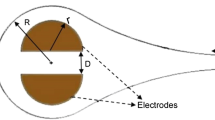
Abstract
This paper numerically studies the mixing quality of an electro-osmotic micro-mixer. An electrode array is symmetrically located on the surface of the micro-chamber with an inner cylindrical obstacle. The simulations are performed to obtain an optimal radius for inner cylinder. The effect of AC frequency, voltage value, liquid inlet velocity and angular velocity of inner cylinder is studied. It is found that the applied electric field significantly enhances the mixing rate. The results reveal that the mixing efficiency increases with the frequency, voltage value and angular velocity and decreases with the inlet velocity of fluids. It is demonstrated that the mixing efficiency is 71.02% and 97.67% for the angular velocity of 0.0148 and 1.148 rad/s, respectively. In addition, the results show that the mixing performance of shear-thinning fluids is higher than that of shear-thickening ones.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Figeys D, Pinto D (2000) Lab-on-a-chip: a revolution in biological and medical sciences. Anal Chem 72:330A–335A
Lee S-J, Choi B-K (2012) The artificial glomerulus design using diffusion in microchannels. Int J Precis Eng Manuf 13:307–310
Fair RB (2007) Digital microfluidics: is a true lab-on-a-chip possible? Microfluid Nanofluid 3:245–281
Bothe D, Stemich C, Warnecke HJ (2006) Fluid mixing in a T-shaped micro-mixer. Chem Eng Sci 61:2950–2958
Rasouli MR, Abouei Mehrizi A, Lashkaripour A (2015) Numerical study on low Reynolds mixing of T-shaped micro-mixers with obstacles. Transp. Phenom. Nano Micro Scales 3(2):68–76
Sayah A, Gijs MAM (2015) Simulation and fabrication of a three-dimensional microfluidic mixer in a monolithic glass substrate. Proc Eng 120:229–232
Cortelezzi L, Ferrari S, Dubini G (2017) A scalable active micro-mixer for biomedical applications. Microfluid Nanofluid 21:21–31
Wang SC, Chen HP, Lee CY, Yu CC, Chang HC (2006) AC electro-osmotic mixing induced by non-contact external electrodes. Biosens Bioelectron 22:263–567
Kazemi S, Nourian V, Nobari MRH, Movahed S (2017) Two dimensional numerical study on mixing enhancement in micro-channel due to induced charge electrophoresis. Chem Eng Process 120:241–250
Daghighi Y, Li D (2013) Numerical study of a novel induced-charge electrokinetic micro-mixer. Anal Chim Acta 763:28–37
Chen L, Deng Y, Zhou T, Pan H, Liu Z (2017) A novel electroosmotic micromixer with asymmetric lateral structures and DC electrode arrays. Micromachines 8:105
Shamloo A, Mirzakhanloo M, Dabirzadeh MR (2016) Numerical simulation for efficient mixing of Newtonian and non-Newtonian fluids in an electro-osmotic micro-mixer. Chem Eng Process 107:11–20
Deng Y, Zhou T, Liu Z, Wu Y, Qian S, Korvink JG (2018) Topology optimization of electrode patterns for electroosmotic micromixer. Int J Heat Mass Transf 126:1299–1315
Li D (2004) Electrokinetics in microfluidics, vol 2. Elsevier Academic Press, Cambridge
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Technical Editor: Jader Barbosa Jr., Ph.D.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Usefian, A., Bayareh, M., Shateri, A. et al. Numerical study of electro-osmotic micro-mixing of Newtonian and non-Newtonian fluids. J Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 41, 238 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-019-1739-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-019-1739-2