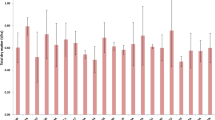
Abstract
To physiologically categorize drought tolerance characteristics of post-rainy sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench], 21 sorghum genotypes were evaluated under well watered and water deficit stress conditions for 2 years. Water deficit stress showed mixed effect among the genotypes for days to flowering, while other traits were adversely affected. Over 35 % reduction in grain yield was recorded due to post-flowering drought. Retention of green leaf area (GLA) during grain filling stage was found to be associated with drought tolerance. Loss of GLA started earlier and faster among high susceptible lines compared to tolerant lines. Based on stability analysis and drought susceptibility indices IS 23514 and Phule Chitra were identified as stable drought tolerant lines. Identified lines can be used in post-rainy sorghum breeding and molecular studies in future. The study also suggests that easily scorable physiological traits such as retention of green leaf area can be combined with stability analysis and DSI to identify drought tolerant genotypes.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Borrell, A. K., Hammer, G. L., & Henzell, R. G. (2000). Does maintaining green leaf area in sorghum improve yield under drought? II. Dry matter production and yield. Crop Science, 40, 1037–1048.
Cooper, M., & Hammer, G. L. (1996). Synthesis of strategies for crop improvement. In M. A. Cooper & G. L. Hammer (Eds.), Plant adaptation and crop improvement (pp. 591–623). Wallingford: ICRISAT and IRRI CAB Int.
Fischer, R. A., & Maurer, R. (1978). Drought resistance in spring wheat cultivars. I. Grain yield response. Australian Journal of Agricultural Research, 29, 897–907.
Ganapathy, K. N., Gomashe, S. S., Rakshit, S., Prabhakar, B., Ambekar, S. S., Ghorade, R. B., et al. (2012). Genetic diversity revealed utility of SSR markers in classifying parental lines and elite genotypes of sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L. Moench). Australian Journal of Crop Science, 6, 1486–1493.
Joshi, D. C., Shrotria, P. K., Singh, R., & Chawla, H. S. (2009). Morphological Characterisation of forage sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L). Moench] varieties for DUS testing. Indian J Genetics and Plant Breeding, 69, 1–11.
Mahalakshmi, V., & Bidinger, F. R. (2002). Evaluation of stay-green sorghum germplasm lines at ICRISAT. Crop Science, 42, 965–974.
Matthews, R. B., Reddy, D. M., Rani, A. U., Azam-Ali, S. N., & Peacock, J. M. (1990). Response of four sorghum lines to mid season drought. I. Growth, water use and yield. Field Crops Research, 25, 279–296.
Mutuva, R. N., Prasad, P. V. V., Tuinstra, M. R., Kofoid, K. D., & Yu, J. (2011). Characterization of sorghum genotypes for traits related to drought tolerance. Field Crops Research, 123, 10–18.
Osmanzai, M. (1994). A Screening method for productivity in moisture deficit environments. International Sorghum and Millets Newsletter, 35, 132.
Patil, J. V., Rakshit, S., & Khot, K. B. (2013). (Sorghum bicolor L. Moench) Genetics of post-flowering drought tolerance traits in post-rainy sorghum. Indian Journal of Genetics and Plant Breeding, 73, 44–50.
Rakshit, S., Ganapathy, K. N., Gomashe, S. S., Rathore, A., Ghorade, R. B., Nagesh Kumar, M. V., et al. (2012a). GGE Biplot analysis to evaluate genotype, environment and their interactions in sorghum multilocation data. Euphytica, 185, 465–479.
Rakshit, S., Gomashe, S. S., Ganapathy, K. N., Elangovan, M., Ratnavathi, C. V., Seetharama, N., & Patil, J. V. (2012b). Morphological and molecular diversity reveal wide variability among sorghum maldandi landraces from India. Journal of Plant Biochemistry Biotechnology, 21, 145–156.
Rakshit, S., Hariprasanna, K., Gomashe, S., Ganapathy, K. N., Das, I. K., Ramana, O. V., et al. (2014). Changes in area, yield gains, and yield stability of sorghum in major sorghum producing countries, 1970 to 2009. Crop Science, 54, 1571–1584.
Reddy, S. P., Reddy, B. V. S., & Kumar, A. A. (2009). M35-1 derived sorghum varieties for cultivation during the postrainy season. SAT eJournal, 7, 1–4.
Rosenow, D. T., Quisenberry, J. E., Wendt, C. W., & Clark, L. E. (1983). Drought tolerant sorghum and cottage germplasm. Agricultural Water Management, 7, 207–222.
Sankarapandian, R., Audilakshmi, S., Sharma, V., Ganesamurthy, K., Talwar, H. S., & Patil, J. V. (2013). Effect of morphological traits on grain yield of sorghum grown under stress at different growth stages, and stability analysis. Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 151, 630–647.
Seetharama, N., Mahalakshmi, V., Bidinger, F. R., & Singh S. (1984). Response of sorghum and pearl millet to drought stress in semi-arid India. In Agrometerology of sorghum and millet in the semi-arid tropics. Proceedings of international symposium, 15–20 Nov 1982, Patancheru, India, ICRISAT (pp. 159–173).
Talwar, H. S., Prabhakar, M. E., Kumari, A., Rao, S. S., Mishra, J. S., & Patil, J. V. (2010). Strategies to improve postflowering drought tolerance in rabi sorghum for predicted climate change scenario. Crop Improvement, 37, 93–98.
van Rensburg, L., & Krueger, G. H. J. (1993). Differential inhibition of photosynthesis (in vivo and in vitro) and changes in chlorophyll-a flourscence induction kinetics of four tobacco cultivars under drought stress. Journal of Plant Physiology, 100, 424–432.
White, J. W., Ochoa, R., Ibarra, P. F., & Singh, S. P. (1994). Inheritance of seed yield, maturity and seed weight of common bean (Phaselous vulgaris) under semi-arid rainfed conditions. Journal of Agricultural Science, 122, 265–273.
Yan, W., Hunt, L. A., Sheng, Q., & Szlavnics, Z. (2000). Cultivar evaluation and mega-environment investigation based on GGE biplot. Crop Science, 40, 597–605.
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by NAIP-ICAR (National Agricultural Innovation project of Indian Council of Agricultural Research) (Project code 4151). Authors thank the Director, ICAR-Indian Institute of Millets Research, Hyderabad for his guidance. They also thank M Elangovan and IK Das of the ICAR-Indian Institute of Millets Research, Hyderabad for providing seeds of mini-core lines and helping in arranging figures, respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rakshit, S., Swapna, M., Dalal, M. et al. Post-flowering drought stress response of post-rainy sorghum genotypes. Ind J Plant Physiol. 21, 8–14 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40502-015-0187-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40502-015-0187-y