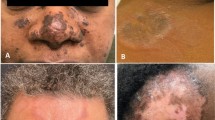
Abstract
Sarcoidosis is a chronic inflammatory disorder that has the potential to affect multiple organs, including the skin. Its cutaneous manifestations are varied and can provide clues to underlying systemic manifestations. Unfortunately, they also can be disfiguring. Therapy is usually directed at the organ system most severely affected, which often may help cutaneous disease. However, cutaneous disease may be recalcitrant to treatment directed at extracutaneous disease, or it may be severe enough to require targeted therapy. This article focuses on the dermatologist’s role in recognizing and diagnosing cutaneous sarcoidosis, evaluating patients for systemic disease involvement, and treating the skin manifestations of sarcoidosis.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
III Italian Conference on Sarcoidosis and Other Granulomatous Disorders. Padua, April 12–13, 1991. Proceedings and abstracts. Sarcoidosis. 1991;8(2):161–202.
Proceedings of the 1991 XIIth World Congress on Sarcoidosis. Kyoto, Japan, September 8–13, 1991. Sarcoidosis. 1992;9 Suppl 1:1–683.
Statement on sarcoidosis. Joint Statement of the American Thoracic Society (ATS), the European Respiratory Society (ERS) and the World Association of Sarcoidosis and Other Granulomatous Disorders (WASOG) adopted by the ATS Board of Directors and by the ERS Executive Committee, February 1999. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999;160(2):736–55.
Rybicki BA, Iannuzzi MC. Epidemiology of sarcoidosis: recent advances and future prospects. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2007;28(1):22–35.
Rybicki BA, Maliarik MJ, Major M, Popovich J Jr, Iannuzzi MC. Epidemiology, demographics, and genetics of sarcoidosis. Semin Respir Infect. 1998;13(3):166–73.
Rybicki BA, Major M, Popovich J Jr, Maliarik MJ, Iannuzzi MC. Racial differences in sarcoidosis incidence: a 5-year study in a health maintenance organization. Am J Epidemiol. 1997;145(3):234–41.
Morimoto T, Azuma A, Abe S, Usuki J, Kudoh S, Sugisaki K, et al. Epidemiology of sarcoidosis in Japan. Eur Respiratory J. 2008;31(2):372–9.
Haimovic A, Sanchez M, Judson MA, Prystowsky S. Sarcoidosis: a comprehensive review and update for the dermatologist: part I. Cutaneous disease. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;66(5):699 e1–18; quiz 717–8.
Noor A, Knox KS. Immunopathogenesis of sarcoidosis. Clin Dermatol. 2007;25(3):250–8.
Iannuzzi MC, Fontana JR. Sarcoidosis: clinical presentation, immunopathogenesis, and therapeutics. JAMA. 2011;305(4):391–9.
Iannuzzi MC, Rybicki BA, Teirstein AS. Sarcoidosis. New Engl J Med. 2007;357(21):2153–65.
Chen ES, Moller DR. Sarcoidosis—scientific progress and clinical challenges. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011;7(8):457–67.
Rossman MD, Thompson B, Frederick M, Iannuzzi MC, Rybicki BA, Pander JP, et al. HLA and environmental interactions in sarcoidosis. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2008;25(2):125–32.
Iannuzzi MC, Iyengar SK, Gray-McGuire C, Elston RC, Baughman RP, Donohue JF, et al. Genome-wide search for sarcoidosis susceptibility genes in African Americans. Genes Immun. 2005;6(6):509–18.
Hofmann S, Fischer A, Nothnagel M, Jacobs G, Schmid B, Wittig M, et al. Genome-wide association analysis reveals 12q13.3-q14.1 as new risk locus for sarcoidosis. Eur Respir J. 2013;41(4):888–900.
Spagnolo P, Schwartz DA. Genetic predisposition to sarcoidosis: another brick in the wall. Eur Respir J. 2013;41(4):778–80.
Franke A, Fischer A, Nothnagel M, Becker C, Grabe N, Till A, et al. Genome-wide association analysis in sarcoidosis and Crohn’s disease unravels a common susceptibility locus on 10p12.2. Gastroenterology. 2008;135(4):1207–15.
Newman KL, Newman LS. Occupational causes of sarcoidosis. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012;12(2):145–50.
Reich JM. Sarcoidosis and World Trade Center disaster. J Occup Environ Med. 2012;54(1):2; author reply -3.
Gupta D, Agarwal R, Aggarwal AN, Jindal SK. Molecular evidence for the role of mycobacteria in sarcoidosis: a meta-analysis. Eur Respir J. 2007;30(3):508–16.
Rutherford RM, Gilmartin JJ. Mycobacteria in pathogenesis of sarcoidosis. Chest. 2004;125(1):354.
Brownell I, Ramirez-Valle F, Sanchez M, Prystowsky S. Evidence for mycobacteria in sarcoidosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2011;45(5):899–905.
Oswald-Richter KA, Beachboard DC, Seeley EH, Abraham S, Shepherd BE, Jenkins CA, et al. Dual analysis for mycobacteria and propionibacteria in sarcoidosis BAL. J Clin Immunol. 2012;32(5):1129–40.
Furusawa H, Suzuki Y, Miyazaki Y, Inase N, Eishi Y. Th1 and Th17 immune responses to viable Propionibacterium acnes in patients with sarcoidosis. Respir Investig. 2012;50(3):104–9.
Chen ES, Song Z, Willett MH, Heine S, Yung RC, Liu MC, et al. Serum amyloid A regulates granulomatous inflammation in sarcoidosis through Toll-like receptor-2. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2010;181(4):360–73.
Parisinos CA. Sarcoidosis is a Th1/Th17 multisystem disorder: wider implications. Thorax. 2011;66(11):1011–2; author reply 1012.
Zissel G, Prasse A, Muller-Quernheim J. Sarcoidosis—immunopathogenetic concepts. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2007;28(1):3–14.
Zissel G, Prasse A, Muller-Quernheim J. Immunologic response of sarcoidosis. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2010;31(4):390–403.
Facco M, Cabrelle A, Teramo A, Olivieri V, Gnoato M, Teolato S, et al. Sarcoidosis is a Th1/Th17 multisystem disorder. Thorax. 2011;66(2):144–50.
Huang H, Lu Z, Jiang C, Liu J, Wang Y, Xu Z. Imbalance between Th17 and regulatory T-Cells in sarcoidosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2013;14(11):21463–73.
Ten Berge B, Paats MS, Bergen IM, van den Blink B, Hoogsteden HC, Lambrecht BN, et al. Increased IL-17A expression in granulomas and in circulating memory T cells in sarcoidosis. Rheumatology. 2012;51(1):37–46.
Urbankowski T, Hoser G, Domagala-Kulawik J. Th1/Th2/Th17 related cytokines in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of patients with sarcoidosis: association with smoking. Pol Arch Med Wewn. 2012;122(7–8):320–5.
Kim HS, Choi D, Lim LL, Allada G, Smith JR, Austin CR, et al. Association of interleukin 23 receptor gene with sarcoidosis. Dis Markers. 2011;31(1):17–24.
Schurmann M, Kwiatkowski R, Albrecht M, Fischer A, Hampe J, Muller-Quernheim J, et al. Study of Toll-like receptor gene loci in sarcoidosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 2008;152(3):423–31.
Veltkamp M, Van Moorsel CH, Rijkers GT, Ruven HJ, Van Den Bosch JM, Grutters JC. Toll-like receptor (TLR)-9 genetics and function in sarcoidosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 2010;162(1):68–74.
Richmond BW, Drake WP. Vitamin D innate immunity, and sarcoidosis granulomatous inflammation: insights from mycobacterial research. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2010;16(5):461–4.
Gazouli M, Koundourakis A, Ikonomopoulos J, Gialafos EJ, Rapti A, Gorgoulis VG, et al. CARD15/NOD2, CD14, and Toll-like receptor 4 gene polymorphisms in Greek patients with sarcoidosis. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2006;23(1):23–9.
Marinis JM, Homer CR, McDonald C, Abbott DW. A novel motif in the Crohn’s disease susceptibility protein, NOD2, allows TRAF4 to down-regulate innate immune responses. J Biol Chem. 2011;286(3):1938–50.
Culver DA, Newman LS, Kavuru MS. Gene-environment interactions in sarcoidosis: challenge and opportunity. Clin Dermatol. 2007;25(3):267–75.
Haimovic A, Sanchez M, Judson MA, Prystowsky S. Sarcoidosis: a comprehensive review and update for the dermatologist: part II. Extracutaneous disease. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;66(5):719 e1–10; quiz 729–30.
Baughman RP, Teirstein AS, Judson MA, Rossman MD, Yeager H Jr, Bresnitz EA, et al. Clinical characteristics of patients in a case control study of sarcoidosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001;164(10 Pt 1):1885–9.
Nozaki K, Judson MA. Neurosarcoidosis: clinical manifestations, diagnosis and treatment. Presse Med. 2012;41(6 Pt 2):e331–48.
Berliner AR, Haas M, Choi MJ. Sarcoidosis: the nephrologist’s perspective. Am J Kidney Dis. 2006;48(5):856–70.
Mantini N, Williams B Jr, Stewart J, Rubinsztain L, Kacharava A. Cardiac sarcoid: a clinician’s review on how to approach the patient with cardiac sarcoid. Clin Cardiol. 2012;35(7):410–5.
Kim JS, Judson MA, Donnino R, Gold M, Cooper LT Jr, Prystowsky EN, et al. Cardiac sarcoidosis. Am Heart J. 2009;157(1):9–21.
English JC 3rd, Patel PJ, Greer KE. Sarcoidosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001;44(5):725–43; quiz 744–6.
Newman LS, Rose CS, Maier LA. Sarcoidosis. New Engl J Med. 1997;336(17):1224–34.
Wilson NJ, King CM. Cutaneous sarcoidosis. Postgrad Med J. 1998;74(877):649–52.
Marchell RM, Judson MA. Cutaneous sarcoidosis. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2010;31(4):442–51.
Marchell RM, Judson MA. Chronic cutaneous lesions of sarcoidosis. Clin Dermatol. 2007;25(3):295–302.
Mana J, Marcoval J. Skin manifestations of sarcoidosis. Presse Med. 2012;41(6 Pt 2):e355–74.
Marcoval J, Mana J, Rubio M. Specific cutaneous lesions in patients with systemic sarcoidosis: relationship to severity and chronicity of disease. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2011;36(7):739–44.
Higgins EM, Salisbury JR, Du Vivier AW. Subcutaneous sarcoidosis. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1993;18(1):65–6.
Ahmed I, Harshad SR. Subcutaneous sarcoidosis: is it a specific subset of cutaneous sarcoidosis frequently associated with systemic disease? J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;54(1):55–60.
El Sayed F, Dhaybi R, Ammoury A. Subcutaneous nodular sarcoidosis and systemic involvement successfully treated with doxycycline. Leban Med J. 2006;54(1):42–4.
Marcoval J, Moreno A, Mana J, Peyri J. Subcutaneous sarcoidosis. Dermatol Clin. 2008;26(4):553–6, ix.
Dalle Vedove C, Colato C, Girolomoni G. Subcutaneous sarcoidosis: report of two cases and review of the literature. Clin Rheumatol. 2011;30(8):1123–8.
Meyer-Gonzalez T, Suarez-Perez JA, Lopez-Navarro N, Hidalgo A, Herrera-Ceballos E. Subcutaneous sarcoidosis: a predictor of systemic disease? Eur J Intern Med. 2011;22(6):e162–3.
Yanardag H, Pamuk ON, Pamuk GE. Lupus pernio in sarcoidosis: clinical features and treatment outcomes of 14 patients. J Clin Rheumatol. 2003;9(2):72–6.
Spiteri MA, Matthey F, Gordon T, Carstairs LS, James DG. Lupus pernio: a clinico-radiological study of thirty-five cases. Br J Dermatol. 1985;112(3):315–22.
Elgart ML. Cutaneous sarcoidosis: definitions and types of lesions. Clin Dermatol. 1986;4(4):35–45.
Elgart ML. Cutaneous lesions of sarcoidosis. Prim Care. 1978;5(2):249–62.
Efthimiou P, Kukar M. Lupus pernio: sarcoid-specific cutaneous manifestation associated with chronic sarcoid arthropathy. J Clin Rheumatol. 2011;17(6):343.
Neville E, Mills RG, Jash DK, Mackinnon DM, Carstairs LS, James DG. Sarcoidosis of the upper respiratory tract and its association with lupus pernio. Thorax. 1976;31(6):660–4.
James DG. Lupus pernio. Lupus. 1992;1(3):129–31.
Baughman RP, Judson MA, Teirstein A, Lower EE, Lo K, Schlenker-Herceg R, et al. Chronic facial sarcoidosis including lupus pernio: clinical description and proposed scoring systems. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2008;9(3):155–61.
Grema H, Greve B, Raulin C. Scar sarcoidosis—treatment with the Q-switched ruby laser. Lasers Surg Med. 2002;30(5):398–400.
Holzmann RD, Astner S, Forschner T, Sterry G. Scar sarcoidosis in a child: case report of successful treatment with the pulsed dye laser. Dermatol Surg. 2008;34(3):393–6.
House NS, Welsh JP, English JC 3rd. Sarcoidosis-induced alopecia. Dermatol Online J. 2012;18(8):4.
Douri T, Chawaf AZ, Alrefaee BA. Cicatricial alopecia due to sarcoidosis. Dermatol Online J. 2003;9(1):16.
Cho HR, Shah A, Hadi S. Systemic sarcoidosis presenting with alopecia of the scalp. Int J Dermatol. 2004;43(7):520–2.
Sakemi H, Oiwa H. Psoriasiform plaques of sarcoidosis. Internal Med. 2009;48(5):391.
Mittal RR, Singh SP, Gill SS. Psoriasiform sarcoidosis associated with depigmentation. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 1996;62(2):103–5.
Mitsuishi T, Nogita T, Kawashima M. Psoriasiform sarcoidosis with ulceration. Int J Dermatol. 1992;31(5):339–40.
Jun L, Jia-Wei L, Hong-Zhong J. Ulcerative sarcoidosis. Int J Dermatol. 2014;53(4):e315–6. doi:10.1111/ijd.12088 (Epub 2013 Oct 14).
Ichiki Y, Kitajima Y. Ulcerative sarcoidosis: case report and review of the Japanese literature. Acta Dermato-Venereol. 2008;88(5):526–8.
Hunt RD, Gonzalez ME, Robinson M, Meehan SA, Franks AG Jr. Ulcerative sarcoidosis. Dermatol Online J. 2012;18(12):29.
Zhang H, Ma HJ, Liu W, Yuan XY. Sarcoidosis characterized as acquired ichthyosiform erythroderma. Eur J Dermatol. 2009;19(5):516–7.
Vasaghi A, Kalafi A. Unusual manifestation of cutaneous sarcoidosis: a case report of morpheaform sarcoidosis. Acta Med Iran. 2012;50(9):648–51.
Kelley BP, George DE, LeLeux TM, Hsu S. Ichthyosiform sarcoidosis: a case report and review of the literature. Dermatol Online J. 2010;16(8):5.
Gangopadhyay AK. Ichthyosiform sarcoidosis. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2001;67(2):91–2.
Rampin L, Musto A, Marzola MC, Tadayyon S, Ferretti A, Chondrogiannis S, et al. Diagnosis of unknown sarcoidosis associated to erythema nodosum with 18F-FDG PET/CT. Revista Espanola de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Mol. 2013;32(3):190–2.
Ohta H, Tazawa R, Nakamura A, Kimura Y, Maemondo M, Kikuchi T, et al. Acute-onset sarcoidosis with erythema nodosum and polyarthralgia (Lofgren’s syndrome) in Japan: a case report and a review of the literature. Intern Med. 2006;45(9):659–62.
O’Connor TM, Cagney D, Jahangir A, Brady A, Fitzgibbon J, Lee G, et al. Characteristics of patients presenting with erythema nodosum and sarcoidosis. Ir Med J. 2009;102(6):181–4.
Donmez S, Kisacik B, Pamuk ON, Pehlivan Y, Aydogdu E, Yurekli OA, et al. Are clinical features in Lofgren’s syndrome-related erythema nodosum different from idiopathic erythema nodosum? Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2012;29(2):128–31.
Hillerdal G, Nou E, Osterman K, Schmekel B. Sarcoidosis: epidemiology and prognosis. A 15-year European study. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984;130(1):29–32.
Pietinalho A, Ohmichi M, Hiraga Y, Lofroos AB, Selroos O. The mode of presentation of sarcoidosis in Finland and Hokkaido, Japan. A comparative analysis of 571 Finnish and 686 Japanese patients. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 1996;13(2):159–66.
Judson MA. The diagnosis of sarcoidosis. Clin Chest Med. 2008;29(3):415–27, viii.
Ivemark BI. Observations on the histopathology of sarcoidosis. Acta Med Scand Suppl. 1956;312:438–42.
Takahashi M. Histopathology of sarcoidosis and its immunological bases. Acta Pathol Jpn. 1970;20(2):171–82.
Marcoval J, Mana J, Moreno A, Gallego I, Fortuno Y, Peyri J. Foreign bodies in granulomatous cutaneous lesions of patients with systemic sarcoidosis. Arch Dermatol. 2001;137(4):427–30.
Costabel U, Guzman J, Baughman RP. Systemic evaluation of a potential cutaneous sarcoidosis patient. Clin Dermatol. 2007;25(3):303–11.
Costabel U, Hunninghake GW. ATS/ERS/WASOG statement on sarcoidosis. Sarcoidosis Statement Committee. American Thoracic Society. European Respiratory Society. World Association for Sarcoidosis and Other Granulomatous Disorders. Eur Respir J. 1999;14(4):735–7.
Bodaghi B, Touitou V, Fardeau C, Chapelon C, LeHoang P. Ocular sarcoidosis. Presse Med. 2012;41(6 Pt 2):e349–54.
Rothova A. Ocular involvement in sarcoidosis. Br J Ophthalmol. 2000;84(1):110–6.
Dubrey SW, Falk RH. Diagnosis and management of cardiac sarcoidosis. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2010;52(4):336–46.
Chapelon-Abric C. Cardiac sarcoidosis. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2013;19(5):493–502.
Martusewicz-Boros MM, Piotrowska-Kownacka D, Domagala J, Kowalewski M, Wiatr E. Cardiac sarcoidosis mimicking ischaemic infarct. Kardiol Pol. 2014;72(1):86.
Nakamura S, Hashimoto Y, Nishi K, Takeda K, Mizumoto T, Demitsu T, et al. High rate of cardiac sarcoidosis presenting with cutaneous plaque type sarcoidosis in 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography-computed tomography: a case series. J Med Case Rep. 2014;8(1):17.
Rosenbach M. Practice gaps. The dermatologist’s role in sarcoidosis. JAMA Dermatol. 2013;149(6):760–1.
Anolik RB, Schaffer A, Kim EJ, Rosenbach M. Thyroid dysfunction and cutaneous sarcoidosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;66(1):167–8.
Sage RJ, Rao DS, Burke RR, Lim HW. Preventing vitamin D toxicity in patients with sarcoidosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64(4):795–6.
Gupta D, Kumar S, Aggarwal AN, Verma I, Agarwal R. Interferon gamma release assay (QuantiFERON-TB Gold In Tube) in patients of sarcoidosis from a population with high prevalence of tuberculosis infection. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2011;28(2):95–101.
Studdy PR, Bird R. Serum angiotensin converting enzyme in sarcoidosis—its value in present clinical practice. Ann Clin Biochem. 1989;26(Pt 1):13–8.
Cox CE, Donohue JF, Brown CD, Kataria YP, Judson MA. The Sarcoidosis Health Questionnaire: a new measure of health-related quality of life. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2003;168(3):323–9.
Victorson DE, Choi S, Judson MA, Cella D. Development and testing of item response theory-based item banks and short forms for eye, skin and lung problems in sarcoidosis. Qual Life Res. 2014;23(4):1301–13. doi:10.1007/s11136-013-0567-6 (Epub 2013 Nov 9).
Rosenbach M, Yeung H, Chu EY, Kim EJ, Payne AS, Takeshita J, et al. Reliability and convergent validity of the cutaneous sarcoidosis activity and morphology instrument for assessing cutaneous sarcoidosis. JAMA Dermatol. 2013;149(5):550–6.
Khatri KA, Chotzen VA, Burrall BA. Lupus pernio: successful treatment with a potent topical corticosteroid. Arch Dermatol. 1995;131(5):617–8.
Wise RD. Clinical resolution of facial cutaneous sarcoidosis with systemic colchicine and a topical corticosteroid ointment. Compr Ther. 2008 Summer;34(2):105–10.
Volden G. Successful treatment of chronic skin diseases with clobetasol propionate and a hydrocolloid occlusive dressing. Acta Dermato-Venereol. 1992;72(1):69–71.
Bersani TA, Nichols CW. Intralesional triamcinolone for cutaneous palpebral sarcoidosis. Am J Ophthalmol. 1985;99(5):561–2.
Callen JP. Intralesional corticosteroids. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1981;4(2):149–51.
Singh SK, Singh S, Pandey SS. Cutaneous sarcoidosis without systemic involvement: response to intralesional corticosteroid. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 1996;62(4):273–4.
Green CM. Topical tacrolimus for the treatment of cutaneous sarcoidosis. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2007;32(4):457–8.
Gutzmer R, Volker B, Kapp A, Werfel T. [Successful topical treatment of cutaneous sarcoidosis with tacrolimus]. Hautarzt. 2003;54(12):1193–7.
Katoh N, Mihara H, Yasuno H. Cutaneous sarcoidosis successfully treated with topical tacrolimus. Br J Dermatol. 2002;147(1):154–6.
Vano-Galvan S, Fernandez-Guarino M, Carmona LP, Harto A, Carrillo R, Jaen P. Lichenoid type of cutaneous sarcoidosis: great response to topical tacrolimus. Eur J Dermatol. 2008;18(1):89–90.
Hasegawa T, Suga Y, Mizuno Y, Haruna K, Ikeda S. Photodynamic therapy using intense pulsed light for cutaneous sarcoidosis. J Dermatol. 2012;39(6):564–5.
Penrose C, Mercer SE, Shim-Chang H. Photodynamic therapy for the treatment of cutaneous sarcoidosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65(1):e12–4.
Karrer S, Abels C, Wimmershoff MB, Landthaler M, Szeimies RM. Successful treatment of cutaneous sarcoidosis using topical photodynamic therapy. Arch Dermatol. 2002;138(5):581–4.
Wilsmann-Theis D, Bieber T, Novak N. Photodynamic therapy as an alternative treatment for cutaneous sarcoidosis. Dermatology. 2008;217(4):343–6.
Kondo C, Watanabe D, Nakaseko H, Morishita M, Tsuboi T, Tamada Y, et al. Photodynamic therapy for recurrent sarcoid flexor tenosynovitis of the finger. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;55(5 Suppl):S99–101.
Green JJ, Lawrence N, Heymann WR. Generalized ulcerative sarcoidosis induced by therapy with the flashlamp-pumped pulsed dye laser. Arch Dermatol. 2001;137(4):507–8.
Roos S, Raulin C, Ockenfels HM, Karsai S. Successful treatment of cutaneous sarcoidosis lesions with the flashlamp pumped pulsed dye laser: a case report. Dermatol Surg. 2009;35(7):1139–40.
Frederiksen LG, Jorgensen K. Sarcoidosis of the nose treated with laser surgery. Rhinology. 1996;34(4):245–6.
Hocar O, Faye O, Wolkenstein P, Goldzal S, Revuz J, Cosnes A. Cutaneous sarcoidosis: efficacy of KTP laser. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2007;134(2):174–5.
James JC, Simpson CB. Treatment of laryngeal sarcoidosis with CO2 laser and mitomycin-C. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2004;130(2):262–4.
Ruff T, Bellens EE. Sarcoidosis of the larynx treated with CO2 laser. J Otolaryngol. 1985;14(4):245–7.
Gleeson CM, Morar N, Staveley I, Bunker CB. Treatment of cutaneous sarcoid with topical gel psoralen and ultraviolet A. Br J Dermatol. 2011;164(4):892–4.
Graefe T, Konrad H, Barta U, Wollina U, Elsner P. Successful ultraviolet al treatment of cutaneous sarcoidosis. Br J Dermatol. 2001;145(2):354–5.
Mahnke N, Medve-Koenigs K, Berneburg M, Ruzicka T, Neumann NJ. Cutaneous sarcoidosis treated with medium-dose UVA1. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50(6):978–9.
Jones E, Callen JP. Hydroxychloroquine is effective therapy for control of cutaneous sarcoidal granulomas. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1990;23(3 Pt 1):487–9.
Marchetti M, Baker MG, Noland MM. Treatment of subcutaneous sarcoidosis with hydroxychloroquine: report of 2 cases. Dermatol Online J. 2014;20(1):21250.
Meyersburg D, Schon MP, Bertsch HP, Seitz CS. Uncommon cutaneous ulcerative and systemic sarcoidosis. Successful treatment with hydroxychloroquine and compression therapy. Hautarzt. 2011;62(9):691–5.
Modi S, Rosen T. Micropapular cutaneous sarcoidosis: case series successfully managed with hydroxychloroquine sulfate. Cutis Cutan Med Pract. 2008;81(4):351–4.
Siltzbach LE, Teirstein AS. Chloroquine therapy in 43 patients with intrathoracic and cutaneous sarcoidosis. Acta Med Scand Suppl. 1964;425:302–8.
Zic JA, Horowitz DH, Arzubiaga C, King LE Jr. Treatment of cutaneous sarcoidosis with chloroquine. Review of the literature. Arch Dermatol. 1991;127(7):1034–40.
Badgwell C, Rosen T. Cutaneous sarcoidosis therapy updated. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;56(1):69–83.
Bachelez H, Senet P, Cadranel J, Kaoukhov A, Dubertret L. The use of tetracyclines for the treatment of sarcoidosis. Arch Dermatol. 2001;137(1):69–73.
Miyazaki E, Ando M, Fukami T, Nureki S, Eishi Y, Kumamoto T. Minocycline for the treatment of sarcoidosis: is the mechanism of action immunomodulating or antimicrobial effect? Clin Rheumatol. 2008;27(9):1195–7.
Schmitt CE, Fabi SG, Kukreja T, Feinberg JS. Hypopigmented cutaneous sarcoidosis responsive to minocycline. J Drugs Dermatol. 2012;11(3):385–9.
Steen T, English JC. Oral minocycline in treatment of cutaneous sarcoidosis. JAMA Dermatol. 2013;149(6):758–60.
Kircik LH. Doxycycline and minocycline for the management of acne: a review of efficacy and safety with emphasis on clinical implications. J Drugs Dermatol. 2010;9(11):1407–11.
Park MK, Fontana JR, Babaali H, Gilbert-McClain LI, Stylianou M, Joo J, et al. Steroid-sparing effects of pentoxifylline in pulmonary sarcoidosis. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2009;26(2):121–31.
Zabel P, Entzian P, Dalhoff K, Schlaak M. Pentoxifylline in treatment of sarcoidosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1997;155(5):1665–9.
Baughman RP, Judson MA, Ingledue R, Craft NL, Lower EE. Efficacy and safety of apremilast in chronic cutaneous sarcoidosis. Arch Dermatol. 2012;148(2):262–4.
Veien NK. Cutaneous sarcoidosis: prognosis and treatment. Clin Dermatol. 1986;4(4):75–87.
Baughman RP, Lower EE. Evidence-based therapy for cutaneous sarcoidosis. Clin Dermatol. 2007;25(3):334–40.
Baughman RP, Nunes H. Therapy for sarcoidosis: evidence-based recommendations. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2012;8(1):95–103.
Doherty CB, Rosen T. Evidence-based therapy for cutaneous sarcoidosis. Drugs. 2008;68(10):1361–83.
Mosam A, Morar N. Recalcitrant cutaneous sarcoidosis: an evidence-based sequential approach. J Dermatol Treat. 2004;15(6):353–9.
Veien NK, Brodthagen H. Cutaneous sarcoidosis treated with methotrexate. Br J Dermatol. 1977;97(2):213–6.
Kouba DJ, Mimouni D, Rencic A, Nousari HC. Mycophenolate mofetil may serve as a steroid-sparing agent for sarcoidosis. Br J Dermatol. 2003;148(1):147–8.
Muller-Quernheim J, Kienast K, Held M, Pfeifer S, Costabel U. Treatment of chronic sarcoidosis with an azathioprine/prednisolone regimen. Eur Respir J. 1999;14(5):1117–22.
Vorselaars AD, Wuyts WA, Vorselaars VM, Zanen P, Deneer VH, Veltkamp M, et al. Methotrexate vs azathioprine in second-line therapy of sarcoidosis. Chest. 2013;144(3):805–12.
Carlesimo M, Giustini S, Rossi A, Bonaccorsi P, Calvieri S. Treatment of cutaneous and pulmonary sarcoidosis with thalidomide. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1995;32(5 Pt 2):866–9.
Hoch O, Muller S, Buttner G, Mensing H. [Thalidomide in the treatment of cutaneous and systemic sarcoidosis]. Hautarzt. 2001;52(10 Pt 2):962–5.
Lee JB, Koblenzer PS. Disfiguring cutaneous manifestation of sarcoidosis treated with thalidomide: a case report. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1998;39(5 Pt 2):835–8.
Nguyen YT, Dupuy A, Cordoliani F, Vignon-Pennamen MD, Lebbe C, Morel P, et al. Treatment of cutaneous sarcoidosis with thalidomide. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50(2):235–41.
Rousseau L, Beylot-Barry M, Doutre MS, Beylot C. Cutaneous sarcoidosis successfully treated with low doses of thalidomide. Arch Dermatol. 1998;134(8):1045–6.
Baughman RP, Lower EE. Newer therapies for cutaneous sarcoidosis: the role of thalidomide and other agents. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2004;5(6):385–94.
Fazzi P, Manni E, Cristofani R, Cei G, Piazza S, Calabrese R, et al. Thalidomide for improving cutaneous and pulmonary sarcoidosis in patients resistant or with contraindications to corticosteroids. Biomed Pharmacother. 2012;66(4):300–7.
Oliver SJ, Kikuchi T, Krueger JG, Kaplan G. Thalidomide induces granuloma differentiation in sarcoid skin lesions associated with disease improvement. Clin Immunol. 2002;102(3):225–36.
Dalm VA, van Hagen PM. Efficacy of lenalidomide in refractory lupus pernio. JAMA Dermatol. 2013;149(4):493–4.
Burns AM, Green PJ, Pasternak S. Etanercept-induced cutaneous and pulmonary sarcoid-like granulomas resolving with adalimumab. J Cutan Pathol. 2012;39(2):289–93.
Field S, Regan AO, Sheahan K, Collins P. Recalcitrant cutaneous sarcoidosis responding to adalimumab but not to etanercept. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2010;35(7):795–6.
Heffernan MP, Smith DI. Adalimumab for treatment of cutaneous sarcoidosis. Arch Dermatol. 2006;142(1):17–9.
Pariser RJ, Paul J, Hirano S, Torosky C, Smith M. A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial of adalimumab in the treatment of cutaneous sarcoidosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;68(5):765–73.
Philips MA, Lynch J, Azmi FH. Ulcerative cutaneous sarcoidosis responding to adalimumab. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;53(5):917.
Fok KC, Ng WW, Henderson CJ, Connor SJ. Cutaneous sarcoidosis in a patient with ulcerative colitis on infliximab. J Crohns Colitis. 2012;6(6):708–12.
Heffernan MP, Anadkat MJ. Recalcitrant cutaneous sarcoidosis responding to infliximab. Arch Dermatol. 2005;141(7):910–1.
Meyerle JH, Shorr A. The use of infliximab in cutaneous sarcoidosis. J Drugs Dermatol. 2003;2(4):413–4.
Rosen T, Doherty C. Successful long-term management of refractory cutaneous and upper airway sarcoidosis with periodic infliximab infusion. Dermatol Online J. 2007;13(3):14.
Sene T, Juillard C, Rybojad M, Cordoliani F, Lebbe C, Morel P, et al. Infliximab as a steroid-sparing agent in refractory cutaneous sarcoidosis: single-center retrospective study of 9 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;66(2):328–32.
Tu J, Chan J. Cutaneous sarcoidosis and infliximab: evidence for efficacy in refractory disease. Aust J Dermatol. 2013. doi:10.1111/ajd.12056 (Epub ahead of print).
Tuchinda P, Bremmer M, Gaspari AA. A case series of refractory cutaneous sarcoidosis successfully treated with infliximab. Dermatol Ther. 2012;2(1):11.
Wanat KA, Rosenbach M. Case series demonstrating improvement in chronic cutaneous sarcoidosis following treatment with TNF inhibitors. Arch Dermatol. 2012;148(9):1097–100.
Utz JP, Limper AH, Kalra S, Specks U, Scott JP, Vuk-Pavlovic Z, et al. Etanercept for the treatment of stage II and III progressive pulmonary sarcoidosis. Chest. 2003;124(1):177–85.
Stagaki E, Mountford WK, Lackland DT, Judson MA. The treatment of lupus pernio: results of 116 treatment courses in 54 patients. Chest. 2009;135(2):468–76.
Thielen AM, Barde C, Saurat JH, Laffitte E. Refractory chronic cutaneous sarcoidosis responsive to dose escalation of TNF-alpha antagonists. Dermatology. 2009;219(1):59–62.
Fraser SJ, Hill AT, McKay DA, Reid WA, Mathers ME, MacDougall G, et al. Cutaneous tuberculosis revealed by infliximab therapy for presumed sarcoidosis. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2010;35(4):e141–2.
Dhaille F, Viseux V, Caudron A, Dadban A, Tribout C, Boumier P, et al. Cutaneous sarcoidosis occurring during anti-TNF-alpha treatment: report of two cases. Dermatology. 2010;220(3):234–7.
Santos G, Sousa LE, Joao AM. Exacerbation of recalcitrant cutaneous sarcoidosis with adalimumab—a paradoxical effect? A case report. An Bras Dermatol. 2013;88(6 Suppl 1):26–8.
Georgiou S, Monastirli A, Pasmatzi E, Tsambaos D. Cutaneous sarcoidosis: complete remission after oral isotretinoin therapy. Acta Dermato-Venereol. 1998;78(6):457–9.
Pignone AM, Rosso AD, Fiori G, Matucci-Cerinic M, Becucci A, Tempestini A, et al. Melatonin is a safe and effective treatment for chronic pulmonary and extrapulmonary sarcoidosis. J Pineal Res. 2006;41(2):95–100.
York EL, Kovithavongs T, Man SF, Rebuck AS, Sproule BJ. Cyclosporine and chronic sarcoidosis. Chest. 1990;98(4):1026–9.
Sahoo DH, Bandyopadhyay D, Xu M, Pearson K, Parambil JG, Lazar CA, et al. Effectiveness and safety of leflunomide for pulmonary and extrapulmonary sarcoidosis. Eur Respir J. 2011;38(5):1145–50.
Acknowledgments
Dr. Rosenbach is supported by a Medical Dermatology Career Development Award through the Dermatology Foundation and has also served as an investigator for a Johnson & Johnson/Centocor clinical trial comparing ustekinumab, golimumab, and placebo. Dr. Wanat has no conflicts of interest that are directly relevant to the content of this review.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wanat, K.A., Rosenbach, M. A Practical Approach to Cutaneous Sarcoidosis. Am J Clin Dermatol 15, 283–297 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40257-014-0079-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40257-014-0079-3