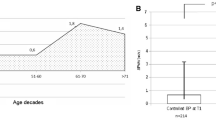
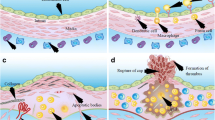
Abstract
Early vascular aging is a process characterized by a reduction in arterial elastin with an increase in collagen that has been related to cardiovascular risk factor and can determine an increased arterial stiffness and central blood pressure. It can be measured by several non invasive methods and in different arterial segment. The present paper will focus on functional (local stiffness parameter) and structural (intima media thickness) carotid arteries alterations typically evaluated by ultrasound methods. Methodological, research and clinical issue has been reviewed.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nilsson PM, Lurbe E, Laurent S. The early origins of vascular ageing and cardiovascular risk: the EVA syndrome. J Hypertens. 2008;26:1049–57.
Nilsson PM, Boutouyrie P, Cunha P, Kotsis V, Narkiewicz K, Parati G, Rietzschel E, Scuteri A, Laurent S. Early vascular ageing in translation: from laboratory investigations to clinical applications in cardiovascular prevention. J Hypertens. 2013;31(8):1517–26.
Laurent S, Cockcroft J, Van Bortel L, Boutouyrie P, Giannattasio C, Hayoz D, Pannier B, Vlachopoulos C, Wilkinson I, Struijker-Boudier H, European Network for Non-invasive Investigation of Large Arteries. Expert consensus document on arterial stiffness: methodological issues and clinical applications. Eur Heart J. 2006;27(21):2588–605.
Bots ML, Hoes AW, Koudstaal PJ, Hofman A, Grobbee DE. Common carotid intima-media thickness and risk of stroke and myocardial infarction: the Rotterdam Study. Circulation. 1997;96:1432–7.
O’Leary DH, Polak JF, Kronmal RA, Manolio TA, Burke GL, Wolfson SK Jr. Carotid-artery intima and media thickness as a risk factor for myocardial infarction and stroke in older adults. Cardiovascular Health Study Collaborative Research Group. N Engl J Med. 1999;340(14–22):5.
Nambi V, Chambless L, Folsom AR, He M, Hu Y, Mosley T, et al. Carotid intima-media thickness and presence or absence of plaque improves prediction of coronary heart disease risk: the ARIC (Atherosclerosis Risk In Communities) study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010;55:1600–7.
Zanchetti A, Bond MG, Hennig M, Neiss A, Mancia G, Dal Palu C, et al. Calcium antagonist lacidipine slows down progression of asymptomatic carotid atherosclerosis: principal results of the European Lacidipine Study on Atherosclerosis (ELSA), a randomized, double-blind, long-term trial. Circulation. 2002;106:2422–7.
Lorenz MW, von Kegler S, Steinmetz H, Markus HS, Sitzer M. Carotid intima-media thickening indicates a higher vascular risk across a wide age range: prospective data from the Carotid Atherosclerosis Progression Study (CAPS). Stroke. 2006;37(1):87–92.
Lorenz MW, Markus HS, Bots ML, Rosvall M, Sitzer M. Prediction of clinical cardiovascular events with carotid intima-media thickness: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Circulation. 2007;115(4):459–67.
Giannattasio C, Failla M, Piperno A, Grappiolo A, Gamba P, Paleari F, Mancia G. Early impairment of large artery structure and function in type I diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 1999;42(8):987–94.
Giannattasio C, Failla M, Grappiolo A, Gamba PL, Paleari F, Mancia G. Progression of large artery structural and functional alterations in Type I diabetes. Diabetologia. 2001;44(2):203–8.
Moon JH, Lim S, Han JW, Kim KM, Choi SH, Park KS, Kim KW, Jang HC. Carotid intima-media thickness is associated with the progression of cognitive impairment in older adults. Stroke. 2015;46(4):1024–30.
Sander K, Bickel H, Förstl H, Etgen T, Briesenick C, Poppert H, Sander D. Carotid- intima media thickness is independently associated with cognitive decline. The INVADE study. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2010;25(4):389–94.
Rosvall M, Persson M, Östling G, Nilsson PM, Melander O, Hedblad B, Engström G. Risk factors for the progression of carotid intima-media thickness over a 16-year follow-up period: the Malmö Diet and Cancer Study. Atherosclerosis. 2015;239(2):615–21.
Gaibazzi N, Rigo F, Facchetti R, Carerj S, Giannattasio C, Moreo A, Mureddu G, Paini A, Grolla E, Faden G, Cesana F, Faggiano P. Ultrasound carotid intima-media thickness, carotid plaque and cardiac calcium incrementally add to the Framingham Risk Score for the prediction of angiographic coronary artery disease: a multicenter prospective study. Int J Cardiol. 2014;177(2):708–10.
Yoshida M, Mita T, Yamamoto R, Shimizu T, Ikeda F, Ohmura C, Kanazawa A, Hirose T, Kawamori R, Watada H. Combination of the Framingham risk score and carotid intima-media thickness improves the prediction of cardiovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2012;35(1):178–80.
Ataoglu HE, Saler T, Uzunhasan I, Yenigun M, Yigit Z, Temiz LU, Saglam Z, Cetin F, Kumbasar B, Sar F. Additional value of carotid artery intima-media thickness in cardiovascular risk assessment by Framingham risk-score in Type 2 diabetes: a retrospective cohort study. J Diabetes. 2009;1(3):188–93.
Fujihara K, Suzuki H, Sato A, Ishizu T, Kodama S, Heianza Y, Saito K, Iwasaki H, Kobayashi K, Yatoh S, Takahashi A, Yahagi N, Sone H, Shimano H. Comparison of the Framingham risk score, UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Risk Engine, Japanese Atherosclerosis Longitudinal Study-Existing Cohorts Combine (JALS-ECC) and maximum carotid intima-media thickness for predicting coronary artery stenosis in patients with asymptomatic type 2 diabetes. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2014;21(8):799–815.
Baldassarre D, Hamsten A, Veglia F, de Faire U, Humphries SE, Smit AJ, Giral P, Kurl S, Rauramaa R, Mannarino E, Grossi E, Paoletti R, Tremoli E, IMPROVE Study Group. Measurements of carotid intima-media thickness and of interadventitia common carotid diameter improve prediction of cardiovascular events: results of the IMPROVE (Carotid Intima Media Thickness [IMT] and IMT-Progression as Predictors of Vascular Events in a High Risk European Population) study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012;60(16):1489–99.
Pignoli P, Tremoli E, Poli A, Oreste P, Paoletti R. Intimal plus medial thickness of the arterial wall: a direct measurement with ultrasound imaging. Circulation. 1986;74(6):1399–406.
Engelen L, Ferreira I, Stehouwer CD, Boutouyrie P, Laurent S, Reference Values for Arterial Measurements Collaboration. Reference intervals for common carotid intima-media thickness measured with echotracking: relation with risk factors. Eur Heart J. 2013;34(30):2368–80.
Touboul PJ, Hennerici MG, Meairs S, Adams H, Amarenco P, Desvarieux M, Ebrahim S, Fatar M, Hernandez Hernandez R, Kownator S, Prati P, Rundek T, Taylor A, Bornstein N, Csiba L, Vicaut E, Woo KS, Zannad F, Advisory Board of the 3rd Watching the Risk Symposium 2004, 13th European Stroke Conference. Mannheim intima-media thickness consensus. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2004;18(4):346–9.
Freire CM, Ribeiro AL, Barbosa FB, Nogueira AI, de Almeida MC, Barbosa MM, Lana AM, e Silva AC, Ribeiro-Oliveira A. Comparison between automated and manual measurements of carotid intima-media thickness in clinical practice. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2009;5:811–7.
Wong M, Edelstein J, Wollman J, Bond MG. Ultrasonic-pathological comparison of the human arterial wall. Verification of intima-media thickness. Arterioscler Thromb. 1993;13(4):482–6.
Touboul PJ, Prati P, Scarabin PY, Adrai V, Thibout E, Ducimetiere P. Use of monitoring software to improve the measurement of carotid wall thickness by B-mode imaging. J Hypertens Suppl. 1992;10(5):S37–41.
Palombo C, Kozakova M, Guraschi N, Bini G, Cesana F, Castoldi G, Stella A, Morizzo C, Giannattasio C. Radiofrequency-based carotid wall tracking: a comparison between two different systems. J Hypertens. 2012;30(8):1614–9.
Blacher J, Pannier B, Guerin AP, Marchais SJ, Safar ME, London GM. Carotid arterial stiffness as a predictor of cardiovascular and all-cause mortality in end-stage renal disease. Hypertension. 1998;32(3):570–4.
Barenbrock M, Kosch M, Jöster E, Kisters K, Rahn KH, Hausberg M. Reduced arterial distensibility is a predictor of cardiovascular disease in patients after renal transplantation. J Hypertens. 2002;20(1):79–84.
Giannattasio C, Capra A, Facchetti R, Viscardi L, Bianchi F, Failla M, Colombo V, Grieco A, Mancia G. Relationship between arterial distensibility and coronary atherosclerosis in angina patients. J Hypertens. 2007;25:593–8.
Failla M, Grappiolo A, Carugo S, Calchera I, Giannattasio C, Mancia G. Effects of cigarette smoking on carotid and radial artery distensibility. J Hypertens. 1997;15:1659–64.
Giannattasio C, Failla M, Capra A, Scanziani E, Amigoni M, Boffi L, Whistock C, Gamba P, Paleari F, Mancia G. Increased arterial stiffness in normoglycemic normotensive offspring of type 2 diabetic parents. Hypertension. 2008;51(2):182–7.
Giannattasio C, Achilli F, Failla M, Capra A, Vincenzi A, Valagussa F, Mancia G. Radial, carotid and aortic distensibility in congestive heart failure: effects of high-dose angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor or low-dose association with angiotensin type 1 receptor blockade. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2002;39(8):1275–82.
Giannattasio C, Achilli F, Grappiolo A, Failla M, Meles E, Gentile G, Calchera I, Capra A, Baglivo J, Vincenzi A, Sala L, Mancia G. Radial artery flow-mediated dilatation in heart failure patients: effects of pharmacological and nonpharmacological treatment. Hypertension. 2001;38(6):1451–5.
Kool MJF, Van Merode T, Reneman RS, Hoeks APG, StruykerBoudier H, Van Bortel LMAB. Evaluation of reproducibility of a vessel wall movement detector system for assessment of large artery properties. Cardiovasc Re. 1994;28:610–4.
Bussy C, Boutouyrie P, Lacolley P, Challande P, Laurent S. Intrinsic stiffness of the carotid artery wall material in essential hypertensives. Hypertension. 2000;35:1049–54.
Giannarelli C, Bianchini E, Bruno RM, Magagna A, Landini L, Faita F, Gemignani V, Penno G, Taddei S, Ghiadoni L. Local carotid stiffness and intima-media thickness assessment by a novel ultrasound-based system in essential hypertension. Atherosclerosis. 2012;223(2):372–7.
Dan HJ, Wang Y, Sha HJ, Wen SB. Quantitative evaluation of the structure and function of the common carotid artery in hypertriglyceridemic subjects using ultrasound radiofrequency-data technology. Eur J Radiol. 2012;81(11):3289–93.
Van Sloten TT, Schram MT, Can den Hurk K, Dekker JM, Nijpels G, Henry RM, Stehouwer CD. Local stiffness of the carotid and femoral artery is associated with incident cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality: the Hoorn study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;63(17):1739–47.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maloberti, A., Meani, P., Varrenti, M. et al. Structural and Functional Abnormalities of Carotid Artery and Their Relation with EVA Phenomenon. High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev 22, 373–379 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40292-015-0100-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40292-015-0100-9