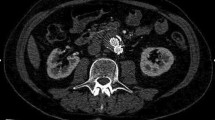
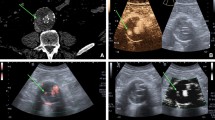
Abstract
Objective
The purpose of this systematic review and meta-analysis was to assess the sensitivity and specificity of contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) compared to computed tomography angiography (CTA) for the detection of endoleaks within endovascular aortic aneurysm repair (EVAR) surveillance at time of follow up.
Methods
A comprehensive literature search was undertaken among the four major databases (PubMed, Embase, Scopus and Ovid) to identify all articles assessing diagnostic specificity and accuracy with comparative modality (CEUS vs CTA) for endoleaks in adult patients at time of follow-up following EVAR. Databases where evaluated and assessed to October 2018.
Results
A total of 1773 patients were analysed from across 18 included studies in the quantitative analysis of the parameters of interest. There was no significant difference in detection rate of endoleak type I with detection rate 4.3% for both groups OR 1.09, 95% CI [0.78, 1.53], p = 0.62; type II endoleak detection rate was 22% in the CEUS group vs 23% in the CTA group OR 1.16, 95% CI [0.75–1.79], p = 0.50; while type III detection rate was 1.8% in CEUS group vs 2% in CTA group OR 0.85, 95% CI [0.43, 1.68], p = 0.64. However, the sensitivity rate for endoleak detection was higher in CEUS (p = 0.001) while no difference in specificity rate was noted (p = 0.28). There was higher rate of missed endoleaks in CTA groups (n = 12 vs n = 20).
Conclusion
Evidences from this study suggest that contrast-enhanced ultrasound scan post-EVAR can be utilised as safe and effective method in screening for endoleaks during post-EVAR surveillance without exposing the patient for additional risk of radiation and contrast. CEUS conveys no inferiority to CTA in detecting endoleaks.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parodi JC, Palmaz JC, Barone HD (1991) Transfemoral intraluminal graft implantation for abdominal aortic aneurysms. Ann Vasc Surg 5(6):491–499
Elkouri S, Gloviczki P, McKusick MA et al (2004) Perioperative complications and early outcome after endovascular and open surgical repair of abdominal aortic aneurysms. J Vasc Surg 39:497–505
Thomas DM, Hulten EA, Ellis ST et al (2014) Open versus endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm in the elective and emergent setting in a pooled population of 37,781 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. ISRN Cardiol 2014:149243
Maleux G, Koolen M, Heye S (2009) Complications after endovascular aneurysm repair. Semin Interv Radiol 26:003–009
Choke E, Thompson M (2004) Endoleak after endovascular aneurysm repair: current concepts. J Cardiovasc Surg 45:349
Brown A, Saggu GK, Bown MJ, Sayers RD, Sidloff DA (2016) Type II endoleaks: challenges and solutions. Vasc Health Risk Manag 12:53–63
Fillinger MF (1999) Postoperative imaging after endovascular AAA repair. Semin Vasc Surg 12:327–338
Walsh SR, Tang TY, Boyle JR (2008) Renal consequences of endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. J Endovasc Ther 15(1):73–82
Weerakkody RA, Walsh SR, Cousins C, Goldstone KE, Gaunt ME (2008) Radiation exposure during endovascular aneurysm repair. Br J Surg 95:699–702
Michaels JA, Drury D, Thomas SM (2005) Cost-effectiveness of endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. Br J Surg 92:960–967
Bendick PJ, Bove PG, Long GW, Zelenock GB, Brown OW, Shanley CJ (2003) Efficacy of ultrasound scan contrast agents in the noninvasive follow-up of aortic stent grafts. J Vasc Surg 37:381–385
Henao EA, Hodge MD, Felkai DD, McCollum CH, Noon GP, Charles H, Lin PH, Lumsden AB, Bush L (2006) Contrast-enhanced duplex surveillance after endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair: improved efficacy using a continuous infusion technique. J Vasc Surg 43:259–264
Partovi S, Kaspar M, Aschwanden M, Lopresti C, Madan S, Uthoff H, Imfeld S, Staub D (2015) Contrast-enhanced ultrasound after endovascular aortic repair—current status and future perspectives. Cardiovasc Diagn Ther 5(6):454–463
Moher D, Cook DJ, Eastwood S et al (1999) Improving the quality of reports of meta-analyses of randomised controlled trials: the QUOROM statement. Quality of reporting of meta-analyses. Lancet 354:1896–1900
Abbas A, Hansrani V, Sedgwick N, Ghosh J, McCollum CN (2014) 3D contrast enhanced ultrasound for detecting endoleak following endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR). Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 47:487–492
Bredahl KK, Taudorf M, Lönn L, Vogt KC, Sillesen H, Eiberg JP (2016) Contrast enhanced ultrasound can replace computed to-mography angiography for surveillance after endovascular aortic aneurysm repair. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 52:729–734
Cantisani V, Ricci P, Grazhdani H et al (2010) Prospective comparative analysis of colour-doppler ultrasound, contrast-enhanced ultrasound, computed tomography and magnetic resonance in detecting endoleak after endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 2011(41):186–192
Clevert D-A, Minaifar N, Kopp R, Stickel M, Meimarakis G, Sommer W et al (2009) Imaging of endoleaks after endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR) with contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS). A pictorial comparison with CTA. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc 41(3):151–168
Clevert DA, Helck A, D'Anastasi M, Gürtler V, Sommer WH, Meimarakis G, Weidenhagen R, Reiser M (2011) Improving the follow up after EVAR by using ultrasound image fusion of CEUS and MS-CT. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc 49(1–4):91–104
Giannoni MF, Palombo G, Sbarigia E, Speziale F, Zaccaria A, Fiorani P (2003) Contrast-enhanced ultrasound imaging for aortic stent-graft surveillance. J Endovasc Ther 10:208–217
Gürtler V, Sommer W, Meimarakis G, Kopp R, Weidenhagen R, Reiser M, Clevert D (2013) A comparison between contrast-enhanced ultrasound imaging and multislice computed tomography in detecting and classifying endoleaks in the follow-up after endovascular aneurysm repair. J Vasc Surg 58:340–345
Houdek K, Třeška V, Čertík B et al (2015) Initial experience of follow up of patients after the endovascular treatment of abdominal aortic aneurysms using contrast-enhanced ultrasound. Cor et Vasa 57:e121–e126
Iezzi R, Basilico R, Giancristofaro D, Pascali D, Cotroneo AR, Storto ML (2009) Contrast-enhanced ultrasound versus color duplex ultrasound imaging in the follow-up of patients after endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. J Vasc Surg 49:552–560
McWilliams RG, Martin J, White D, Gould DA, Rowlands PC, Haycox A, Brennan J, Gilling-Smith GL, Harris PL (2002) Detection of endoleak with enhanced ultrasound imaging: comparison with biphasic computed tomography. J Endovasc Ther 9:170–179
Millen A, Canavati R, Harrison G et al (2013) Defining a role for contrast-enhanced ultrasound in endovascular aneurysm repair surveillance. J Vasc Surg 58:18–23
Motta R, Rubaltelli L, Vezzaro R et al (2012) Role of multidetector CT angiography and contrast-enhanced ultrasound in redefining follow-up protocols after endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. Radiol Med (Torino) 117:1079–1092
Perini P, Sediri I, Midulla M, Delsart P, Gautier C, Haulon S (2012) Contrast-enhanced ultrasound vs. CT angiography in fenestrated EVAR surveillance: a single-center comparison. J Endovasc Ther 19:648–655
Perini P, Sediri I, Midulla M et al (2011) Single-centre prospective comparison between contrast-enhanced ultrasound and computed tomography angiography after EVAR. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 42:797–802
Schaeffer JS, Shakhnovich I, Sieck KN, Kallies KJ, Davis CA, Cogbill TH (2017) Duplex ultrasound surveillance after uncomplicated endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. Vasc Endovasc Surg 51:295–300
Ten Bosch JA, Rouwet EV, Peters CTH, Jansen L, Verhagen HJM, Prins MH, Teijink JAW (2010) Contrast-enhanced ultrasound versus computed tomographic angiography for surveillance of endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. J Vasc Interv Radiol 21:638–643
Bargellini I, Napoli V, Petruzzi P et al (2005) Type II lumbar endoleaks: Hemodynamic differentiation by contrast-enhanced ultrasound scanning and influence on aneurysm enlargement after endovascular aneurysm repair. J Vasc Surg 41:10–18
Harky A, Khan D, Singh VP, Sajid MM, Zywicka E (2018) What is the optimal imaging modality to detect endoleaks following elective endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm. Ann Vasc Med Res 5(3):1094
Mirza TA, Karthikesalingam A, Jackson D et al (2010) Duplex ultrasound and contrast-enhanced ultrasound versus computed tomography for the detection of endoleak after EVAR: systematic review and bivariate meta-analysis. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 39:418–428
Karthikesalingam A, Al-Jundi W, Jackson D et al (2012) Systematic review and meta-analysis of duplex ultrasonography, contrast-enhanced ultrasonography or computed tomography for surveillance after endovascular aneurysm repair. Br J Surg 99:1514–1523
Funding
No funding obtained for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors wish to disclose no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any direct studies with human participants performed by any of the authors of this paper.
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Harky, A., Zywicka, E., Santoro, G. et al. Is contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) superior to computed tomography angiography (CTA) in detection of endoleaks in post-EVAR patients? A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Ultrasound 22, 65–75 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40477-019-00364-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40477-019-00364-7