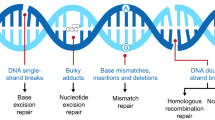
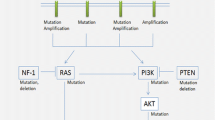
Abstract
Mutations in the isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) 1 gene are commonly found in human glioma, with the majority of low-grade gliomas harboring a recurrent point mutation (IDH1 R132H). Mutant IDH reveals an altered enzymatic activity leading to the synthesis of 2-hydroxyglutarate, which has been implicated in epigenetic mechanisms of oncogenesis. Nevertheless, it is unclear exactly how IDH mutations drive glioma initiation and progression, and it is also not clear why tumors with this mutation generally have a better prognosis than IDH wild-type tumors. Recognition of the high frequency of IDH mutations in glioma [and also in other malignancies, including acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and cholangiocarcinoma] have led to the development of a number of targeted agents that can inhibit these enzymes. Enasidenib and ivosidenib have both gained regulatory approval for IDH mutant AML. Both agents are still in early clinical phases for glioma therapy, as are a number of additional candidates (including AG-881, BAY1436032, and DS1001). A marked clinical problem in the development of these agents is overcoming the blood–brain barrier. An alternative approach to target the IDH1 mutation is by the induction of synthetic lethality with compounds that target poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP), glutamine metabolism, and the Bcl-2 family of proteins. We conclude that within the last decade, several approaches have been devised to therapeutically target the IDH1 mutation, and that, potentially, both IDH1 inhibitors and synthetic lethal approaches might be relevant for future therapies.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sjoblom T, Jones S, Wood LD, Parsons DW, Lin J, Barber TD, et al. The consensus coding sequences of human breast and colorectal cancers. Science. 2006;314(5797):268–74.
Miller JJ, Shih HA, Andronesi OC, Cahill DP. Isocitrate dehydrogenase-mutant glioma: evolving clinical and therapeutic implications. Cancer. 2017;123(23):4535–46.
Parsons DW, Jones S, Zhang X, Lin JC, Leary RJ, Angenendt P, et al. An integrated genomic analysis of human glioblastoma multiforme. Science. 2008;321(5897):1807–12.
Yan H, Parsons DW, Jin G, McLendon R, Rasheed BA, Yuan W, et al. IDH1 and IDH2 mutations in gliomas. N Engl J Med. 2009;360(8):765–73.
Hartmann C, Meyer J, Balss J, Capper D, Mueller W, Christians A, et al. Type and frequency of IDH1 and IDH2 mutations are related to astrocytic and oligodendroglial differentiation and age: a study of 1,010 diffuse gliomas. Acta Neuropathol. 2009;118(4):469–74.
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network, Brat DJ, Verhaak RG, Aldape KD, Yung WK, Salama SR, et al. Comprehensive, integrative genomic analysis of diffuse lower-grade gliomas. N Engl J Med. 2015;372(26):2481–98.
Paschka P, Schlenk RF, Gaidzik VI, Habdank M, Kronke J, Bullinger L, et al. IDH1 and IDH2 mutations are frequent genetic alterations in acute myeloid leukemia and confer adverse prognosis in cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia with NPM1 mutation without FLT3 internal tandem duplication. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(22):3636–43.
Fack F, Tardito S, Hochart G, Oudin A, Zheng L, Fritah S, et al. Altered metabolic landscape in IDH-mutant gliomas affects phospholipid, energy, and oxidative sn= s pathways. EMBO Mol Med. 2017;9(12):1681–95.
Molenaar RJ, Maciejewski JP, Wilmink JW, van Noorden CJF. Wild-type and mutated IDH1/2 enzymes and therapy responses. Oncogene. 2018;37(15):1949–60.
Horbinski C. What do we know about IDH1/2 mutations so far, and how do we use it? Acta Neuropathol. 2013;125(5):621–36.
Mullarky E, Mattaini KR, Vander Heiden MG, Cantley LC, Locasale JW. PHGDH amplification and altered glucose metabolism in human melanoma. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2011;24(6):1112–5.
Gross S, Cairns RA, Minden MD, Driggers EM, Bittinger MA, Jang HG, et al. Cancer-associated metabolite 2-hydroxyglutarate accumulates in acute myelogenous leukemia with isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 and 2 mutations. J Exp Med. 2010;207(2):339–44.
Hilf N, Kuttruff-Coqui S, Frenzel K, Bukur V, Stevanovic S, Gouttefangeas C, et al. Actively personalized vaccination trial for newly diagnosed glioblastoma. Nature. 2019;565(7738):240–5.
Bunse L, Pusch S, Bunse T, Sahm F, Sanghvi K, Friedrich M, et al. Suppression of antitumor T cell immunity by the oncometabolite (R)-2-hydroxyglutarate. Nat Med. 2018;24(8):1192–203.
Golub D, Iyengar N, Dogra S, Wong T, Bready D, Tang K, et al. Mutant isocitrate dehydrogenase inhibitors as targeted cancer therapeutics. Front Oncol. 2019;9:417.
Bardella C, Al-Dalahmah O, Krell D, Brazauskas P, Al-Qahtani K, Tomkova M, et al. Expression of Idh 1(R132H) in the murine subventricular zone stem cell niche recapitulates features of early gliomagenesis. Cancer Cell. 2016;30(4):578–94.
Philip B, Yu DX, Silvis MR, Shin CH, Robinson JP, Robinson GL, et al. Mutant IDH1 promotes glioma formation in vivo. Cell Rep. 2018;23(5):1553–64.
Fu X, Chin RM, Vergnes L, Hwang H, Deng G, Xing Y, et al. 2-Hydroxyglutarate inhibits ATP synthase and mTOR signaling. Cell Metab. 2015;22(3):508–15.
Chan SM, Thomas D, Corces-Zimmerman MR, Xavy S, Rastogi S, Hong WJ, et al. Isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 and 2 mutations induce BCL-2 dependence in acute myeloid leukemia. Nat Med. 2015;21(2):178–84.
Sullivan LB, Gui DY, Hosios AM, Bush LN, Freinkman E, Vander Heiden MG. Supporting aspartate biosynthesis is an essential function of respiration in proliferating cells. Cell. 2015;162(3):552–63.
Turcan S, Rohle D, Goenka A, Walsh LA, Fang F, Yilmaz E, et al. IDH1 mutation is sufficient to establish the glioma hypermethylator phenotype. Nature. 2012;483(7390):479–83.
Xu W, Yang H, Liu Y, Yang Y, Wang P, Kim SH, et al. Oncometabolite 2-hydroxyglutarate is a competitive inhibitor of alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenases. Cancer Cell. 2011;19(1):17–30.
Luchman HA, Stechishin OD, Dang NH, Blough MD, Chesnelong C, Kelly JJ, et al. An in vivo patient-derived model of endogenous IDH1-mutant glioma. Neuro Oncol. 2012;14(2):184–91.
Wu F, Cheng G, Yao Y, Kogiso M, Jiang H, Li XN, et al. Inhibition of mutated isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 in cancer. Med Chem. 2018;14(7):715–24.
Nunez FJ, Mendez FM, Kadiyala P, Alghamri MS, Savelieff MG, Garcia-Fabiani MB, et al. IDH1-R132H acts as a tumor suppressor in glioma via epigenetic up-regulation of the DNA damage response. Sci Transl Med. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.aaq1427.
Li S, Chou AP, Chen W, Chen R, Deng Y, Phillips HS, et al. Overexpression of isocitrate dehydrogenase mutant proteins renders glioma cells more sensitive to radiation. Neuro Oncol. 2013;15(1):57–68.
Shi J, Sun B, Shi W, Zuo H, Cui D, Ni L, et al. Decreasing GSH and increasing ROS in chemosensitivity gliomas with IDH1 mutation. Tumour Biol. 2015;36(2):655–62.
Wang P, Wu J, Ma S, Zhang L, Yao J, Hoadley KA, et al. Oncometabolite d-2-hydroxyglutarate inhibits ALKBH DNA repair enzymes and sensitizes IDH mutant cells to alkylating agents. Cell Rep. 2015;13(11):2353–61.
Tateishi K, Wakimoto H, Iafrate AJ, Tanaka S, Loebel F, Lelic N, et al. Extreme vulnerability of IDH1 mutant cancers to NAD+ depletion. Cancer Cell. 2015;28(6):773–84.
Tateishi K, Higuchi F, Miller JJ, Koerner MVA, Lelic N, Shankar GM, et al. The alkylating chemotherapeutic temozolomide induces metabolic stress in IDH1-mutant cancers and potentiates NAD(+) depletion-mediated cytotoxicity. Cancer Res. 2017;77(15):4102–15.
McBrayer SK, Mayers JR, DiNatale GJ, Shi DD, Khanal J, Chakraborty AA, et al. Transaminase inhibition by 2-hydroxyglutarate impairs glutamate biosynthesis and redox homeostasis in glioma. Cell. 2018;175(1):101-16 e25.
Molenaar RJ, Radivoyevitch T, Nagata Y, Khurshed M, Przychodzen B, Makishima H, et al. IDH1/2 mutations sensitize acute myeloid leukemia to PARP inhibition and this is reversed by IDH1/2-mutant inhibitors. Clin Cancer Res. 2018;24(7):1705–15.
Souers AJ, Leverson JD, Boghaert ER, Ackler SL, Catron ND, Chen J, et al. ABT-199, a potent and selective BCL-2 inhibitor, achieves antitumor activity while sparing platelets. Nat Med. 2013;19(2):202–8.
Davids MS, Letai A. ABT-199: taking dead aim at BCL-2. Cancer Cell. 2013;23(2):139–41.
Lessene G, Czabotar PE, Sleebs BE, Zobel K, Lowes KN, Adams JM, et al. Structure-guided design of a selective BCL-X(L) inhibitor. Nat Chem Biol. 2013;9(6):390–7.
Merino D, Kelly GL, Lessene G, Wei AH, Roberts AW, Strasser A. BH3-mimetic drugs: blazing the trail for new cancer medicines. Cancer Cell. 2018;34(6):879–91.
Karpel-Massler G, Ishida CT, Bianchetti E, Shu C, Perez-Lorenzo R, Horst B, et al. Inhibition of mitochondrial matrix chaperones and antiapoptotic Bcl-2 family proteins empower antitumor therapeutic responses. Cancer Res. 2017;77(13):3513–26.
Karpel-Massler G, Ishida CT, Bianchetti E, Zhang Y, Shu C, Tsujiuchi T, et al. Induction of synthetic lethality in IDH1-mutated gliomas through inhibition of Bcl-xL. Nat Commun. 2017;8(1):1067.
Saha SK, Gordan JD, Kleinstiver BP, Vu P, Najem MS, Yeo JC, et al. Isocitrate dehydrogenase mutations confer dasatinib hypersensitivity and SRC dependence in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Cancer Discov. 2016;6(7):727–39.
Boddu P, Borthakur G. Therapeutic targeting of isocitrate dehydrogenase mutant AML. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2017;26:525–30.
Dang L, Su SM. Isocitrate dehydrogenase and (R)-2-hydroxyglutarate: from basic discovery to therapeutics development. Annu Rev Biochem. 2017;86:305–31.
Urban DJ, Martinez NJ, Davis MI, Brimacombe KR, Cheff DM, Lee TD, et al. Assessing inhibitors of mutant isocitrate dehydrogenase using a suite of pre-clinical discovery assays. Sci Rep. 2017;7:12758.
Fan B, Mellinghoff IK, Wen PY, Lowery MA, Goyal L, Tap WD, et al. Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of ivosidenib, an oral, targeted inhibitor of mutant IDH1, in patients with advanced solid tumors. Investig New Drugs. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-019-00771-x(epub 26 Apr 2019).
Mellinghoff IK, Touat M, Maher E, De La Fuente M, Cloughesy TF, Holdhoff M, et al. ACTR-46. AG-120, a first-in-class mutant IDH1 inhibitor in patients with recurrent or progressive IDH1 mutant glioma: updated results from the phase 1 non-enhancing glioma population. Neuro Oncol. 2017;19(Suppl 6):vi10–1.
Mellinghoff I, Maher E, Wen P, Cloughesy T, Peters K, Choi C, et al. RBTT-03. A phase 1, multi-center, randomized, open-label, perioperative study of AG-120 (Ivosidenib) and AG-881 in patients with recurrent, non-enhancing, IDH1-mutant, low-grade glioma. Neuro Oncol. 2018;20(Suppl 6):vi234.
Stein EM, DiNardo CD, Pollyea DA, Fathi AT, Roboz GJ, Altman JK, et al. Enasidenib in mutant IDH2 relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2017;130:722–31.
Hartmann C, Meyer J, Balss J, Capper D, Mueller W, Christians A, et al. Type and frequency of IDH1 and IDH2 mutations are related to astrocytic and oligodendroglial differentiation and age: a study of 1,010 diffuse gliomas. Acta Neuropathol. 2009;118:469–74.
Molina JR, Sun Y, Protopopova M, Gera S, Bandi M, Bristow C, et al. An inhibitor of oxidative phosphorylation exploits cancer vulnerability. Nat Med. 2018;24(7):1036–46.
Mellinghoff IK, Penas-Prado M, Peters KB, Cloughesy TF, Burris HA III, Maher EA, et al. ACTR-31. Phase 1 study of AG-881, an inhibitor of mutant IDH1 and IDH2: results from the recurrent/progressive glioma population. Neuro Oncol. 2018;20(Suppl 6):vi18.
Nicolay B, Narayanaswamy R, Amatangelo MD, Aguado E, Nagaraja R, Murtie J, et al. EXTH-34. Combined use of the pan IDH mutant inhibitor AG-881 with radiation therapy shoes added benefit in an orthotopic IDH1 mutant glioma model in vivo. Neuro Oncol. 2017;19(Suppl 6):vi79.
Pusch S, Krausert S, Fischer V, Balss J, Ott M, Schrimpf D, et al. Pan-mutant IDH1 inhibitor BAY 1436032 for effective treatment of IDH1 mutant astrocytoma in vivo. Acta Neuropathol. 2017;133:629–44.
Nakagawa M, Nakatani F, Matsunaga H, Seki T, Endo M, Ogawara Y, et al. Selective inhibition of mutant IDH1 by DS-1001b ameliorates aberrant histone modifications and impairs tumor activity in chondrosarcoma. Oncogene. 2019;38:6835–49.
Natsume AWT, Miyakita Y, Narita Y, Mineharu Y, Arakawa Y, Yamasaki F, et al. Phase I study of a brain penetrant mutant IDH1 inhibitor DS-1001b in patients with recurrent or progressive IDH1 mutant gliomas. J Clin Oncol. 2019;15(Suppl):2004.
Lu Y, Kwintkiewicz J, Liu Y, Tech K, Frady LN, Su YT, et al. Chemosensitivity of IDH1-mutated gliomas due to an impairment in PARP1-mediated DNA repair. Cancer Res. 2017;77(7):1709–18.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
Markus D. Siegelin: NIH NINDS R01NS095848, R01NS102366, K08NS083732, Louis V. Gerstner Jr. Scholars Program (2017–2020) and American Brain Tumor Association Discovery Grant 2017 (DG1700013). Trang T. T. Nguyen: American Brain Tumor Association Basic Research Fellowship (BRF1900018).
Conflict of interest
Georg Karpel-Massler, Trang T. T. Nguyen, Enyuan Shang, and Markus D. Siegelin declare that they have no conflicts of interest that might be relevant to the contents of this manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karpel-Massler, G., Nguyen, T.T.T., Shang, E. et al. Novel IDH1-Targeted Glioma Therapies. CNS Drugs 33, 1155–1166 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40263-019-00684-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40263-019-00684-6