Abstract
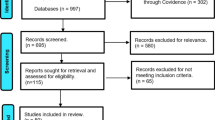
Due to the increasing volume and variety of data on the Internet as well as in organizations, the role of data has changed from a passive entity to an active asset. Data are considered as a novel source of revenue, and the process of creating wealth from it is called “data monetization.” Data monetization is used for realizing a type of competitive capability for organizations. It provides organizations with flexibility for using information assets in response to customer expectations and environmental pressures. The present study, hence, is aimed to clarify the configuration of data monetization by conducting a systematic review. The thematic analysis based on inductive approach was used to construct the configuration. The global themes, namely “monetization layer,” “data refinement process layer,” “base layer,” and “accessing and processing restrictions layer” with their related themes as the subset components were obtained. Each of these global themes represents the constructive layers which play an important role in data monetization mechanism. All extracted themes were synthesized as a configurational model called “data monetization configuration” (DaMoC). This proposed configuration is validated by a real application, i.e., Cardlytics.











Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
There are a lots of websites selling satellite imagery such as http://www.landinfo.comt, https://apollomapping.com/buy-imagery, https://geocento.com/imagery-pricing-plans/, so on.
https://www.linkedin.com/company/cardlytics [Accessed 25 July 2019].
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TBxysWjMfZg [Accessed 25 July 2019].
References
Agarwal, V., Mittal, S., Mukherjea, S., & Dalal, P. (2012). Exploiting rich telecom data for increased monetization of telecom application stores. In Proceedings - 2012 IEEE 13th international conference on mobile data management, MDM 2012 (pp. 63–68). https://doi.org/10.1109/mdm.2012.28.
Akred, J., & Samani, A. (2018). Your data is worth more than you think. MIT sloan Management Review. [Online]. Available at https://sloanreview.mit.edu/article/your-data-is-worth-more-than-you-think/. Retrieved December 17, 2018.
Attride-Stirling, J. (2001). Thematic networks: An analytic tool for qualitative research. Qualitative Research,1(3), 385–405.
Bergström, F. (2018). Data is the new gold. [Online]. Available at https://www.tieto.com/insights-and-opinions/data-is-the-new-gold. Retrieved December 17, 2018.
Birasnav, M., Mittal, R., & Loughlin, S. (2015). Linking leadership behaviors and information exchange to improve supply chain performance: A conceptual model. Global Journal of Flexible Systems Management,16(2), 205–217.
Bram, J. T., Warwick-Clark, B., Obeysekare, E., & Mehta, K. (2015). Utilization and monetization of healthcare data in developing countries. Big Data,3(2), 59–66.
Braun, V., & Clarke, V. (2006). Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qualitative Research in Psychology,3(2), 77–101.
Braun, V., Clarke, V., Hayfield, N., & Terry, G. (2018). Thematic analysis. Handbook of research methods in health social sciences (pp. 1–18). Singapore: Springer.
Buff, A., Wixom, B. H., & Tallon, P. (2015). Foundation for data monetization. MIT Center for Information Systems Research, 1–16. Retrieved December 17, 2018 from https://cisr.mit.edu/blog/documents/2015/08/17/mit_cisrwp402_foundationsfordatamonetization_buffwixomtallon-pdf/.
Chen, H., Chiang, R. H. L., & Storey, V. C. (2012). Business intelligence and analytics: From big data to big impact. MIS Quarterly,36(4), 1165–1188.
Chowdary, B. V., & Muthineni, S. (2012). Selection of a flexible machining centre through a knowledge based expert system. Global Journal of Flexible Systems Management,13(1), 3–10.
Demirkan, H., & Delen, D. (2013). Leveraging the capabilities of service-oriented decision support systems: Putting analytics and big data in cloud. Decision Support Systems,55(1), 412–421.
European Parliament & Council. (2016). The general data protection regulation. [Online]. Available at https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32018R1725&from=EN. Retrieved December 17, 2018.
Franzetti, A. (2017). Data monetization in the big data era: Evidence from the Italian market. Italy: Polytechnic University of Milan.
Fred, J. (2017). Data monetization-how an organization can generate revenue with data. Finland: Tampere University of Technology.
Gartner. (2018). Data monetization - gartner IT glossary. [Online]. Available at https://www.gartner.com/it-glossary/data-monetization. Retrieved December 17, 2018.
Grant, M. J., & Booth, A. (2009). A typology of reviews: An analysis of 14 review types and associated methodologies. Health Information & Libraries Journal,26(2), 91–108.
Gromoff, A., Bilinkis, Y., & Kazantsev, N. (2017). Business architecture flexibility as a result of knowledge-intensive process management. Global Journal of Flexible Systems Management, 18(1), 73–86.
Grover, P., & Kar, A. K. (2017). Big data analytics: A review on theoretical contributions and tools used in literature. Global Journal of Flexible Systems Management,18(203), 203–229. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40171-017-0159-3.
Gupta, P. J., & Suri, P. K. (2018). Analysing the influence of improved situation, capability level of actors and flexible process workflow on public value of e-governance projects in India. Global Journal of Flexible Systems Management, 19(4), 349–372.
Hashem, I. A. T., Yaqoob, I., Anuar, N. B., Mokhtar, S., Gani, A., & Khan, S. U. (2015). The rise of ‘‘big data’’ on cloud computing: Review and open research issues. Information Systems,47, 98–115.
Huang, E. H. (2016). Maintaining the ownership of information in the digital age. USA: Stanford University.
Jones, M. V., Coviello, N., & Tang, Y. K. (2011). International entrepreneurship research (1989–2009): A domain ontology and thematic analysis. Journal of Business Venturing,26(6), 632–659.
Kar, A. K., & Rakshit, A. (2015). Flexible pricing models for cloud computing based on group decision making under consensus. Global Journal of Flexible Systems Management,16(2), 1–14.
Laitila, M. (2017). Data monetization: Utilizing data as an asset to generate new revenues for firms. Finland: Aalto University.
Lambert, S. C., & Davison, R. A. (2013). Applications of the business model in studiesof enterprise success, innovation and classification: An analysis of empirical research from 1996 to 2010. European Journal of Management,31, 668–681.
Liñán, F., & Fayolle, A. (2015). A systematic literature review on entrepreneurial intentions: Citation, thematic analyses, and research agenda. International Entrepreneurship and Management Journal,11(4), 907–933.
Liu, C., & Chen, C.-L. (2015). A review of data monetization: Strategic Use of Big Data. In The fifteenth international conference of electronic business. Hong Kong.
Manyika, J., Chui, M., Brown, B., Bughin, J., Dobbs, R., Roxburgh, C., et al. (2011). Big data: The next frontier for innovation, competition, and productivity. New York: The McKinsey Global Institute.
McAfee, A., Brynjolfsson, E., Davenport, T. H., Patil, D. J., & Barton, D. (2012). Big data: The management revolution. Harvard Business Review,90(10), 60–68.
Miles, M. B., Huberman, A. M., Huberman, M. A., & Huberman, M. (1994). Qualitative data analysis: An expanded sourcebook. London: Sage.
Mohasseb, S. (2014). Framing a winning data monetization strategy. Amstelveen: KPMG.
Moore, S. (2015). How to monetize your customer data.[Online]. Available at https://www.gartner.com/smarterwithgartner/how-to-monetize-your-customer-data/. Retrieved December 17, 2018.
Moro Visconti, R., Larocca, A., & Marconi, M. (2017). Big data-driven value chains and digital platforms: From value co-creation to monetization. SSRN Electronic Journal. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.2903799.
Najjar, M. S., & Kettinger, W. J. (2013). Data monetization: Lessons from a retailer’s journey. MIS Quarterly Executive,12(4), 213–225.
Odiete, O. O. (2018). Using blockchain to support data & service monetization. Saskatchewan: University of Saskatchewan.
Onggo, B. S. S. (2010). Methods for Conceptual Model Representation. In S. Robinson, K. Kothiadis, R. Brooks (eds.) Conceptual Modelling for Discrete-Event Simulation, pp. 337–354. New York: Academic Press.
Palanisamy, R., & Foshay, N. (2013). Impact of user’s internal flexibility and participation on usage and information systems flexibility. Global Journal of Flexible Systems Management,14(4), 195–209.
Palvia, P., Mao, E., Salam, A. F., & Soliman, K. S. (2003). Management information systems research: What’s there in a methodology? CAIS,11, 16.
Parmar, R., Mackenzie, I., Cohn, D., & Gann, D. (2014). The new patterns of innovation. Harvard Business Review,92(1), 2.
Patrick, C. (2015). Market insight: Opportunities for CSPs to monetize to data and analytics value chain. Gartner Institute: Gartner Report.
Piotrowska, A. M., & Klonowski, M. (2015). Some remarks and ideas about monetization of sensitive data. In Data privacy management, and security assurance (pp. 118–133). Springer.
Prakash, S. D. (2014). Big data led big monetization. Vidwat,7(1), 6.
Rao, D., & Ng, W. K. (2015, October). How much is your information worth—a method for revenue generation for your information. In 2015 IEEE international conference on big data (big data) (pp. 2320-2326). IEEE.
Rathore, A. K., Das, S., & Ilavarasan, P. V. (2018). Social media data inputs in product design: Case of a smartphone. Global Journal of Flexible Systems Management,19(3), 255–272.
Renken, J., & Heeks, R. (2019). Champions of IS innovations. Communications of the Association for Information Systems,44(1), 38.
Santani, S. (2018). Why data is the new oil. Retrieved December 17, 2018 from https://ischool.syr.edu/infospace/2018/02/26/why-data-is-the-new-oil/.
Sarkar, S. (2015). Analyzing the Indian subscriber behavior towards mobile social media-a data monetization & customer engagement perspective. Telecom Business Review,8(1), 48.
Shukla, V., & Dubey, P. K. (2014). Big data: Beyond data handling. International Journal of Scientific Research and Education,2(09), 1929–1935.
Shukla, K., Sushil, S., & Sharma, K. M. (2019). Managerial paradox toward flexibility: Emergent views using thematic analysis of literature. Global Journal of Flexible Systems Management,20(4), 349–370.
Singh, A. (2013). Social media and corporate agility. Global Journal of Flexible Systems Management,14(4), 255–260.
Smailovic, V., Galetic, V., & Podobnik, V. (2013). Implicit social networking for mobile users: Data monetization for telcos through context-aware services. In 2013 12th international conference on telecommunications (ConTEL) (pp. 163–170). IEEE.
Sushil, (2016). Theory of flexible systems management. In Sushil, Connel J. & Burgess J. (Eds.), Flexible Work Organizations: The Challenges of Capacity Building in Asia, Flexible Systems Management, pp. 3–20. Springer: New Delhi.
Sushil. (2019). Theory building using SAP-LAP linkages: an application in the context of disaster management. Annals of Operations Research, 283(1–2), 811–836.
Thenuan, P., & Raina, A. (2016). Data privacy concerns for big data monetization in mobile application. Prayukti-Student Research Journal.
Thomas, L. D. W., & Leiponen, A. (2016). Big data commercialization. IEEE Engineering Management Review,44(2), 74–90. https://doi.org/10.1109/EMR.2016.2568798.
Tranfield, D., Denyer, D., & Smart, P. (2003). Towards a methodology for developing evidence-informed management knowledge by means of systematic review. British Journal of Management,14(3), 207–222.
Uddin, M. F., & Gupta, N. (2014). Seven V’s of big data understanding big data to extract value. In 2014 zone 1 conference of the american society for engineering education (ASEE zone 1) (pp. 1–5). IEEE.
Van der Aalst, W. M. P. (2016a). Process mining: Data science in action (2nd ed., pp. 3–7). Berlin: Springer.
Van der Aalst, W. M. P. (2016b). Green data science: using big data in an” environmentally friendly” manner. In 18th international conference on enterprise information systems (ICEIS 2016), April 25–28, 2016, Rome, Italy.
Van’t Spijker, A. (2014). The new oil: Using innovative business models to turn data into profit. Denville: Technics Publications.
Wadhwa, S., & Rao, K. S. (2002). Framework for a flexibility maturity model. Global Journal of Flexible Systems Management, 3(2/3), 45–55.
Wells, A. R., & Chiang, K. (2017). Monetization strategy: Making data pay. In A. R. Wells & K. Chiang (Eds.), Monetizing your data: A guide to turning data into profit-driving strategies and solutions (pp. 77–97). New York: Wiley.
Wixom, B. H. (2014). Cashing in on your data. CISR Research Briefing,XIV(8), 124.
Wixom, B. H., & Ross, J. W. (2015). Profiting from the data Deluge. MIT Sloan School of Management, Center for Information Systems Research, XV, NO. 12 (Research Briefing).
Wixom, B. H., & Ross, J. W. (2017). How to monetize your data. MIT Sloan Management Review,58(3), 10–13.
Wolfe, J. (2017). Roomba vacuum maker iRobot betting big on the “smart” home. REUTERS. [Online]. Available at https://www.reuters.com/article/us-irobot-strategy/roomba-vacuum-maker-irobot-betting-big-on-the-smart-home-idUSKBN1A91A5. Retrieved December 17, 2018.
Ylijoki, O., & Porras, J. (2016). Perspectives to definition of big data: A mapping study and discussion. Journal of Innovation Management,4(1), 69.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hanafizadeh, P., Harati Nik, M.R. Configuration of Data Monetization: A Review of Literature with Thematic Analysis. Glob J Flex Syst Manag 21, 17–34 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40171-019-00228-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40171-019-00228-3