Abstract
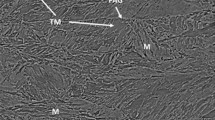
The effect of electron beam welding parameters on microstructure and ductile-to-brittle transition temperature (DBTT) of a boron-added modified 9Cr-1Mo steel weld is presented in this paper. Compared to the base metal, for the weld, the upper shelf energy is lower and the DBTT is significantly lower. While the influence of welding parameters on the upper shelf energy of the weld is insignificant, its influence on the transition region and the lower shelf region is quite significant due to the presence of delta-ferrite in the weld. High welding speed reduces the time available for transformation of delta-ferrite to austenite and results in retention of delta-ferrite in weld. Lower welding speed promotes completion of delta-ferrite to austenite transformation as cooling rate reduces which improves lower shelf energy.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Klueh RL and Harries DR (2001) High-chromium ferritic and martensitic steels for nuclear applications, American Society for Testing and Materials, West Conshohocken, Pa, USA
Ennis PJ, Czyrska-Filemonowicz A (2003) Recent advances in creep-resistant steels for power plant applications. Sadhana 28:709–730
Das CR, Albert SK, Swaminathan J, Raju S, Bhaduri AK, Murty BS (2012) Transition of crack from type IV to type II resulting from improved utilisation of boron in the modified 9Cr-1Mo steel weldment. Metall Mater Trans 43A:3724–3741
Abe F, Tabuchi M, Kondo M, Tsukamoto S (2007) Suppression of type IV fracture and improvement of creep strength of 9Cr steel welded joints by boron addition. Int J Press Vessel Pip 84:44–52
Mayr P (2007) Evolution of microstructure and mechanical properties of the heat affected zone in B-containing 9 % chromium steels. Ph. D. Thesis, University of Graz, Austria
Krishnamraju P (2014) Influence of weld chemistry and post weld heat treatment on micro structure and mechanical properties of P91 weld steels, M.Tech. Thesis, National Institute of Technology, Tiruchirapalli, India
Klueh RL (2008) Reduced-activation steels: future development for improved creep strength. J Nucl Mater 378:159–166
Yamada K, Igarashi M, Muneki S, Abe F (2002) Effect of heat treatment on precipitation kinetics in high-Cr ferritic steels. ISIJ Int 42:779–784
Onoro J (2006) J Mater Process Technol 180:137–142
Patriarca P et al. (1976) Nucl Technol 28:516–536
Divya M, Das CR, Mahadevan S, Albert SK, Pandian P, Kar SK, Bhaduri AK, Jayakumar T (2015) Metall Mater Trans 46A:2554–2567
Acknowledgments
The support of Mrs. N. Sreevidya for SEM studies is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Recommended for publication by Commission IX - Behaviour of Metals Subjected to Welding
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Das, C.R., Bhaduri, A.K., Raju, S. et al. Influence of electron beam welding parameters on microstructure and Charpy impact properties of boron-added modified 9Cr-1Mo steel weld. Weld World 60, 1141–1146 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40194-016-0369-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40194-016-0369-x