Abstract
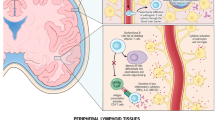
The anti-interleukin-6 (IL-6) chimeric monoclonal antibody siltuximab is the first drug to be approved for the treatment of multicentric Castleman’s disease (MCD) in the US and European union (EU), having gained approval under the FDA priority review program in the US and from an accelerated assessment and recommendation by the Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) in the EU. Development of the drug is continuing in smoldering multiple myeloma. This article summarizes the milestones in the development of siltuximab leading to this first approval for MCD.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Van Rhee F, Stone K, Szmania S, et al. Castleman disease in the 21st century: an update on diagnosis, assessment, and therapy. Clin Adv Hematol Oncol. 2010;8(7):486–98.
El-Osta HE, Kurzrock R. Castleman’s disease: from basic mechanisms to molecular therapeutics. Oncologist. 2011;16(4):497–511.
Fajgenbaum D, van Rhee F, Nabel C. HHV-8-negative, idiopathic multicentric Castleman disease: novel insights into biology, pathogenesis, and therapy. Blood. 2014. doi:10.1182/blood-2013-12-545087.
Chugai Pharmaceutical. Chugai Pharmaceutical’s innovative Castleman’s disease drug ACTEMRA now available in Japan (media release), 14 June 2005. www.japancorp.net.
US Food and Drug Administration. FDA approves Sylvant for rare Castleman’s disease (media release), 23 April 2014. http://www.fda.gov/newsevents/newsroom/pressannouncements/ucm394522.htm.
Janssen Biotech. SYLVANT(Tm) (siltuximab) Receives FDA Approval to treat multicentric Castleman’s disease (MCD): first treatment approved for patients with rare blood disorder (media release), 23 April 2014. http://www.janssenbiotech.com.
US Food and Drug Administration. SYLVANT prescribing information. http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2014/125496s000lbl.pdf. Accessed 15 May 2014.
European Commission. Community register of medicinal products for human use: SYLANT authorisation 2014. http://ec.europa.eu/health/documents/community-register/html/h928.htm. Accessed 10 Jun 2014.
Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) EMA. Summary of opinion (initial authorisation) Sylvant Siltuximab. 2014. Available at http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/Press_release/2014/03/WC500163529.pdf.
Guo Y, Nemeth J, O’Brien C, et al. Effects of siltuximab on the IL-6-induced signaling pathway in ovarian cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2010;16(23):5759–69.
Cavarretta IT, Neuwirt H, Zaki MH, et al. Mcl-1 is regulated by IL-6 and mediates the survival activity of the cytokine in a model of late stage prostate carcinoma. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008;617:547–55.
Hunsucker SA, Magarotto V, Kuhn DJ, et al. Blockade of interleukin-6 signalling with siltuximab enhances melphalan cytotoxicity in preclinical models of multiple myeloma. Br J Haematol. 2011;152(5):579–92.
Voorhees PM, Chen Q, Small GW, et al. Targeted inhibition of interleukin-6 with CNTO 328 sensitizes pre-clinical models of multiple myeloma to dexamethasone-mediated cell death. Br J Haematol. 2009;145(4):481–90.
Karkera J, Steiner H, Li W, et al. The anti-interleukin-6 antibody siltuximab down-regulates genes implicated in tumorigenesis in prostate cancer patients from a phase I study. Prostate. 2011;71(13):1455–65.
van Zaanen HC, Koopmans RP, Aarden LA, et al. Endogenous interleukin 6 production in multiple myeloma patients treated with chimeric monoclonal anti-IL6 antibodies indicates the existence of a positive feed-back loop. J Clin Invest. 1996;98(6):1441–8.
Coward J, Kulbe H, Leader D, et al. Interleukin-6 as a therapeutic target in advanced ovarian cancer [abstract no. 5331]. In: 101st Annual Meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research; 17-21 Apr 2010; Washington, DC.
Trikha M, Corringham R, Klein B, et al. Targeted anti-interleukin-6 monoclonal antibody therapy for cancer: a review of the rationale and clinical evidence. Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9(13):4653–65.
Puchalski T, Prabhakar U, Jiao Q, et al. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic modeling of an anti-interleukin-6 chimeric monoclonal antibody (siltuximab) in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2010;16(5):1652–61.
Xie L, Li LY, Kurzrock R, et al. Population pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic modeling of an anti-interleukin-6 chimeric monoclonal antibody, siltuximab (CNTO 328), in patients with B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, multiple myeloma, or Castleman’s disease. In: Blood Conference: 54th Annual Meeting of the American Society of Hematology, ASH. 2012;120(21).
Kurzrock R, Voorhees PM, Casper C, et al. A phase I, open-label study of siltuximab, an anti-IL-6 monoclonal antibody, in patients with B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma, multiple myeloma, or Castleman disease. Clin Cancer Res. 2013;19(13):3659–70.
Angevin E, Elez E, Cohen SJ, et al. Phase I/II, two-part, open-label, multiple-dose, dose-escalation study of siltuximab in patients with solid tumors [abstract no. 2583]. J Clin Oncol Conf. 2012;30(15 suppl).
Wong RS, Casper C, Munshi N, et al. A multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of the efficacy and safety of siltuximab, an anti-interleukin-6 monoclonal antibody, in patients with multicentric Castleman’s disease. In: Blood Conference: 55th Annual Meeting of the American Society of Hematology, ASH. 2013;122(21).
Van Rhee F, Casper C, Voorhees PM, et al. An open-label, phase 2, multicenter study of the safety of long-term treatment with siltuximab (an anti-interleukin-6 monoclonal antibody) in patients with multicentric Castleman’s disease. In: Blood Conference: 55th Annual Meeting of the American Society of Hematology, ASH. 2013;122(21).
Kirk M, Kurzrock R, Van Rhee F, et al. Siltuximab reverses muscle wasting in patients with multicentric Castleman’s disease. In: Blood Conference: 55th Annual Meeting of the American Society of Hematology, ASH. 2013;122(21).
San Miguel J, Blade J, Shpilberg O, et al. Randomized, open label, phase 2 study of siltuximab (an anti IL 6 mAb) and bortezomib melphalan prednisone versus bortezomib-melphalan-prednisone in patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma. Blood. 2014. doi:10.1182/blood-2013-12-546374.
Orlowski RZ, Gercheva L, Williams C, et al. Phase II, randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled study comparing siltuximab plus bortezomib versus bortezomib alone in pts with relapsed/ refractory multiple myeloma [abstract no. 8018]. J Clin Oncol 2012;30(Suppl).
Voorhees PM, Manges RF, Sonneveld P, et al. A phase 2 multicentre study of siltuximab, an anti-interleukin-6 monoclonal antibody, in patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma. Br J Haematol. 2013;161(3):357–66.
Disclosure
The preparation of this report was not supported by any external funding. During the peer review process the manufacturer of the agent under review was offered an opportunity to comment on the article. Changes resulting from any comments received were made by the authors on the basis of scientific completeness and accuracy. A. Markham is a contracted employee of Adis, Springer SBM. T. Patel is a salaried employee of Adis, Springer SBM.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This profile has been extracted and modified from the Adis R&D Insight drug pipeline database. Adis R&D Insight tracks drug development worldwide through the entire development process, from discovery, through pre-clinical and clinical studies to market launch.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Markham, A., Patel, T. Siltuximab: First Global Approval. Drugs 74, 1147–1152 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-014-0249-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-014-0249-x