio P, Capranica L (2012) Orthorexia nervosa: a frequent eating disordered behavior in athletes. Eat Weight Disord 17(4):226–233. doi:10.3275/8272
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Both authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barnes, M.A., Caltabiano, M.L. The interrelationship between orthorexia nervosa, perfectionism, body image and attachment style. Eat Weight Disord 22, 177–184 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40519-016-0280-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40519-016-0280-x