Abstract
Purpose
This study tests the Emotional Eating Scale (EES) psychometric properties and correlates, and the moderator effect of body image flexibility on the association between emotional eating and binge eating.
Methods
The EES factorial structure was examined in female college students and women from the general population, through a principal component analysis and a confirmatory factor analysis. EES psychometric properties and moderation analyses were further conducted.
Results
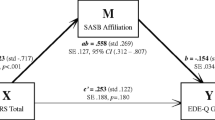
The EES presented a three-factor structure—Depression, Anxiety and Anger—a good model fit, internal consistency, construct validity and temporal stability. EES was positively associated with general and eating psychopathology, binge eating, and negatively associated with mindfulness and body image flexibility. Body image flexibility moderated the association between emotional eating and binge eating.
Conclusions
Findings showed that EES is a valid measure of emotional eating, and clarified the association between emotional eating and binge eating moderated by body image flexibility.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnow B, Kenardy J, Agras WS (1995) The emotional eating scale: the development of a measure to assess coping with negative affect by eating. Int J Eat Disord 18(1):79–90. doi:10.1002/1098-108X(199507)18:1%3C79::AID-EAT2260180109%3E3.0.CO;2-V
Ganley R (1989) Emotion and eating in obesity: a review of the literature. Int J Eat Disord 8(3):343–361. doi:10.1002/1098-108x(198905)8:3%3c343:aid-eat2260080310%3e3.0.co;2-c
Bruch H (1964) Psychological aspects in overeating and obesity. Psychosomatics 5:269–274. doi:10.1016/S0033-3182(64)72385-7
Heatherton T, Baumeister R (1991) Binge eating as escape from self-awareness. Psychol Bull 110(1):86–108. doi:10.1037/0033-2909.110.1.86
van Strien T, Ouwens M (2007) Effects of distress, alexithymia and impulsivity on eating. Eat Behav 8(2):251–257. doi:10.1016/j.eatbeh.2006.06.004
Allen K, Byrne S, La Puma M, McLean N, Davis E (2008) The onset and course of binge eating in 8- to 13-year-old healthy weight, overweight and obese children. Eat Behav 9(4):438–446. doi:10.1016/j.eatbeh.2008.07.008
Ricca V, Castellini G, Fioravanti G, Lo Sauro C, Rotella F, Ravaldi C, Lazzeretti L, Faravelli C (2012) Emotional eating in anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa. Compr Psychiatry 53(3):245–251. doi:10.1016/j.comppsych.2011.04.062
Waller G, Osman S (1998) Emotional eating and eating psychopathology among non-eating-disordered women. Int J Eat Disord 23(4):419–424. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1098-108X(199805)23:4%3c419:AID-EAT9%3e3.0.CO;2-L
Stice E, Presnell K, Spangler D (2002) Risk factors for binge eating onset in adolescent girls: a 2-year prospective investigation. Health Psychol 21(2):131–138. doi:10.1037/0278-6133.21.2.131
Masheb R, Grilo C (2006) Emotional overeating and its associations with eating disorder psychopathology among overweight patients with binge eating disorder. Int J Eat Disord 39:141–146. doi:10.1002/eat.20221
Stice E (2002) Risk and maintenance factors for eating pathology: a meta-analytic review. Psychol Bull 128(5):825–848. doi:10.1037//0033-2909.128.5.825
Polivy J, Herman CP (2002) Causes of eating disorders. Annu Rev Psychol 53(1):187–213. doi:10.1146/annurev.psych.53.100901.135103
Hilbert A, Tuschen-Caffier B (2007) Maintenance of binge eating through negative mood: a naturalistic comparison of binge eating disorder and bulimia nervosa. Int J Eat Disord 40(6):521–530. doi:10.1002/eat.20401
Kessler R, Berglund P, Chiu W-, Deitz A, Hudson J, Shahly V, Aguilar-Gaxiola S, Alonso J, Angermeyer M, Benjet C, Bruffaerts R, de Girolamo G, de Graaf R, Maria Haro J, Kovess-Masfety V, O’Neill S, Posada-Villa J, Sasu C, Scott K, Viana M, Xavier M (2013) The prevalence and correlates of binge eating disorder in the WHO health surveys. Biol Psychiatr 73(9):904–914. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2012.11.020
Katterman S, Kleinman B, Hood M, Nackers L, Corsica J (2014) Mindfulness meditation as an intervention for binge eating, emotional eating, and weight loss: a systematic review. Eat Behav 15(2):197–204. doi:10.1016/j.eatbeh.2014.01.005
Sandoz EK, Wilson KG, DuFrene TO (2010) Acceptance and commitment therapy for eating disorders: a process-focused guide to treating anorexia and bulimia. New Harbinger, Oakland
Wanden-Berghe RG, Sanz-Valero J, Wanden-Berghe C (2010) The application of mindfulness to eating disorders treatment: a systematic review. Eat Disord 19(1):34–48. doi:10.1080/10640266.2011.533604
Hayes S, Villatte M, Levin M, Hildebrandt M (2011) Open, aware, and active: contextual approaches as an emerging trend in the behavioral and cognitive therapies. Annu Rev Clin Psychol 7(1):141–168. doi:10.1146/annurev-clinpsy-032210-104449
Ferreira C, Pinto-Gouveia J, Duarte C (2011) The validation of the body image acceptance and action questionnaire: exploring the moderator effect of acceptance on disordered eating. Int J Psychol Psychol Ther 11(2):327–345
Sandoz E, Wilson K, DuFrene T (2010) Acceptance and commitment therapy for eating disorders: a process-focused guide to treating anorexia and bulimia. New Harbinge, Oakland
Sandoz E, Wilson K, Merwin R, Kate K (2013) Assessment of body image flexibility: the body image-acceptance and action questionnaire. J Context Behav Sci 2(1–2):39–48. doi:10.1016/j.jcbs.2013.03.002
Hill M, Masuda A, Melcher H, Morgan J, Twohig M (2014) Acceptance and commitment therapy for women diagnosed with binge eating disorder: a case-series study. Cognit Behav Pract. doi:10.1016/j.cbpra.2014.02.005
Stunkard A, Messick S (1985) The three-factor eating questionnaire to measure dietary restraint, disinhibition and hunger. J Psychosom Res 29(1):71–83. doi:10.1016/0022-3999(85)90010-8
Goldbacher E, Grunwald H, LaGrotte C, Klotz A, Oliver T, Musliner K, VanderVeur S, Foster G (2012) Factor structure of the emotional eating scale in overweight and obese adults seeking treatment. Appetite 59(2):610–615. doi:10.1016/j.appet.2012.04.005
Tanofsky-Kraff M, Theim K, Yanovski S, Bassett A, Burns N, Ranzenhofer L, Glasofer D, Yanovski J (2007) Validation of the emotional eating scale adapted for use in children and adolescents (EES-C). Int J Eat Disord 40:232–240. doi:10.1002/eat.20362
Kenardy J, Butler A, Carter C, Moor S (2003) Eating, mood, and gender in a noneating disorder population. Eat Behav 4(2):149–158. doi:10.1016/s1471-0153(03)00019-9
Zhu H, Cai T, Chen G, Zhang B (2013) Validation of the emotional eating scale among Chinese undergraduates. Soc Behav Pers Int J 41(1):123–134. doi:10.2224/sbp.2013.41.1.123
Watson D, O’Hara MW, Stuart S (2008) Hierarchical structures of affect and psychopathology and their implications for the classification of emotional disorders. Depress Anxiety 25(4):282–288. doi:10.1002/da.20496
Fairburn C, Beglin S (1994) Assessment of eating disorders: interview or self-report questionnaire? Int J Eat Disord 16(4):363–370. doi:10.1002/1098-108X(199412)16:4%3c363:AID-EAT2260160405%3e3.0.CO;2-#
Ribeiro M, Conceição E, Vaz A, Machado P (2014) The prevalence of binge eating disorder in a sample of college students in the north of Portugal. Eur Eat Disord Rev 22(3):185–190. doi:10.1002/erv.2283
Gormally J, Black S, Daston S, Rardin D (1982) The assessment of binge eating severity among obese persons. Addict Behav 7(1):47–55. doi:10.1016/0306-4603(82)90024-7
Duarte C, Pinto-Gouveia J, Ferreira C (2014) Expanding binge eating assessment: validity and screening value of the binge eating scale in women from the general population
Brown K, Ryan R (2003) The benefits of being present: mindfulness and its role in psychological well-being. J Pers Soc Psychol 84(4):822–848. doi:10.1037/0022-3514.84.4.822
Gregório S, Pinto-Gouveia J (2013) Mindful attention and awareness: relationships with psychopathology and emotion regulation. Span Psychol. doi:10.1017/sjp.2013.79
Lovibond S, Lovibond P (1995) Manual for the depression anxiety stress scales, 2nd edn. Psychology Foundation, Sydney
Pais-Ribeiro J, Honrado A, Leal I (2004) Contribuição para o estudo da adaptação portuguesa das escalas de ansiedade, depressão e stress de 21 itens de Lovibond e Lovibond. Psicologia, Saúde Doenças 5(2):229–239
Kline RB (2005) Principles and practice of structural equation modeling, 2nd edn. The Guilford Press, New York
Tabachnick B, Fidell L (2013) Using multivariate statistics, 6th edn. Pearson, Boston
Cohen J (1988) Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences, 2nd edn. Lawrence Erlbaum, New Jersey
Cohen J, Cohen P, West S, Aiken L (2003) Applied multiple regression/correlation analysis for the behavioural sciences, 3rd edn. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, New Jersey
Acknowledgments
Research was supported by the author Cristiana Duarte PhD Grant (SFRH/BD/76858/2011) by FCT (Portuguese Foundation for Science and Technology).
Conflict of interest
Cristiana Duarte declares that she has no conflict of interest. José Pinto-Gouveia declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duarte, C., Pinto-Gouveia, J. Returning to emotional eating: the emotional eating scale psychometric properties and associations with body image flexibility and binge eating. Eat Weight Disord 20, 497–504 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40519-015-0186-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40519-015-0186-z