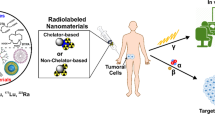
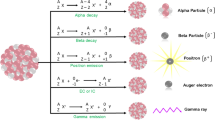
Abstract
Purpose
Recently, nanomedicine emerged as one of the most promising branches in biomedical field with the development of new tools for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes such as functionalized nanoparticles for the detection and prevention of cancer. Here, we systematically reviewed different types of radiolabelled nanoparticles for tumor imaging focusing on nuclear medicine applications.
Methods
A systematic analysis of literature was performed using the following string: “[ALL (label* AND diagnosis AND tumor AND nanoparticle* AND radio*) AND PUBYEAR > 2006]” on PubMed and Scopus, limiting the analysis to English articles and original papers from 2007 to 2018. Seventy-one original papers were included in the analysis, second divided between radiolabelled NPs for SPECT (n = 34) and PET imaging (n = 37).
Results
Among 34 original articles that analysed radiolabelled NPs for tumor SPECT imaging, 12 were radiolabelled with indium-111, 6 with iodine (3 with iodine-125; 3 with iodine-131), 14 with Technetium-99m, 1 with lutetium-177, and 1 with rhenium-188. Among 37 original papers regarding radiolabelled NPs for tumor PET imaging, 16 were radiolabelled with copper-64, 5 with fluorine-18, 5 with gallium (4 with gallium-68, 1 with gallium-66), 4 with iodine-124, 1 with titanium 45, 6 with zirconium-89.
Conclusions
Several NPs can be engineered to achieve suitable chemistry, physical properties, and morphology, overcoming many limitations of other conventional approaches. By modifying their size, it is possible to increase or decrease their biological half-life and maximize uptake in tumors due to the enhanced permeability and retention effect. It is also possible to bind to their surface different ligands like monoclonal antibodies or peptides to increase their specificity for tumor antigens.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
[ESF] European Science Foundation (2004) Nanomedicine—an ESF—European Medical Research Councils (EMRC) forward look report. Strasbourg cedex, France
ISO 2008 (2015) International Organization for Standardization. Technical specification: nanotechnologies—Terminology and definitions for nano objects—nanoparticle, nanofibre and nanoplate. ISO/TS 80004-2:2015. https://www.iso.org/standard/44278.html. Accessed 2015
ASTM E2456-06 (2012) Standard Terminology Relating to Nanotechnology. ASTM International. www.astm.org. Accessed 2012
Slamon DJ, Clark GM, Wong SG, Levin WJ, Ullrich A, McGuire WL (1987) Human breast cancer: correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene. Science 9(235):177–182
Wu X, Liu H, Liu J, Haley KN, Treadway JA, Larson JP, Ge N, Peale F, Bruchez MP (2003) Immunofluorescent labeling of cancer marker Her2 and other cellular targets with semiconductor quantum dots. Nat Biotechnol 21:41–46
El-Sayed IH, Huang X, El-Sayed MA (2005) Surface plasmon resonance scattering and absorption of anti-EGFR antibody conjugated gold nanoparticles in cancer diagnostics: applications in oral cancer. Nano Lett 5:829–834
Barenholz YY (2012) Doxil®—the first FDA-approved nano-drug: lessons learned. J Control Release 160:117–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2012.03.020
Bobo D, Robinson K, Islam J, Thurecht JK, Corrie SR (2016) Nanoparticle-based medicines: a review of FDA-approved materials and clinical trials to date. Pharm Res 33:2373–2387. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-016-1958-5
Blanco E, Shen H, Ferrari M (2015) Principles of nanoparticle design for overcoming biological barriers to drug delivery. Nat Biotechnol 33:941–951. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.3330
Chakravarty R, Goel S, Dash A, Cai W (2017) Radiolabeled inorganic nanoparticles for positron emission tomography imaging of cancer: an overview. Q J Nucl Med 1:181–204. https://doi.org/10.23736/S1824-4785.17.02969-7
Choi CHJ, Zuckerman JE, Webster P, Davis ME (2011) Targeting kidney mesangium by nanoparticles of defined size. Proc Natl Acad Sci 108:6656–6661. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1103573108
Kulkarni SA, Feng SS (2013) Effects of particle size and surface modification on cellular uptake and biodistribution of polymeric nanoparticles for drug delivery. Pharmaceut. Res. 30:2512–2522. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-012-0958-3
Liu D, Mori A, Huang L (1992) Role of liposome size and RES blockade in controlling biodistribution and tumor uptake of GM1-containing liposomes. Biochim Biophys Acta 17(1104):95–101
Sankaranarayanan J, Mahmoud EA, Kim G, Morachis JM, Almutairi A (2010) Multiresponse strategies to modulate burst degradation and release from nanoparticles. ACS Nano 4:5930–5936. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn100968e
Morachis JM, Mahmoud EA, Almutairi A (2012) Physical and chemical strategies for therapeutic delivery by using polymeric nanoparticles. Pharmacol Rev 64:505–519. https://doi.org/10.1124/pr.111.005363
Juliano RL, Stamp D (1975) The effect of particle size and charge on the clearance rates of liposomes and liposome encapsulated drugs. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 63:651–658
Zhang JS, Liu F, Huang L (2005) Implications of pharmacokinetic behavior of lipoplex for its inflammatory toxicity. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 57:689–698
Yamamoto Y, Nagasaki Y, Kato Y, Sugiyama Y, Kataoka K (2001) Long-circulating poly (ethylene glycol)-poly(d,l-lactide) block copolymer micelles with modulated surface charge. J Control Release 77:27–38
Xiao K, Li Y, Luo J, Lee JS, Xiao W, Gonik AM, Agarwal RG, Lam KS (2011) The effect of surface charge on in vivo biodistribution of PEG-oligocholic acid based micellar nanoparticles. Biomaterials 32:3435–3446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.01.021
Jokerst VJ, Lobovkina T, Zare RN, Gambhir SS (2011) Nanoparticle PEGylation for imaging and therapy. Nanomedicine 6:715–728
Matsumura Y, Maeda H (1986) A new concept for macromolecular therapeutics in cancer chemotherapy: mechanism of tumoritropic accumulation of proteins and the antitumor agent smancs. Cancer Res 46:6387–6392
Hobbs SK, Monsky WL, Yuan F, Roberts WG, Griffith L, Torchilin VP, Jain RK (1998) Regulation of transport pathways in tumor vessels: role of tumor type and microenvironment. Proc Natl Acad Sci 14(95):4607–4612
Hashizume H, Baluk P, Morikawa S, McLean JW, Thurston G, Roberge S, Jain RK, McDonald DM (2000) Openings between defective endothelial cells explain tumor vessel leakiness. Am J Pathol 156:1363–1380
LaRocque J, Bharali DJ, Mousa SA (2009) Cancer detection and treatment: the role of nanomedicines. Mol Biotechnol 42:358–366. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-009-9161-0
Morgan MA, Darcy KM, Rose PG, DeGeest K, Bookman MA, Aikins JK, Sill MW, Mannel RS, Allievi C, Egorin MJ (2008) Paclitaxel poliglumex and carboplatin as first-line therapy in ovarian, peritoneal or fallopian tube cancer: a phase I and feasibility trial of the gynecologic oncology group. Gynecol Oncol 110:329–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygyno.2008.05.008
Cho K, Wang X, Nie S, Chen ZG, Shin DM (2008) Therapeutic nanoparticles for drug delivery in cancer. Clin Cancer Res 14:1310–1316. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-1441
Hadjipanayis CG, Machaidze R, Kaluzova M, Wang L, Schuette AJ, Chen H, Wu X, Mao H (2010) EGFRvIII antibody-conjugated iron oxide nanoparticles for magnetic resonance imaging-guided convection-enhanced delivery and targeted therapy of glioblastoma. Cancer Res 70:6303–6312. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472
McQuade P, KnIght LC (2003) Radiopharmaceuticals for targeting the angiogenesis marker αvβ3. Q J Nucl Med 47:209–220
Torchilin VP, Lukyanov AN, Gao Z, Papahadjopoulos-Sternberg B (2003) Immunomicelles: targeted pharmaceutical carriers for poorly soluble drugs. Proc Natl Acad Sci 100:6039–6044. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0931428100
Galli F, Artico M, Taurone S, Manni I, Bianchi E, Piaggio G, Weintraub BD, Szkudlinski MW, Agostinelli E, Dierckx RAJO, Signore A (2017) Radiolabeling of VEGF165 with 99mTc to evaluate VEGFR expression in tumor angiogenesis. Int J Oncol 50:2171–2179. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2017.3989
Galli F, Iodice V, Lauri C, Signore A (2015) New approaches to image thyroid cancer cells and microenvironment. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 59:184–196
de la Fuente Jesus M, Grazu V (2012) Nanobiotechnology: inorganic nanoparticles vs organic nanoparticles. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Rudin M, Weissleder R (2003) Molecular imaging in drug discovery and development. Nat Rev 2:123–131
Arbab AS, Bashaw LA, Miller BR, Jordan EK, Lewis BK, Kalish H, Frank JA (2003) Characterization of biophysical and metabolic properties of cells labeled with superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles and transfection agent for cellular MR imaging. Radiology 229:838–846
Das M, Mishra D, Dhak P, Gupta S, Maiti TK, Basak A, Pramanik P (2009) Biofunctionalized, phosphonate-grafted, ultrasmall iron oxide nanoparticles for combined targeted cancer therapy and multimodal imaging. Small. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.200901219
Welch MJ, Hawker CJ, Wooley KL (2009) The advantages of nanoparticles for PET. Journal of Nuclear Med. https://doi.org/10.2967/jnumed.109.061846
Morales-Avila E, Ferro-Flores G, Ocampo-García BE, De León-Rodríguez LM, Santos-Cuevas CL, García-Becerra R, Medina LA, Gómez-Oliván L (2011) Multimeric system of 99mTc-labeled gold nanoparticles conjugated to c[RGDfK(C)] for molecular imaging of tumor α(v)β(3) expression. Bioconjug Chem 22:913–922. https://doi.org/10.1021/bc100551s
Mendoza-Sánchez AN, Ferro-Flores G, Ocampo-García BE, Morales-Avila E, Ramirez Fde M, De León-Rodríguez LM, Santos-Cuevas CL, Medina LA, Rojas-Calderon EL, Camacho-Lopez MA (2010) Lys3-bombesin conjugated to 99mTc-labelled gold nanoparticles for in vivo gastrin releasing peptide-receptor imaging. J Biomed Nanotechnol 6:375–384
Tsiapa I, Efthimiadou EK, Fragogeorgi E, Loudos G, Varvarigou AD, Bouziotis P, Kordas GC, Mihailidis D, Nikiforidis GC, Xanthopoulos S, Psimadas D, Paravatou-Petsotas M, Palamaris L, Hazle JD, Kagadis GC (2014) (99m) Tc-labeled aminosilane-coated iron oxide nanoparticles for molecular imaging of ανβ3-mediated tumor expression and feasibility for hyperthermia treatment. J Colloid Interface Sci 433:163–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2014.07.032
Peiris PM, Deb P, Doolittle E, Doron G, Goldberg A, Govender P, Shah S, Rao S, Carbone S, Cotey T, Sylvestre M, Sohaj S, Schiemann WP, Lee Z, Karathanasis E (2015) Vascular targeting of a gold nanoparticle to breast cancer metastasis. J Pharm Sci 104:2600–2610. https://doi.org/10.1002/jps.24518
Oda CMR, Fernandes RS, de Araújo Lopes SC, de Oliveira MC, Cardoso VN, Santos DM, de Castro Pimenta AM, Malachias A, Paniago R, Townsend DM, Colletti PM, Rubello D, Alves RJ, de Barros ALB, Leite EA (2017) Synthesis, characterization and radiolabeling of polymeric nano-micelles as a platform for tumor delivering. Biomed Pharmacother 89:268–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.01.144
Mondal N, Halder KK, Kamila MM, Debnath MC, Pal TK, Ghosal SK, Sarkar BR, Ganguly S (2010) Preparation, characterization, and biodistribution of letrozole loaded PLGA nanoparticles in Ehrlich Ascites tumor bearing mice. Int J Pharm 397:194–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2010.06.049
Liu X, Wang Y, Nakamura K, Kawauchi S, Akalin A, Cheng D, Chen L, Rusckowski M, Hnatowich DJ (2009) Auger radiation-induced, antisense-mediated cytotoxicity of tumor cells using a 3-component streptavidin-delivery nanoparticle with 111In. J Nucl Med 50:582–590. https://doi.org/10.2967/jnumed.108.056366
Yang Y, Zhang L, Cai J, Li X, Cheng D, Su H, Zhang J, Liu S, Shi H, Zhang Y, Zhang C (2016) Tumor angiogenesis targeted radiosensitization therapy using gold nanoprobes guided by MRI/SPECT imaging. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:1718–1732. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b09274
Felber M, Bauwens M, Mateos JM, Imstepf S, Mottaghy FM, Alberto RA (2015) 99mTc radiolabeling and biological evaluation of nanoparticles functionalized with a versatile coating ligand. Chemistry 16:6090–6099. https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201405704
Polyák A, Hajdu I, Bodnár M, Trencsényi G, Pöstényi Z, Haász V, Jánoki G, Jánoki GA, Balogh L, Borbély J (2013) 99mTc-labelled nanosystem as tumour imaging agent for SPECT and SPECT/CT modalities. Int J Pharm 449:10–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2013.03.049
Polyák A, Hajdu I, Bodnár M, Dabasi G, Jóba RP, Borbély J, Balogh L (2014) Folate receptor targeted self-assembled chitosan-based nanoparticles for SPECT/CT imaging: demonstrating a preclinical proof of concept. Int J Pharm 474:91–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2014.07.055
Veres DS, Máthé D, Futó I, Horváth I, Balázs A, Karlinger K, Mol Szigeti K (2014) Quantitative liver lesion volume determination by nanoparticle-based SPECT. Imaging Biol 16:167–172. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-013-0679-y
Santos do Carmo F, Ricci E, Cerqueira-Coutinho C, De Souza Albernaz M, Bernardes EM, Missailidis S, Santos-Oliveira R (2017) Anti-MUC1 nano-aptamers for triple-negative breast cancer imaging by single-photon emission computed tomography in inducted animals: initial considerations. Int J Nanomed 12:53–60. https://doi.org/10.2147/ijn.s118482
Fernandes RS, Mota LG, Kalbasi A, Moghbel M, Werner TJ, Alavi A, Rubello D, Cardoso VN, de Barros AL (2015) 99mTc-phytate as a diagnostic probe for assessing inflammatory reaction in malignant tumors. Nucl Med Commun 36:1042–1048. https://doi.org/10.1097/MNM.0000000000000358
Ng QK, Olariu CL, Yaffee M, Taelman VF, Marincek N, Krause T, Meier L, Walter MA (2014) Indium-111 labeled gold nanoparticles for in vivo molecular targeting. Biomaterials 35:7050–7057. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2014.04.098
Kao HW, Lin YY, Chen CC, Chi KH, Tien DC, Hsia CC, Lin WJ, Chen FD, Lin MH, Wang HE (2014) Biological characterization of cetuximab-conjugated gold nanoparticles in a tumor animal model. Nanotechnology 25:295102. https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/25/29/295102
Melancon MP, Zhou M, Zhang R, Xiong C, Allen P, Wen X, Huang Q, Wallace M, Myers JN, Stafford RJ, Liang D, Ellington AD, Li C (2014) Selective uptake and imaging of aptamer- and antibody-conjugated hollow nanospheres targeted to epidermal growth factor receptors overexpressed in head and neck cancer. ACS Nano 8:4530–4538. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn406632u
Cheng SH, Yu D, Tsai HM, Morshed RA, Kanojia D, Lo LW, Leoni L, Govind Y, Zhang L, Aboody KS, Lesniak MS, Chen CT, Balyasnikova IV (2016) Dynamic in vivo SPECT imaging of neural stem cells functionalized with radiolabeled nanoparticles for tracking of glioblastoma. J Nucl Med 57:279–284. https://doi.org/10.2967/jnumed.115.163006
Wang CF, Sarparanta MP, Mäkilä EM, Hyvönen ML, Laakkonen PM, Salonen JJ, Hirvonen JT, Airaksinen AJ, Santos HA (2015) Multifunctional porous silicon nanoparticles for cancer theranostics. Biomaterials 48:108–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.01.008
Banerjee SR, Foss CA, Horhota A, Pullambhatla M, McDonnell K, Zale S, Pomper MG (2017) 111In- and IRDye800CW-labeled PLA–PEG nanoparticle for imaging prostate-specific membrane antigen-expressing tissues. Biomacromol 18:201–209. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biomac.6b01485
Zhang R, Lu W, Wen X, Huang M, Zhou M, Liang D, Li C (2011) Annexin A5-conjugated polymeric micelles for dual SPECT and optical detection of apoptosis. J Nucl Med 52:958–964. https://doi.org/10.2967/jnumed.110.083220
Zhang R, Huang M, Zhou M, Wen X, Huang Q, Li C (2013) Annexin A5-functionalized nanoparticle for multimodal imaging of cell death. Mol Imaging 12:182–190
Zhang R, Xiong C, Huang M, Zhou M, Huang Q, Wen X, Liang D, Li C (2011) Peptide-conjugated polymeric micellar nanoparticles for Dual SPECT and optical imaging of EphB4 receptors in prostate cancer xenografts. Biomaterials 32:5872–5879. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.04.070
Zhu H, Zhao J, Lin X, Hong Y, Li C, Yang Z (2013) Design, synthesis and evaluation of dual-modality glyco-nanoparticles for tumor imaging. Molecules 30(18):6425–6438. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18066425
Rangger C, Helbok A, Sosabowski J, Kremser C, Koehler G, Prassl R, Andreae F, Virgolini I, von Guggenberg E, Decristoforo C (2013) Tumor targeting and imaging with dual-peptide conjugated multifunctional liposomal nanoparticles. Int J Nanomed 8:4659–4671. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S51927
Slastnikova TA, Rosenkranz AA, Morozova NB, Vorontsova MS, Petriev VM, Lupanova TN, Ulasov AV, Zalutsky MR, Yakubovskaya RI, Sobolev AS (2017) Preparation, cytotoxicity, and in vivo antitumor efficacy of 111In-labeled modular nanotransporters. Int J Nanomed 10(12):395–410. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S125359
Kim YH, Jeon J, Hong SH, Rhim WK, Lee YS, Youn H, Chung JK, Lee MC, Lee DS, Kang KW, Nam JM (2011) Tumor targeting and imaging using cyclic RGD-PEGylated gold nanoparticle probes with directly conjugated iodine-125. Small 7:2052–2060. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201100927
Farrag NS, El-Sabagh HA, Al-Mahallawi AM, Amin AM, AbdEl-Bary Mamdouh W (2017) Comparative study on radiolabeling and biodistribution of core-shell silver/polymeric nanoparticles-based theranostics for tumor targeting. Int J Pharm 30(529):123–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2017.06.044
Lee CM, Cheong SJ, Kim EM, Lim ST, Jeong YY, Sohn MH, Jeong HJ (2013) Nonpolymeric surface-coated iron oxide nanoparticles for in vivo molecular imaging: biodegradation, biocompatibility, and multiplatform. J Nucl Med 54:1974–1980. https://doi.org/10.2967/jnumed.113.122267
Lee BS, Park K, Park S, Kim GC, Kim HJ, Lee S, Kil H, Oh SJ, Chi D, Kim K, Choi K, Kwon IC, Kim SY (2010) Tumor targeting efficiency of bare nanoparticles does not mean the efficacy of loaded anticancer drugs: importance of radionuclide imaging for optimization of highly selective tumor targeting polymeric nanoparticles with or without drug. J Control Release 147:253–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2010.07.096
Tian L, Chen Q, Yi X, Wang G, Chen J, Ning P, Yang K, Liu Z (2017) Radionuclide I-131 labeled albumin-paclitaxel nanoparticles for synergistic combined chemo-radioisotope therapy of cancer. Theranostics 7:614–623. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.17381
Chen L, Zhong X, Yi X, Huang M, Ning P, Liu T, Ge C, Chai Z, Liu Z, Yang K (2015) Radionuclide (131)I labeled reduced graphene oxide for nuclear imaging guided combined radio- and photothermal therapy of cancer. Biomaterials 66:21–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.06.043
Yook S, Cai Z, Lu Y, Winnik MA, Pignol JP, Reilly RM (2016) Intratumorally injected 177Lu-labeled gold nanoparticles: gold nanoseed brachytherapy with application for neoadjuvant treatment of locally advanced breast cancer. J Nucl Med 57:936–942. https://doi.org/10.2967/jnumed.115.168906
Tsai CC, Chang CH, Chen LC, Chang YJ, Lan KL, Wu YH, Hsu CW, Liu IH, Ho CL, Lee WC, Ni HC, Chang TJ, Ting G, Lee TW (2011) Biodistribution and pharmacokinetics of 188Re-liposomes and their comparative therapeutic efficacy with 5-fluorouracil in C26 colonic peritoneal carcinomatosis mice. Int J Nanomed 6:2607–2619. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S23834
Petersen AL, Binderup T, Jølck RI, Rasmussen P, Henriksen JR, Pfeifer AK, Kjær A, Andresen TL (2012) Positron emission tomography evaluation of somatostatin receptor targeted 64Cu-TATE-liposomes in a human neuroendocrine carcinoma mouse model. J Control Release 10(160):254–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2011
Wong AW, Ormsby E, Zhang H, Seo JW, Mahakian LM, Caskey CF, Ferrara KW (2013) A comparison of image contrast with 64Cu-labeled long circulating liposomes and 18F-FDG in a murine model of mammary carcinoma. Am J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 3:32–43
Janib SM, Liu S, Pastuszka M, Shi P, Moses A, Orosco M, Lin YA, Cui Hm Conti P, Li Z, MacKay JA (2013) Kinetic quantification of protein polymer nanoparticles using non-invasive imaging. Integr Biol. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2ib20169k
Chen F, Hong H, Zhang Y, Valdovinos HF, Shi S, Kwon GS, Theuer CP, Barnhart TE, Cai W (2013) In vivo tumor targeting and image-guided drug delivery with antibody-conjugated, radiolabeled mesoporous silica nanoparticles. ACS Nano. 22:7. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn403617j
Chen F, Nayak TR, Goel S, Valdovinos HF, Hong H, Theuer CP, Barnhart TE, Cai W (2014) In vivo tumor vasculature targeted PET/NIRF imaging with TRC105(Fab)-conjugated, dual-labeled mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Mol Pharm 11:4007–4014. https://doi.org/10.1021/mp500306k
Chen F, Valdovinos HF, Hernandez R, Goel S, Barnhart TE, Cai W (2017) Intrinsic radiolabeling of titanium-45 using mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Acta Pharmacol Sin 38:907–913. https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2017.1
Shi S, Fliss BC, Gu Z, Zhu Y, Hong H et al (2015) Chelator-free labeling of layered double hydroxide nanoparticles for in vivo PET imaging. Sci Rep 5:16930. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep16930
Hu H, Li D, Liu S, Wang M, Moats R, Conti PS, Li Z (2014) Integrin α2β1 targeted GdVO4: Eu ultrathin nanosheet for multimodal PET/MR imaging. Biomaterials 35:8649–8658. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2014.06.059
Lee DE, Na JH, Lee S, Kang CM, Kim HN, Han SJ, Kim H, Choe YS, Jung KH, Lee KC, Choi K, Kwon IC, Jeong SY, Lee KH, Kim K (2013) Facile method to radiolabel glycol chitosan nanoparticles with (64) Cu via copper-free click chemistry for MicroPET imaging. Mol Pharm 3(10):2190–2198. https://doi.org/10.1021/mp300601r
Liu TW, MacDonald TD, Shi J, Wilson BC, Zheng G (2012) Intrinsically copper-64-labeled organic nanoparticles as radiotracers. Angew Chem Int Ed 51:13128–13131. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201206939
Xie H, Wang ZJ, Bao A, Goins B, Phillips WT (2010) In vivo PET imaging and biodistribution of radiolabeled gold nanoshells in rats with tumor xenografts. Int J Pharm 395:324–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2010.06.005
Xiao Y, Hong H, Matson VZ, Javadi A, Xu W, Yang Y et al (2012) Gold nanorods conjugated with doxorubicin and cRGD for combined anti-cancer drug delivery and PET imaging. Theranostics 2:757–768. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.4756
Tian M, Lu W, Zhang R, Xiong C, Ensor J, Nazario J, Jackson J, Shaw C et al (2013) Tumor uptake of hollow gold nanospheres after intravenous and intra-arterial injection: PET/CT study in a rabbit VX2 liver cancer model. Mol Imaging Biol 15:614–624. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-013-0635-x
Zhao Y, Sultan D, Detering L, Cho S, Sun G, Pierce R, Wooley KL, Liu Y (2014) Copper-64-alloyed gold nanoparticles for cancer imaging: improved radiolabel stability and diagnostic accuracy. Angew Chem Int Ed 53:156–159. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201308494
Xie J, Chen K, Huang J, Lee S, Wang J, Gao J, Li X, Chen X (2010) PET/NIRF/MRI triple functional iron oxide nanoparticles. Biomaterials 31:3016–3022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.01.010
Lee H, Li Z, Chen K, Hsu AR, Xu C, Xie J, Sun S, Chen X (2008) PET/MRI dual-modality tumor imaging using arginine–glycine–aspartic (RGD)-conjugated radiolabeled iron oxide nanoparticles. J Nucl Med 49:1371–1379. https://doi.org/10.2967/jnumed.108.051243
Chen K, Li Z, Wang H, Cai W, Chen X (2008) Dual-modality optical and positron emission tomography imaging of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor on tumor vasculature using quantum dots. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 35:2235–2244. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-008-0860-8
Hu K, Wang H, Tang G, Huang T, Tang X, Liang X, Yao S, Nie D (2015) In vivo cancer dual-targeting and dual-modality imaging with functionalized quantum dots. J Nucl Med 56:1278–1284. https://doi.org/10.2967/jnumed.115.158873
Allmeroth M, Moderegger D, Gündel D, Koynov K, Buchholz HG, Mohr K, Rösch F, Zentel R, Thews O (2013) HPMA-LMA copolymer drug carriers in oncology: an in vivo PET study to assess the tumor line-specific polymer uptake and body distribution. Biomacromol 14:3091–3101. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm400709z
Oku N, Yamashita M, Katayama Y, Urakami T et al (2011) PET imaging of brain cancer with positron emitter-labeled liposomes. Int J Pharm 403:170–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2010.10.001
Lee SB, Kim HL, Jeong HJ, Lim ST, Sohn MH, Kim DW (2013) Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticle pretargeting for PET imaging based on a rapid bioorthogonal reaction in a living body. Angew Chem Int Ed 52:10549–10552. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201304026
Chopra A (2013) 18F-labeled poly(l-lactic acid)-block-poly(sarcosine) lactosome, a polymer micelle. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. National Center for Biotechnology Information (US), Bethesda, MD
Hong H, Zhang Y, Engle JW, Nayak TR, Theuer CP, Nickles RJ, Barnhart TE, Cai W (2012) In vivo targeting and positron emission tomography imaging of tumor vasculature with 66Ga-labeled nano-graphene. Biomaterials 33:4147–4156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2012.02.031
Stelter L, Pinkernelle JG, Michel R, Schwartlander R, Raschzok N, Morgul MH et al (2010) Modification of aminosilanized superparamagnetic nanoparticles: feasibility of multimodal detection using 3 T MRI, small animal PET, and fluorescence imaging. Mol Imaging Biol. 12:25–34. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-009-0237-9
Ghai A, Singh B, Hazari PP, Schultz MK, Parmar A et al (2015) Radiolabeling optimization and characterization of 68Ga labeled DOTA–polyamido-amine dendrimer conjugate—animal biodistribution and PET imaging results. Appl Radiat Isot 105:40–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apradiso.2015.07.021
Kang WJ, Lee J, Lee YS, Cho S, Ali BA et al (2015) Multimodal imaging probe for targeting cancer cells using uMUC-1aptamer. Coll Surf B Biointerfaces 136:134–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2015.09.004
Bouziotis P, Stellas D, Thomas E, Truiller C, Tsoukalas C, Lux F et al (2017) 68Ga-radiolabeled AGuIX nanoparticles as dual-modality imaging agents for PET/MRI-guided radiation therapy. Nanomedicine. https://doi.org/10.2217/nnm-2017-0032
Benezra M, Penate-Medina O, Zanzonico PB, Schaer D, Ow H et al (2011) Multimodal silica nanoparticles are effective cancer-targeted probes in a model of human melanoma. J Clin Investig 121:2768–2780. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI45600
Gupta A, Wang S, Marko A, Joshi P et al (2014) Polyacrylamide-based biocompatible nanoplatform enhances the tumor uptake, PET/fluorescence imaging and anticancer activity of a chlorophyll analog. Theranostics 4:614–628. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.8478
Lee J, Lee TS, Ryu J, Hong S et al (2013) RGD peptide-conjugated multimodal NaGdF4:Yb31/Er31 nanophosphors for upconversion luminescence, MR, and PET imaging of tumor angiogenesis. J Nucl Med 54:96–103. https://doi.org/10.2967/jnumed.112.108043
Blanco VM, Chu Z, LaSance K, Gray BD et al (2016) Optocal and nuclear imaging of glioblastoma with phosphatidylserine-targeted nanovescicles. Oncotarget 7:32866–32875
Pérez-Medina C, Tang J, Abdel-Atti D, Hogstad B, Merad M, Fisher EA, Fayad ZA, Lewis JS, Mulder WJ, Reiner T (2015) PET imaging of tumor-associated macrophages with 89Zr-labeled high-density lipoprotein nanoparticles. J Nucl Med 56:1272–1277. https://doi.org/10.2967/jnumed.115.158956
Pérez-Medina C, Abdel-Atti D, Zhang Y, Longo VA, Irwin CP, Binderup T, Ruiz-Cabello J, Fayad ZA, Lewis JS, Mulder WJ, Reiner T (2014) A modular labeling strategy for in vivo PET and near-infrared fluorescence imaging of nanoparticle tumor targeting. J Nucl Med 55:1706–1711. https://doi.org/10.2967/jnumed.114.141861
Li N, Yu Z, Pham TT, Blower PJ, Yan R (2017) A generic 89Zr labeling method to quantify the in vivo pharmacokinetics of liposomal nanoparticles with positron emission tomography. Int J Nanomed 20(12):3281–3294. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S134379
Zhao Y, Shaffer TM, Das S, Pérez-Medina C, Mulder WJM, Grimm J (2017) Near-infrared quantum dot and 89Zr dual-labeled nanoparticles for in vivo Cerenkov imaging. Bioconjug Chem 28:600–608. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.6b00687
Karmani L, Labar D, Valembois V, Bouchat V, Nagaswaran PG, Bol A, Gillart J, Levêque P, Bouzin C, Bonifazi D, Michiels C, Feron O, Grégoire V, Lucas S, Vander Borght T, Gallez B (2013) Antibody-functionalized nanoparticles for imaging cancer: influence of conjugation to gold nanoparticles on the biodistribution of 89Zr-labeled cetuximab in mice. Contrast Media Mol Imaging 8:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1002/cmmi.1539
Cheng L, Kamkaew A, Shen S, Valdovinos HF, Sun H, Hernandez R, Goel S, Liu T, Thompson CR, Barnhart TE, Liu Z, Caicorresponding W (2016) Facile preparation of multifunctional WS2/WOx nanodots for chelator-free 89Zr-labeling and in vivo PET imaging. Small 12:5750–5758. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201601696
Phillips E, Penate-Medina O, Zanzonico PB, Carvajal DR, Mohan P, Ye Y, Humm J, Gönen M, Kalaigian H, Schöder H, Strauss HW, Larson SM, Wiesner U, Bradbury MS (2014) Clinical translation of an ultrasmall inorganic optical-PET imaging nanoparticle probe. Sci Transl Med 6:260ra149. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.3009524
Acknowledgements
Funding was supported by Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro (AIRC IG-Grant 20411).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Varani, M., Galli, F., Auletta, S. et al. Radiolabelled nanoparticles for cancer diagnosis. Clin Transl Imaging 6, 271–292 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40336-018-0283-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40336-018-0283-x