Abstract
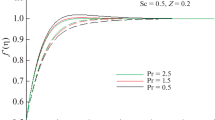
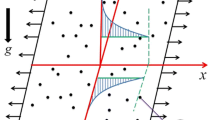
In this study, the problem of boundary layer flow of magnetohydrodynamic stagnation point flow past a stretching sheet with convective heating is examined. Condition of zero normal flux of nanoparticles at the wall for the stretched flow is the most recent phenomena that have yet to be explored in the literature. The nanoparticle fractions on the boundary are considered to be passively controlled. Similarity transformation is used to reduce the governing non-linear boundary value problems into coupled high-order non-linear ordinary differential equation. These equations were numerically solved using the function bvp4c from the matlab for different values of governing parameters. Numerical results are obtained for velocity, temperature and concentration, as well as the skin friction coefficient and local Nusselt number. The results indicate that the skin friction coefficient \(C_\mathrm{f}\) increases as the values of magnetic parameter \(M\) increase and decreases as the values of velocity ratio parameter \(A\) increase. The local Nusselt number \(\theta ^{\prime }(0)\) decreases as the values of thermophoresis parameter \(Nt\) increase and increases as the values of both Biot number \(Bi\) and Prandtl number \(Pr\) increase. A comparison with previous studies available in the literature has been done and an excellent agreement has been confirmed.


















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- \(A\) :
-
Velocity ratio parameter
- \(B_{0}\) :
-
Magnetic field strength
- \(Bi\) :
-
Biot number
- \(C\) :
-
Concentration at the surface
- \(C_\mathrm{f}\) :
-
Skin friction coefficient
- \(C_{\infty }\) :
-
Ambient concentration
- \(D_\mathrm{B}\) :
-
Brownian diffusion coefficient
- \(D_\mathrm{T}\) :
-
Thermophoresis diffusion coefficient
- \(f\) :
-
Dimensionless stream function
- \(k\) :
-
Thermal conductivity
- \(Le\) :
-
Lewis number
- \(M\) :
-
Magnetic parameter
- \(Nb\) :
-
Brownian motion parameter
- \(Nt\) :
-
Thermophoresis parameter
- \(Nu_{x}\) :
-
Local Nusselt number
- \(Pr\) :
-
Prandtl number
- \(q_{w}\) :
-
Wall heat flux
- \(Re_{x}\) :
-
Local Reynolds number
- \(T\) :
-
Temperature of the fluid inside the boundary layer
- \(T_\mathrm{f}\) :
-
Temperature of a hot fluid
- \(T_\infty\) :
-
Ambient temperature
- \(U_{\infty }\) :
-
Free stream velocity
- \({u},{v}\) :
-
Velocity component along x- and y-direction
- \(\eta\) :
-
Dimensionless similarity variable
- \(\mu\) :
-
Dynamic viscosity of the fluid
- \(\upsilon\) :
-
Kinematic viscosity of the fluid
- \((\rho )_\mathrm{f}\) :
-
Density of the basefluid
- \((\rho c)_\mathrm{f}\) :
-
Heat capacity of the base fluid
- \((\rho c)_\mathrm{p}\) :
-
Effective heat capacity of a nanoparticle
- \(\psi\) :
-
Stream function
- \(\alpha\) :
-
Thermal diffusivity
- \(\sigma\) :
-
Electrical conductivity
- \(\theta\) :
-
Dimensionless temperature
- \(\tau _{w}\) :
-
Wall shear stress
- \(\Gamma\) :
-
Parameter defined by \(\frac{(\rho c)_{\rm p}}{(\rho c)_{\rm f}}\)
- \(\infty\) :
-
Condition at the free stream
- w :
-
Condition at the surface
References
Mahapatra TR, Gupta AG (2002) Heat transfer instagnation point flow towards a stretching sheet. Heat Mass Transf 38:517–521
Ishak A, Nazar R, Pop I (2006) Mixed convection boundary layers in the stagnation point flow towards a stretching vertical sheet. Meccanica 41:509–518
Hayat T, Mustafa M, Shehzad SA, Obaidat S (2012) Melting heat transfer in the stagnation-point flow of an upper-convected Maxwell (UCM) fluid past a stretching sheet. Int J Numer Methods Fluids 68:233–243
Choi S (1995) Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticle. In: Development and applications of non-Newtonian flow, vol 66. ASME FED-vol 231/MD, pp 99–105
Buongionro J (2006) Convective transport in nanofluids. J Heat Transf ASME 128(3):240–250
Kuznetsov AV, Nield DA (2010) Natural convective boundary-layer flow of a nanofluid past a vertical plate. Int J Thermal Sci 49:243–247
Khan WA, Pop I (2010) Boundary layer flow of a nanofluid past a stretching sheet. Int J Heat Mass Transf 53:2477–2483
Bachok N, Ishak A, Pop I (2010) Boundary-layer flow of nanofluids over a moving surface in a flowing fluid. Int J Thermal Sci 49:1663–1668
Hamad MA, Pop I, Ismali AI (2011) Magnetic field effects on free convection flow of a nanofluid past a verical semi-infinite flat plate. Nonlinear Anal Real World Appl 12:1338–1346
Ahmad S, Rohni AM, Pop I (2011) Blasius and Sakiadis problems in nanofluids. Acta Mechanica 218:195–204
Makinde OD, Aziz A (2011) Boundary layer flow of a nanofluid past a stretching sheet with convective boundary condition. Int J Thermal Sci 50:1326–1332
Bachok N, Ishak A, Nazar R, Pop I (2010) Flow and heat transfer at a general three-dimensional stagnation point in nanofluid. J Physica B 405:4914–4918
Hamad A, Ferdows M (2012) Similarity solution of boundary layer stagnation point flow towards a heated porous stretching sheet saturated with nanofluid with heat absorption/generation and suction/blowing: A lie group analysis. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 17:132–140
Nazar R, Jaradat M, Arifin M, Pop I (2011) Stagnation-point flow past a shrinking sheet in a nanofluid. Central Eur J Phys 9(5):1195–1202
Anbuchezhian N, Srinivasan K, Chandrasekaran K, Kanasamy R (2012) Thermophoresis and Brownian motion effects on boundary layer flow of nanofluid in presence of thermal stratification due to solar energy. Appl Math Mech (English Edition) 33(6):765–780. doi:10.1007/s10483-012-1585-8
Mostafa M, Hayat T, Pop I, Asghar S, Obaidat S (2011) Stagnation point flow of a nanofluid towards a stretching sheet. Int J Heat Mass Transf 54:5588–5594
Ibrahim W, Shankar B, Mahantesh MM (2013) MHD stagnation point flow and heat transfer due to nanofluid towards a stretching sheet. Int J Heat Mass Transf 56:1–9
Ibrahim W, Shankar B (2012) Boundary-layer flow and heat transfer of nanofluid over a vertical plate with convective surface boundary condition. J Fluids Eng ASME 134(8):081203. doi:10.1115/1.4007075
Ibrahim W, Makinde OD (2013) The effect of double stratification on boundary layer flow and heat transfer of nanofluid over a vertical plate. J Comput Fluids 86:433–441
Ibrahim W, Shankar B (2014) Magnetohydrodynamic boundary layer flow and heat transfer of a nanofluid over non-isothermal stretching sheet. J Heat Transf Trans ASME 136(5):051701. doi:10.1115/1.4026118
Ibrahim W, Shankar B (2013) MHD boundary layer flow and heat transfer of a nanofluid past a permeable stretching sheet with velocity, thermal and solutal slip boundary conditions. J Comput Fluids 75:1–10
Ibrahim W, Shankar B (2015) MHD boundary layer flow and heat transfer due to a nanofluid over an exponentially stretching non-isothermal sheet. J Nanofluids 4(1):16–27
Ibrahim W (2015) Double-diffusive in MHD stagnation point flow and heat transfer of nano fluid over a stretching sheet. J Nanofluids 4(2):157–166
Ibrahim W (2015) The effect of induced magnetic field and convective boundary condition on MHD stagnation point flow and heat transfer of nanofluid over a stretching sheet. IEEE Trans Nanotechnol 14(1):178–186
Ibrahim W, Makinde OD (2015) MHD stagnation point flow of a power-law nanofluid towards a convectively heated stretching sheet with slip. J Process Mech Eng (accepted for publication)
Ibrahim W, Makinde OD (2015) Double-diffusive in mixed convection flow of MHD stagnation point flow and heat transfer due to nanofluid over a stretching vertical sheet. J Nanofluids 4(1):28–37
Kuznetsov AV, Nield DA (2014) Natural convective boundary-layer flow of a nanofluid past a vertical plate: a revisited model. Int J Thermal Sci 77:126–129
Khan ZH, Khan WA, Pop I (2013) Triple diffusive free convection along a horizontal plate in porous media saturated by nanofluid with convective boundary condition. Int J Heat Mass Transf 66:603–612
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to express their very sincere thanks to referees for their valuable comments and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Technical Editor: Francisco Ricardo Cunha.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ibrahim, W., Ul Haq, R. Magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) stagnation point flow of nanofluid past a stretching sheet with convective boundary condition. J Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 38, 1155–1164 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-015-0347-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-015-0347-z