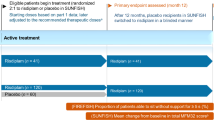
Abstract
Risdiplam (Evrysdi™) is an orally administered, survival motor neuron 2 (SMN2)-directed RNA splicing modifier being developed by Roche, PTC Therapeutics Inc and the SMA Foundation for the treatment of the spinal muscular atrophy. The small molecule is designed to treat spinal muscular atrophy caused by mutations in chromosome 5q leading to SMN protein deficiency. The drug boosts the ability of an alternative gene SMN2 to produce full-length and functional SMN protein. In August 2020, Evrysdi™ (risdiplam) received its first approval in the USA for the treatment of spinal muscular atrophy in patients 2 months of age and older. Risdiplam is in pre-registration for this indication in numerous countries worldwide, including the European Union, Brazil, Chile, China, Indonesia, Russia, South Korea and Taiwan. This article summarizes the milestones in the development of risdiplam leading to this first approval for spinal muscular atrophy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ratni H, Ebeling M, Baird J, et al. Discovery of risdiplam, a selective survival of motor neuron-2 ( SMN2) gene splicing modifier for the treatment of spinal muscular atrophy (SMA). J Med Chem. 2018;61(15):6501–17.
Poirier A, Weetall M, Heinig K, et al. Risdiplam distributes and increases SMN protein in both the central nervous system and peripheral organs. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2018;6(6):e00447.
Schorling DC, Pechmann A, Kirschner J. Advances in treatment of spinal muscular atrophy: new phenotypes, new challenges, new implications for care. J Neuromuscul Dis. 2020;7(1):1–13.
Wang J, Schultz PG, Johnson KA. Mechanistic studies of a small-molecule modulator of SMN2 splicing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2018;115(20):E4604–E46124612.
Food and Drug Administration (FDA). FDA approves oral treatment for spinal muscular atrophy [media release]. 7 Aug 2020. https://www.fda.gov/news-events/.
Genentech Inc. Evrysdi™ (risdiplam): US prescribing information. 2020. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/213535s000lbl.pdf. Accessed 24 Aug 2020.
SMA Foundation. SMA Foundation announces collaboration with PTC Therapeutics [media release]. 7 June 2006. https://smafoundation.org/sma-press.
Roche. Roche signs agreement with PTC Therapeutics to advance treatment for spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) [media release]. 29 Nov 2011. https://www.roche.com.
PTC Therapeutics. PTC Therapeutics announces achievement of major milestone in SMA collaboration [media release]. 8 Aug 2013. https://ir.ptcbio.com.
PTC Therapeutics. Joint program in spinal muscular atrophy enters first stage of clinical development [media release]. 22 Jan 2014. https://ir.ptcbio.com.
PTC Therapeutics. PTC therapeutics announces FDA grants priority review to risdiplam for the treatment of spinal muscular atrophy [media release]. 25 Nov 2019. https://ir.ptcbio.com.
PTC Therapeutics. PTC announces the acceptance of the European Marketing Authorization application for Evrysdi™ (risdiplam) for the treatment of spinal muscular atrophy [media release]. 17 Aug 2020. https://ir.ptcbio.com.
PTC Therapeutics. PTC Therapeutics announces first commercial milestone payment following US FDA approval of Evrysdi™ (risdiplam) [media release]. 26 Aug 2020. https://ir.ptcbio.com.
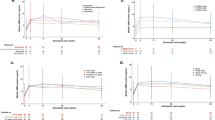
Baranello G, Bertini E, Chiriboga C, et al. Pooled safety data from the risdiplam (RG7916) clinical trial development program [abstract no. 1267 plus oral presentation]. Neurology. 2020;94(15 Suppl).
Sturm S, Gunther A, Jaber B, et al. A Phase 1 healthy male volunteer single escalating dose study of the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of risdiplam (RG7916, RO7034067), a SMN2 splicing modifier. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2018;10.
Baranello G, Servais L, Day JW, et al. FIREFISH Part 1: 16-month safety and exploratory outcomes of risdiplam (RG7916) treatment in infants with Type 1 spinal muscular atrophy (SMA). Dev Med Child Neurol. 2020;62(Suppl 1):6.
Servais L, Baranello G, Masson R, et al. FIREFISH Part 2: efficacy and safety of risdiplam (RG7916) in infants with type 1 spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) [abstract no. 1302 plus oral presentation]. Neurology. 2020;94(15 Suppl).
Vlodavets D, Servais L, Baranello G, et al. FIREFISH Part 1: survival, ventilation and swallowing ability in infants with type 1 spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) treated with risdiplam (RG7916). Eur J Neurol. 2019;26(Suppl 1):310–1.
Finkel RS, McDermott MP, Kaufmann P, et al. Observational study of spinal muscular atrophy type I and implications for clinical trials. Neurology. 2014;83(9):810–7.
Mercuri E, Barisic N, Boespflug-Tanguy O, et al. SUNFISH Part 2: efficacy and safety of risdiplam (RG7916) in patients with type 2 or non-ambulant type 3 spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) [abstract no. 1260 plus oral presentation]. Neurology. 2020;94(15 Suppl).
PTC Therapeutics. PTC Therapeutics announces 2-year data from Part 1 of SUNFISH and new data from JEWELFISH trials for risdiplam in patients with spinal muscular atrophy [media release]. 12 Jun 2020. https://ir.ptcbio.com.
Chiriboga C, Bruno C, Day JW, et al. JEWELFISH: safety and pharmacodynamic data in non-naïve patients with spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) receiving treatment with risdiplam (RG7916) [abstract no. 772 plus oral presentation]. Neurology. 2020;94(15 Suppl).
Bertini E, Day J, Muhaizea M, et al. RAINBOWFISH: a study of risdiplam (RG7916) in newborns with pre-symptomatic spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) [abstract no. P.362]. Neuromuscul Disord. 2019;29 (Suppl 1):S187.
Acknowledgements
During the peer review process, the manufacturer of risdiplam was also offered an opportunity to review this article. Changes resulting from comments received were made on the basis of scientific and editorial merit.
Funding
The preparation of this review was not supported by any external funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Authorship and Conflicts of Interest
Sohita Dhillon is a contracted employee of Adis International Ltd/Springer Nature and declares no relevant conflicts of interest. All authors contributed to the review and are responsible for the article content.
Ethics approval, Consent to participate and consent for publication, Availability of data and material, Code availability
Not applicable.
Additional information
Enhanced material
for this AdisInsight Report can be found at https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.12960173.
This profile has been extracted and modified from the AdisInsight database. AdisInsight tracks drug development worldwide through the entire development process, from discovery, through pre-clinical and clinical studies to market launch and beyond.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dhillon, S. Risdiplam: First Approval. Drugs 80, 1853–1858 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-020-01410-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-020-01410-z