Abstract
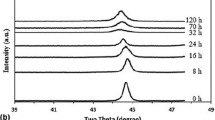
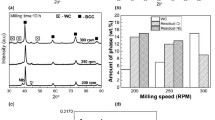
This paper systematically reports the thermodynamic characteristic and phase evolution of immiscible Cr–Mo binary alloy during mechanical alloying (MA) process. The Cr–35Mo (in at%) powder mixture was milled at 243 and 258 K, respectively, for different time. For comparative study, Cr–15Mo and Cr–62Mo powder mixtures were milled at 243 K for 18 h. Solid solution Cr(Mo) with body-centered cubic (bcc) crystal structure and amorphous Cr(Mo) alloy was obtained during MA process caused by high-energy ball milling. Based on the Miedema’s model, the free-energy change for forming either a solid solution or an amorphous in Cr–Mo alloy system is positive but small at a temperature range between 200 and 300 K. The thermodynamical barrier for forming alloy in Cr–Mo system can be overcome when MA occurs at 243 K, and the supersaturated solid solution crystal nuclei with bcc structure form continually, and three supersaturated solid solutions of Cr–62Mo, Cr–35Mo and Cr–15Mo formed. Milling the Cr–35Mo powder mixture at 258 K, the solid solution Cr(Mo) forms firstly, and then the solid solution Cr(Mo) transforms into the amorphous Cr(Mo) alloy with a few of nanocrystallines when milling is prolonged. At higher milling temperature, it is favorable for the formation of the amorphous phase, as indicated by the thermodynamical calculation for immiscible Cr–Mo alloy system.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Fhilip, P.E. Schweitzer, Metallic Materials: Physical, Mechanical, and Corrosion Properties (Marcel Dekker, New York, 2003), pp. 537–571
S. Sheibani, S. Heshmati-Manesh, A. Ataie, J. Alloys Compd. 495, 59 (1994)
E. Botcharova, J. Freudenberger, L. Schultz, J. Alloys Compd. 365, 157 (2004)
C. Suryanarayana, E. Ivanov, V.V. Boldyrev, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 304, 151 (2001)
W.D. Callister, D.G. Rethwisch, Materials Science and Engineering: An Introduction (Wiley, New York, 2007), pp. 332–380
S.Q. Xi, K.S. Zuo, X.G. Li, G. Ran, J.E. Zhou, Acta Mater. 56, 6050 (2008)
V.P. de Martínez, C. Aguilar, J. Marín, S. Ordoñez, F. Castro, Mater. Lett. 61, 929 (2007)
C. Aguilar, F. Castro, V. Martínez, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 548, 189 (2012)
C. Aguilar, D. Guzmán, F. Castro, V. Martínez, F. Cuevas de las, S. Lascano, T. Muthiah, Mater. Chem. Phys. 146, 493 (2014)
C. Suryanarayana, Prog. Mater. Sci. 46, 1 (2001)
E. Ma, Prog. Mater. Sci. 50, 413 (2005)
E. Ma, M. Atzmon, Mater. Chem. Phys. 39, 249 (1995)
C. Suryanarayana, Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 18, 203 (2008)
A.R. Miedema, P.F. De Chatel, F.R. De Boer, Phys. B, C 100, 1 (1980)
A.K. Niessen, A.R. Miedema, F.R. De Boer, Alloy. Cobalt 151, 401 (1988)
E.A. Brands, Smithells Metals Reference Book, 6th edn. (Butterworths, London, 1983), pp. 15.1–15.3
G. Veltel, B. Scholz, H.D. Kunze, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 134, 1410 (1991)
E. Ma, J.H. He, P.J. Schilling, Phys. Rev. B 55, 5542 (1997)
C. Aguilar, V.P. Martinez, J.M. Palacios, Scr. Mater. 57, 213 (2007)
M.M. Woolfson, An Introduction to X-Ray Crystallography (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1979), pp. 67–75
R.A. Donald, P.P. Pradeep, D.K. Bhattacharya, Essentials of Materials Science and Engineering (Thomson, London, 2004), pp. 46–75
C. Suryanarayana, M. Norton, X-ray Diffraction: A Practical Approach (Springer, New York, 1998), pp. 153–165
G.V. Raynor, Trans. Faraday Soc. 45, 698 (1949)
F. Wu, P. Bellon, A.J. Melmed, Acta Mater. 49, 453 (2001)
H.F. Rizzo, T.B. Massalski, M. Nastasi, Metall. Trans. A 24, 1027 (1993)
A. Bachmaier, M. Kerber, D. Setman, R. Pippan, Acta Mater. 60, 860 (2012)
H. Bai, C. Michaelsen, C. Gente, R. Bormann, Phys. Rev. B 63, 811 (2001)
G. Liang, R. Schulz, J. Mater. Sci. 38, 1179 (2003)
Q.W. Guo, G.S. Wang, G.C. Guo, Common Non-ferrous Metal Binary Phase Atlas (Chemical Industry Press, Beijing, 2010), pp. 248–249. (in Chinese)
C. Suryanarayana, A.A. Nasser, Prog. Mater. Sci. 58, 383 (2013)
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support of National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51271143 and 51302247). The transmission electron microscopy work was performed at the State Key Laboratory for Mechanical Behavior of Material at the Xi’an Jiaotong University. The authors are grateful to Jinyu Zhang (Associate Professor) for his generous support. And, the authors wish to thank Ruihua Zhu and Shengwu Guo from this Laboratory for their kindly assistance in sample preparation and transmission electron microscopy analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Available online at http://link.springer.com/journal/40195
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, CF., Xi, SQ., Zhang, Y. et al. Thermodynamic Characteristic and Phase Evolution in Immiscible Cr–Mo Binary Alloys. Acta Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett.) 28, 1074–1081 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40195-015-0297-6
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40195-015-0297-6