Abstract
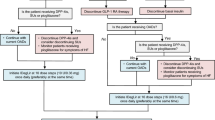
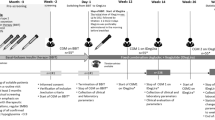
Insulin degludec/liraglutide (Xultophy®), a fixed-ratio combination of an ultra-long-acting insulin analogue and a glucagon-like protein-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist, is available in the EU for the management of inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes. Once-daily subcutaneous insulin degludec/liraglutide as add-on therapy to oral antidiabetics was effective and generally well tolerated in adults with inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes in several well designed 26-week phase III trials. In insulin-naive patients, add-on insulin degludec/liraglutide provided significantly greater improvements in glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c) levels than add-on insulin degludec, liraglutide or placebo, or unchanged GLP-1 receptor agonists (i.e. liraglutide or exenatide). In the extension of one of these trials, the efficacy of add-on insulin degludec/liraglutide was maintained for a total of 52 weeks. In insulin-experienced patients, add-on insulin degludec/liraglutide was significantly more effective with regard to improvements in HbA1c levels than add-on insulin degludec (at equivalent doses) or ongoing insulin glargine therapy. Add-on insulin degludec/liraglutide was associated with a lower incidence of confirmed hypoglycaemia than add-on insulin degludec in insulin-naive patients or ongoing insulin glargine in insulin-experienced patients, and a lower initial rate of nausea than add-on liraglutide. Thus, once-daily subcutaneous insulin degludec/liraglutide is a useful add-on therapy option for adult patients with inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ross SA. Breaking down patient and physician barriers to optimize glycemic control in type 2 diabetes. Am J Med. 2013;126(9 Suppl 1):S38–48.
Eng C, Kramer CK, Zinman B, et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist and basal insulin combination treatment for the management of type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. 2014;384(9961):2228–34.
Sorli C. New developments in insulin therapy for type 2 diabetes. Am J Med. 2014;127(10 Suppl):S39–48.
Inzucchi SE, Bergenstal RM, Buse JB, et al. Management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes: a patient-centered approach: position statement of the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetes Care. 2012;35(6):1364–79.
Carris NW, Taylor JR, Gums JG. Combining a GLP-1 receptor agonist and basal insulin: study evidence and practical considerations. Drugs. 2014;74(18):2141–52.
Ahrén B. Insulin plus incretin: a glucose-lowering strategy for type 2-diabetes. World J Diabetes. 2014;5(1):40–51.
Goldenberg R. Insulin plus incretin agent combination therapy in type 2 diabetes: a systematic review. Curr Med Res Opin. 2013;30(3):431–45.
Kumar A. Insulin degludec/liraglutide: innovation-driven combination for advancement in diabetes therapy. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2014;14(6):869–78.
Novo Nordisk A/S. Xultophy 100 units/mL + 3.6 mg/mL solution for injection: EU summary of product characteristics. 2014. http://www.ema.europa.eu. Accessed 21 Jul 2015.
Keating GM. Insulin degludec and insulin degludec/insulin aspart: a review of their use in the management of diabetes mellitus. Drugs. 2013;73(6):575–93.
Scott LJ. Liraglutide: a review of its use in adult patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Drugs. 2014;74(18):2161–74.
Vora J, Linjawi S, Gough SC, et al. Improved postprandial glycaemic control in Type 2 diabetes with a combination of insulin degludec and liraglutide: results from a meal test [abstract no. P113]. Diabet Med. 2014;31(Suppl 1):61.
Gough SC, Bode B, Woo V, et al. Efficacy and safety of a fixed-ratio combination of insulin degludec and liraglutide (IDegLira) compared with its components given alone: results of a phase 3, open-label, randomised, 26-week, treat-to-target trial in insulin-naive patients with type 2 diabetes. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014;2(11):885–93.
Kapitza C, Bode B, Ingwersen SH, et al. Preserved pharmacokinetic exposure and distinct glycemic effects of insulin degludec and liraglutide in IDegLira, a fixed-ratio combination therapy. J Clin Pharmacol. 2015. doi:10.1002/jcph.549.
Novo Nordisk A/S. Victoza 6 mg/ml solution for injection in pre-filled pen: EU summary of product characteristics. 2014. http://www.ema.europa.eu. Accessed 21 Jul 2015.
Novo Nordisk A/S. Tresiba 100 units/mL solution for injection in pre-filled pen: EU summary of product characteristics. 2014. http://www.ema.europa.eu. Accessed 21 Jul 2015.
Buse JB, Vilsboll T, Thurman J, et al. Contribution of liraglutide in the fixed-ratio combination of insulin degludec and liraglutide (IDegLira). Diabetes Care. 2014;37(11):2926–33.
Linjawi S, Bode B, Chaykin LB, et al. Efficacy and safety of IDegLira (combination of insulin degludec + liraglutide), in insulin-naive patients with T2D uncontrolled on GLP-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1RA) therapy [abstract no. 1002-P plus poster]. In: American Diabetes Association 75th Scientific Sessions. 2015.
Rodbard HW, Bode B, Harris SB, et al. IDegLira in insulin-naive patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D) inadequately controlled on sulfonylureas (SU) alone or in combination with metformin: the DUAL IV study [abstract no. 1003-P plus poster]. In: American Diabetes Association 75th Scientific Sessions. 2015.
Buse J, Pérez Manghi FC, García-Hernández PA, et al. Insulin degludec/liraglutide (IDegLira) is superior to insulin glargine (IG) in A1c reduction, risk of hypoglycemia, and weight change: DUAL V study [abstract no. 166-OR]. In: American Diabetes Association 75th Scientific Sessions. 2015.
Gough SC, Bode B, Woo VC, et al. One-year efficacy and safety of a fixed combination of insulin degludec and liraglutide in patients with type 2 diabetes: results of a 26-week extension to a 26-week main trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2015. doi:10.1111/dom.12498.
US National Institutes of Health. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier NCT01676116. 2012. http://www.clinicaltrials.gov. Accessed 21 Jul 2015.
US National Institutes of Health. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier NCT01952145. 2013. http://www.clinicaltrials.gov. Accessed 21 Jul 2015.
US National Institutes of Health. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier NCT01618162. 2012. http://www.clinicaltrials.gov. Accessed 21 Jul 2015.
Rodbard HW, Buse JB, Woo VC, et al. Novel combination of insulin degludec and liraglutide (IDegLira) is efficacious across the range of disease progression in type 2 diabetes [abstract no. 835]. Diabetologia. 2014;57(Suppl 1):S338–9.
Buse JB, Rodbard HW, Woo VC, et al. Impact of BMI on HbA1c reduction, hypoglycemia rates, and insulin requirements in response to IDegLira in patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D) [abstract no. 66-OR]. Diabetes. 2014;63(Suppl 1):A18.
Vilsboll T, Vora J, Jarlov H, et al. IDegLira, a combination of insulin degludec and liraglutide, enables patients with type 2 diabetes to reach target glycaemic control faster than its individual components alone [abstract no. 836 plus poster]. Diabetologia. 2014;57(Suppl 1):S339.
King A, Philis-Tsimikas A, Langbakke IH, et al. IDegLira, a combination of insulin degludec and liraglutide, improves both pre- and postprandial plasma glucose in patients with type 2 diabetes [abstract no. 243]. Diabetologia. 2014;57(Suppl 1):S108–9.
King AB, Philis-Tsimikas A, Kilpatrick ES, et al. Assessment of glycemic control by CGM in patients with T2D treated with IDegLira [abstract no. 170-OR]. In: American Diabetes Association 75th Scientific Sessions. 2015.
Linjawi S, Brod M, Bode B, et al. In insulin-naive patient with T2DM uncontrolled on GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RA), IDegLira (novel combination of insulin degludec + liraglutide) resulted in improved patient-reported outcomes vs. unchanged GLP-1RA [abstract no. 1150-P plus poster]. In: American Diabetes Association 75th Scientific Sessions. 2015.
Aroda VR, Jaeckel E, Jarlov H, et al. Incidence of gastrointestinal side effects similar between IDegLira and non-GLP-1RA comparators [abstract no. 1009-P plus poster]. In: American Diabetes Association 75th Scientific Sessions. 2015.
Disclosure
The preparation of this review was not supported by any external funding. During the peer review process, the manufacturer of the agent under review was offered an opportunity to comment on this article. Changes resulting from comments received were made by the authors on the basis of scientific and editorial merit. Sarah Greig and Lesley Scott are salaried employees of Adis/Springer.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The manuscript was reviewed by: S. Linjawi, Coffs Endocrine and Diabetes Services, Coffs Harbour, NSW, Australia; J. E. Thurman, SSM Medical Group—Endocrinology, St. Louis, MO, USA; V. C. Woo, Section of Endocrinology and Metabolism, University of Manitoba, Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Greig, S.L., Scott, L.J. Insulin Degludec/Liraglutide: A Review in Type 2 Diabetes. Drugs 75, 1523–1534 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-015-0448-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-015-0448-0