Abstract
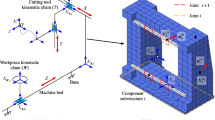
The static stiffness of machine tools can be used for the analysis of thermal deformation because of the uneven temperature field and can further be applied in the thermal error compensation. The prediction of static performance of machine tools is fundamental and essential during the design period. The purpose of this paper is to establish a precise static stiffness model for machine tools. Different from previous models, the proposed method in this paper, basing on the Fractal Geometry, takes both the elastoplastic deformation mechanism and friction into account. By analyzing the normal stiffness and tangential stiffness of joints, equivalent virtual material parameters are acquired for the finite element analysis calculation. An experimental set-up has been established to test X, Y and Z directional deformation of a vertical machine center with a magnitude of 200 kgf load applied to the node of the spindle along the respective direction. The results demonstrate that the proposed model can accurately simulate static characteristics of machine tools.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zaeh MF, Rebelein C, Semm T (2019) Predictive simulation of damping effects in machine tools. CIRP Ann 68:393–396
Semm T, Spannagl MF, Zaeh MF (2018) Dynamic substructuring of machine tools considering local damping models. Procedia CIRP 77:670–674
Xiang S, Yao X, Du Z et al (2018) Dynamic linearization modeling approach for spindle thermal errors of machine tools. Mechatronics 53:215–228
Yang Y, Wan M, Ma YC et al (2017) A new method using double distributed joint interface model for three-dimensional dynamics prediction of spindle-holder-tool system. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 95(5–8):2729–2745
Ye H, Huang Y, Li P et al (2016) Virtual material parameter acquisition based on the basic characteristics of the bolt joint interfaces. Tribol Int 95:109–117
Zhang Z, Xiao Y, Xie Y et al (2019) Effects of contact between rough surfaces on the dynamic responses of bolted composite joints: multiscale modeling and numerical simulation. Compos Struct 211:13–23
Yang Y, Wan M, Ma Y-C et al (2018) A new method using double distributed joint interface model for three-dimensional dynamics prediction of spindle-holder-tool system. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 95(5–8):2729–2745
Ahmadi K, Ahmadian H (2007) Modelling machine tool dynamics using a distributed parameter tool–holder joint interface. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 47(12–13):1916–1928
Kono D, Inagaki T, Matsubara A et al (2013) Stiffness model of machine tool supports using contact stiffness. Precis Eng 37(3):650–657
Yang Y, Muñoa J, Altintas YJ et al (2010) Optimization of multiple tuned mass dampers to suppress machine tool chatter. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 50(9):834–842
Wang M, Zan T, Gao X et al (2016) Suppression of the time-varying vibration of ball screws induced from the continuous movement of the nut using multiple tuned mass dampers. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 107:41–49
Wang W, Zhang Y, Li C (2017) Dynamic reliability analysis of linear guides in positioning precision. Mech Mach Theory 116:451–464
Liu J, Zhang P (2018) Thermo-mechanical behavior analysis of motorized spindle based on a coupled model. Adv Mech Eng 10(1):1687814017747144
Pedersen NL, Pedersen P (2009) Bolt–plate contact assemblies with prestress and external loads: solved with super element technique. Comput Struct 87(21–22):1374–1383
Cai LG, Wang F, Guo TN et al (2013) Experimental analysis of the nonlinear normal static stiffness of bolted joints. Appl Mech Mater 395–396(395–396):1104–1109
Adel F, Shokrollahi S, Jamal-Omidi M et al (2017) A model updating method for hybrid composite/aluminum bolted joints using modal test data. J Sound Vib 396:172–185
Mishra SK, Ghosh S, Aravindan S (2019) Performance of laser processed carbide tools for machining of Ti6Al4V alloys: a combined study on experimental and finite element analysis. Precis Eng 56:370–385
Greenwood JA, Williamson JB (1966) Contact of nominally flat surfaces. Proc R Soc Lond Ser A. Math Phys Sci 295(1442):300–319
Derjaguin BV, Muller VM, Toporov YP et al (1975) Effect of contact deformations on the adhesion of particles. J Colloid Interface Sci 53(2):314–326
Majumdar A, Bhushan B (1990) Role of fractal geometry in roughness characterization and contact mechanics of surfaces. J Tribol 112(2):205–216
Yan W, Komvopoulos K (1998) Contact analysis of elastic-plastic fractal surfaces. J Appl Phys 84(7):3617–3624
Tian H, Li B, Liu H et al (2011) A new method of virtual material hypothesis-based dynamic modeling on fixed joint interface in machine tools. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 51(3):239–249
Zhao Y, Yang C, Cai L et al (2016) Surface contact stress-based nonlinear virtual material method for dynamic analysis of bolted joint of machine tool. Precis Eng 43:230–240
Liao J, Zhang J, Feng P et al (2016) Interface contact pressure-based virtual gradient material model for the dynamic analysis of the bolted joint in machine tools. J Mech Sci Technol 30(10):4511–4521
Kogut L, Etsion I (2002) Elastic-plastic contact analysis of a sphere and a flat surface. J Appl Mech 69(5):657–662
Wang S, Komvopoulos KJ (1995) A fractal theory of the temperature distribution at elastic contacts of fast sliding surfaces. J Tribol 117(2):203–214
Chen Z, Etsion I (2019) The elastic-plastic contact behavior of rough surfaces with hard coatings. Tribol Int 134:435–442
Pan W, Li X, Wang L et al (2017) A normal contact stiffness fractal prediction model of dry-friction rough surface and experimental verification. Eur J Mech A Solids 66:94–102
Pan WJ, Xiaopeng LI, Muyan LI et al (2017) Three-dimensional fractal theory modeling of tangential contact stiffness of mechanized joint surfaces. J Vib Eng 30(4):577–586
Liou JL, Lin JF (2010) A modified fractal microcontact model developed for asperity heights with variable morphology parameters. Wear 268(1):133–144
Acknowledgements
Authors are grateful to the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.51605091 and 51605094), the National Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province (Grant No. 2017J05073) and the Educational Commission Foundation of Fujian Province (Grant No. JAT160162).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Technical Editor: Lincoln Cardoso Brandao.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, B., Ye, J., Ye, D. et al. An improved static stiffness analysis model for machine tools based on virtual material method. J Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 42, 357 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-020-02445-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-020-02445-9