Abstract
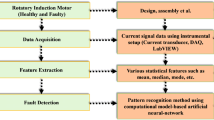
This paper presents a fault identification system for doubly fed induction generator. The proposed system is designed to identify single-phase faults and load switching events on an isolated load. Firstly, the system preprocess the stator line current data by the fast Fourier transform (FFT). In order to reduce the dimensionality of the FFT output data, the principal component analysis method is used. The fault identification stage is based on artificial neural network (ANN). Also, a post-processing is employed in order to increase the network reliability, which reduces the error of ANN. The proposed system is simulated and experimentally validated on different voltage, speed and load conditions.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alaya, J. B., Khedher, A., & Mimouni, M. F. (2011). Nonlinear vector control strategy applied to a variable speed DFIG generation system. In Eighth International Multi-Conference on Systems, Signals and Devices, pp 1–8.
Attoui, I., & Omeiri, A. (2014). Contribution to the fault diagnosis of a doubly fed induction generator for a closed-loop controlled wind turbine system associated with a two-level energy storage system. Electric Power Components and Systems, 42, 1727–1742.
Boldea, I. (2006). Variable speed generators. Timisoaria: Taylor & Francis.
Decanini, J. G. M. S., Tonelli-Neto, M. S., Malange, F. C. V., & Minussi, C. R. (2011). Detection and classification of voltage disturbances using a Fuzzy-ARTMAP-wavelet network. Electric Power Systems Research, 81, 2057–2065.
El-Naggar, A., & Erlich, I. (2016). Analysis of fault current contribution of Doubly-Fed Induction Generator Wind Turbines during unbalanced grid faults. Renewable Energy, 91, 137–146.
Frigo, M., & Johnson, S. G. (2005). The design and implementation of FFTW3. Proceedings of the IEEE, 93, 216–231.
Granados-Lieberman, D., Romero-Troncoso, R. J., Osornio-Rios, R. A., Garcia-Perez, A., & Cabal-Yepez, E. (2011). Techniques and methodologies for power quality analysis and disturbances classification in power systems: A review. IET Generation, Transmission & Distribution, 5, 519.
Haykin, S., & Wichern, D. W. (1999). Redes neurais - princípios e prática (neural networks - principles and practice). Porto Alegre: Bookman.
Huang, N., Xu, D., Liu, X., & Lin, L. (2012). Power quality disturbances classification based on S-transform and probabilistic neural network. Neurocomputing, 98, 12–23.
Johnson, R. A., & Wichern, D. W. (2007). Applied multivariate statistical analysis. New Jersey, EUA: Prentice Hall.
Justo, J. J., Mwasilu, F., & Jung, J. (2015). Doubly-fed induction generator based wind turbines: A comprehensive review of fault ride-through strategies. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 45, 447–467.
Marquardt, D. (1963). An algorithm for least squares estimation of non-linear parameters. Journal of the Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, 11, 431–441.
Masoum, M. A. S., Jamali, S., & Ghaffarzadeh, N. (2010). Detection and classification of power quality disturbances using discrete wavelet transform and wavelet networks. IET Science, Measurement & Technology, 4, 193–205.
Rodríguez, A., Aguado, J. A., Martín, F., López, J. J., Munhõz, F., & Ruiz, J. E. (2012). Rule-based classification of power quality disturbances using S-transform. Electric Power Systems Research, 86, 113–121.
Silva, I. N., Spatti, D. H., & Flauzino, R. A. (2010). Redes Neurais artificiais para engenharia e ciencias aplicadas - curso prático (Artificial Neural Networks for engineering and applied science - practical course.). São Paulo, SP: Artliber editora Ltda.
Smith, L.I. (2002). A tutorial on principal components analysis. http://www.ce.yildiz.edu.tr/personal/songul/file/1097/principal_components.
Smith, S. (1999). The scientist and engineer’s guide to digital signal processing. San Diego, CA: California Technical Publishing.
Stojcic, G., Pasanbegovic, K., & Wolbank, T.M. (2013). Detecting faults in Doubly fed induction generator by rotor side transient current measurement. IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition, 50, 4420–4425.
Uyar, Mu, Yildirim, S., & Gencoglu, Muhsin Tunay. (2009). An expert system based on S-transform and neural network for automatic classification of power quality disturbances. Expert Systems with Applications, 36, 5962–5975.
Ventosa, Se, Simon, C., Schimmel, M., Danobeitia, J. J., & Manuel, A. (2008). S-transform, time-frequency analysis, wavelet transform. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 56, 2771–2780.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Patrício de Santana, M., Boffino de Almeida Monteiro, J.R., Silva Borges, F.A. et al. Fault Identification in Doubly fed Induction Generator using FFT and Neural Networks. J Control Autom Electr Syst 28, 228–237 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40313-016-0298-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40313-016-0298-3