Abstract
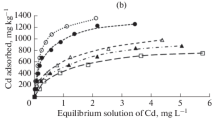
The thermodynamic characteristics of heavy metals adsorbed onto urban soil and the relative adsorption mechanisms were studied by the batch experiment. The results show that there existed dynamic adsorption-desorption equilibrium processes of cationic and anionic ions of heavy metals onto urban soil, which may have an impact on the pH of the adsorption system. The amounts of heavy metals adsorbed onto urban soil increased with the increase of the equilibrium concentration, but their adsorption amounts were not the maximum adsorption amounts. The higher the pH was, the greater the adsorption capacity of the urban soil at the same equilibrium concentration was, and the adsorption amounts of heavy metals onto urban soil followed the order of Pb>Cu>Cd>Zn>Ni. There were coordination reaction, hydrolysis reaction, exchange reaction in the adsorption processes of heavy metals onto urban soil. With the increase of pH, the influencing degree of pH on the different reactions of heavy metals in the soil increased, meanwhile the effects of other physicochemical properties of soil on the adsorption of heavy metals were weakened.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bockheim J. G., Nature and Properties of Highly-disturbed Urban Soil, Annual Meeting of the Soil Society of America, Chicago, 1974
Zhang G. L., Zhu Y. G., Fu B. J., Acta Ecologica. Sinica, 2003, 2(3), 539
Zhang J. E., Xu Q., Soil, 1997, 4, 189
Zhang G. L., Zhao Y. G., Yang J. L., Zhao W. J., Gong Z. T., Acta Pedologica. Sinica, 2007, 44(5), 925
Díaz R. O., Hernández M. M., Echeverrá C. F., Arado L. J. O., Bul. Environ. Contam. Tox., 2011, 87(4), 414
Zhang J. M., Chi F. Q., Su Q. R., Kuang E. J., Journal of Northeast Agricultural University, 2010, 41(7), 56
Khan S., Khan M. A., Rehman S., Pedosphere, 2011, 21(3), 351
Luo X. S., Yu S., Li, X. D., Environ. Pollut., 2011, 159(5), 1317
Iqbal J., Shah M. H., J. Hazard. Mater., 2011, 192(2), 887
Wang Y. Y., Qian Y., Zhu J. W., Wang L., Journal of Anhui Agricultural Science, 2008, 36(11), 4680
Nanjing Soil Research Institute of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Soil Physical and Chemical Analysis, Shanghai Science and Technology Press, Shanghai, 1983
Hua X. Y., Dong D. M., Jiang X., Hu J. R., Guo Z. Y., Liang D. P., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(9), 2005
Liu X. L., Zhang S. Z., Wu W. Y., Liu H. L., J. Hazard. Mater., 2007, 149(2), 399
Ottosen L. M., Hansen H. K., Jensen P. E., Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 2009, 201(l), 295
Malandrino M., Abollino O., Giaeomino A., Aeeto M., J. Colloid. Interf. Sci., 2006, 299(2), 537
Mustafa G., Singh B., Kookana R. S., Chemosphere, 2004, 57(10), 1325
Karathanasis A. D., Pils J., Soil and Sediment Contamination, 2005, 14(4), 293
Guo P. R., Wang C., Fang J., Mou D. H., Qiu R. L., Wang Z. H., J. Insturn. Anal, 2009, 28(12), 1384
Brümmer G. W., Ed.: Bernhard M., Brinckman F. E., Sadler P. J., The Importance of Chemical Speciation in Environmental Processes, Springer-verlag, Berlin, 1986, 169
Stumm W., Morgan J. J., Aquatic Chemistry, John Wiley & Son. Inc., New York, 1981, 789
Temminghoff E. J. M., vander Zee S. E. A. T. M., de Haan F. A. M., Eur. J. Soil. Sci., 1995, 46, 649
Anderson M. A., Morel M. M., Limnol. Oceanogr., 1982, 27, 789
Tiller K. G., Gerth J., Brummer G., Geoderma, 1984, 34, 17
He H. P., Guo J. G., Xie X. D., Pen J. L., Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 1999, 19(2), 231
Xiong L. M., Research of Environmental Science., 1994, 7(1), 35
Xu M. G., Soil and Fertilizer, 1997, 5, 3
Santillan-Medrano M. J., Jurina J. J., Soil. Sci. Soc. Am. Pro, 1975, 39, 851
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China(No.40971248).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Ym., Kang, Cl., Chen, Ww. et al. Thermodynamic characteristics and mechanisms of heavy metals adsorbed onto urban soil. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 29, 42–47 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40242-013-2200-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40242-013-2200-1