Abstract
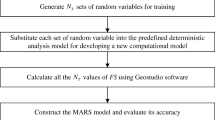
In this study, reliability analysis of slope failure of Durgawati earthen embankment has been performed using two different methods specifically multivariate adaptive regression splines (MARS) and relevance vector machine (RVM). Reliability index \((\beta )\) is calculated using both MARS and RVM under steady-state and transient-state seepage conditions. The analyses are performed for two different sections CH 21.0 and CH 22.0 at RD 640.09 m and RD 670.57 m, respectively. The Durgawati dam is situated in Kaimur district of Bihar, India. The FOS values of Durgawati earthen dam is calculated for using modified Bishop’s method for different seepage conditions, i.e., steady state and transient state. The seepage and slope failure analysis of Durgawati earthen dam is performed using SEEP-W and SLOPE-W modules of Geo-Studio 2007 software. The FOS values are calculated for these conditions for different realizations of the material parameters \((c,\varphi ,\gamma )\). After that, MARS and RVM have been applied to estimate the reliability index \((\beta )\) for the estimated FOS values for different realizations over the body of the dam. The computed reliability index \((\beta )\) under different situations indicates that the performance of the dam is satisfactory.

Source: [41]
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
El-Ramly H, Morgenstern NR, Cruden DM (2002) Probabilistic slope stability analysis for practice. Can Geotech J 39:665–683. https://doi.org/10.1139/t02-034
Liang RY, Nusier OK, Malkawi AH (1999) A reliability based approach for evaluating the slope stability of embankment dams. Eng Geol. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0013-7952(99)00017-4
Salgado R, Kim D (2014) Reliability analysis of load and resistance factor design of slopes. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 140:57–73. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0000978
Roh G, Hong HP (2009) Calibration of information-sensitive partial factors for assessing earth slopes. J Geoengin. https://doi.org/10.6310/jog.2009.4(3).3
Christian JT, Ladd CC, Baecher GB (1994) Reliability applied to slope stability analysis. J Geotech Eng. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9410(1994)120:12(2180)
Li DQ, Jiang SH, Cao ZJ et al (2015) A multiple response-surface method for slope reliability analysis considering spatial variability of soil properties. Eng Geol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2014.12.003
Griffiths DV, Fenton GA (2004) Probabilistic slope stability analysis by finite elements. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 130:507–518. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2004)130:5(507)
Griffiths DV, Huang J, Fenton GA (2009) Influence of spatial variability on slope reliability using 2-D random fields. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0000099
Ji J (2014) A simplified approach for modeling spatial variability of undrained shear strength in out-plane failure mode of earth embankment. Eng Geol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2014.09.004
Zeng P, Jimenez R (2014) An approximation to the reliability of series geotechnical systems using a linearization approach. Comput Geotech 62:304–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2014.08.007
Hong HP, Roh G (2008) Reliability evaluation of earth slopes. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2008)134:12(1700)
Cho SE (2007) Effects of spatial variability of soil properties on slope stability. Eng Geol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2007.03.006
Suchomel R, Mašín D (2010) Comparison of different probabilistic methods for predicting stability of a slope in spatially variable c-φ soil. Comput Geotech. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2009.08.005
Xue J-F, Gavin K (2007) Simultaneous determination of critical slip surface and reliability index for slopes. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2007)133:7(878)
Duncan JM (2000) Factors of Safety and Reliability in Geotechnical Engineering. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 126:307–316. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2000)126:4(307)
Tang XS, Li DQ, Zhou CB, Phoon KK (2015) Copula-based approaches for evaluating slope reliability under incomplete probability information. Struct Saf. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.strusafe.2014.09.007
Hsu S, Nelson PP (2006) Material spatial variability and slope stability for weak rock masses. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 132:183–193. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2006)132:2(183)
El-Ramly H, Morgenstern NR, Cruden DM (2005) Probabilistic assessment of stability of a cut slope in residual soil. Géotechnique. https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.2005.55.1.77
Jiang S-H, Li D-Q, Cao Z-J et al (2014) Efficient system reliability analysis of slope stability in spatially variable soils using Monte Carlo simulation. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)gt.1943-5606.0001227
Jiang S-H, Huang J-S (2016) Efficient slope reliability analysis at low-probability levels in spatially variable soils. Comput Geotech 75:18–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2016.01.016
Fellenius W (1936) Calculation of stability of earth dams. Proc Second Congr large dams 4:445–463
Bishop AW (1955) The use of the slip circle in the stability analysis of slopes. Géotechnique 5:7–17. https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.1955.5.1.7
Morgenstern NR, Price VE (1965) The analysis of the stability of general slip surfaces. Géotechnique. https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.1965.15.1.79
Wu TH, Kraft LM (1970) Safety analysis of slopes. J Soil Mech Found Div ASCE 96:609–630
Alonso EE (1977) Discussion: risk analysis of slopes and its application to slopes in Canadian sensitive clays. Géotechnique 27:254–258. https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.1977.27.2.254
Husein Malkawi AI, Hassan WF, Abdulla FA (2000) Uncertainty and reliability analysis applied to slope stability. Struct Saf 22:161–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-4730(00)00006-0
Wong FS (1985) Slope reliability and response surface method. J Geotech Eng 111:32–53. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9410(1985)111:1(32)
Faravelli L (1989) Response-surface approach for reliability analysis. J Eng Mech 115:2763–2781. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9399(1989)115:12(2763)
Bucher CG, Bourgund U (1990) A fast and efficient response surface approach for structural reliability problems. Struct Saf. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-4730(90)90012-E
Guan XL, Melchers RE (1997) Multitangent-plane surface method for reliability calculation. J Eng Mech 123:996–1002. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9399(1997)123:10(996)
Friedman JH (1991) Rejoinder: multivariate adaptive regression splines. Ann Stat. https://doi.org/10.1214/aos/1176347973
Zhang WG, Goh ATC (2013) Multivariate adaptive regression splines for analysis of geotechnical engineering systems. Comput Geotech 48:82–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2012.09.016
Liu LL, Cheng YM (2016) Efficient system reliability analysis of soil slopes using multivariate adaptive regression splines-based Monte Carlo simulation. Comput Geotech. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2016.05.001
Samui P (2013) Multivariate adaptive regression spline (mars) for prediction of elastic modulus of jointed rock mass. Geotech Geol Eng 31:249–253. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-012-9584-4
Metya S, Mukhopadhyay T, Adhikari S, Bhattacharya G (2017) System reliability analysis of soil slopes with general slip surfaces using multivariate adaptive regression splines. Comput Geotech. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2017.02.017
Liu L, Zhang S, Cheng YM, Liang L (2019) Advanced reliability analysis of slopes in spatially variable soils using multivariate adaptive regression splines. Geosci Front. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2018.03.013
Tipping ME (2001) Sparse Bayesian learning and the relevance vector machine. J Mach Learn Res. https://doi.org/10.1162/15324430152748236
Samui P, Lansivaara T, Kim D (2011) Utilization relevance vector machine for slope reliability analysis. Appl Soft Comput J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2011.03.009
Ji J, Zhang C, Gui Y et al (2017) New observations on the application of LS-SVM in slope system reliability analysis. J Comput Civ Eng 31:06016002. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)CP.1943-5487.0000620
Li S, Zhao H, Ru Z (2017) Relevance vector machine-based response surface for slope reliability analysis. Int J Numer Anal Methods Geomech 41:1332–1346. https://doi.org/10.1002/nag.2683
Himanshu N, Burman A (2017) Seepage and stability analysis of Durgawati earthen dam: a case study. Indian Geotech J. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40098-017-0283-1
Samui P, Dixon B (2012) Application of support vector machine and relevance vector machine to determine evaporative losses in reservoirs. Hydrol Process 26:1361–1369. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.8278
Zhao H, Yin S, Ru Z (2012) Relevance vector machine applied to slope stability analysis. Int J Numer Anal Methods Geomech. https://doi.org/10.1002/nag.1037
MacKay DJC (1992) Bayesian interpolation. Neural Comput 4:415–447. https://doi.org/10.1162/neco.1992.4.3.415
Wahba G (1985) A comparison of GCV and GML for choosing the smoothing parameter in the generalized spline smoothing problem. Ann Stat 13:1378–1402. https://doi.org/10.1214/aos/1176349743
Ghosh M, Berger J (1988) Stastical decision theory and bayesian analysis. J Am Stat Assoc 83:266. https://doi.org/10.2307/2288950
Lee IK, White W, Ingles OG (1983) Soil Variability. In: Geotechnical engineering
Harr ME (1987) Reliability-based design in civil engineering. McGraw-Hill, New York
Baecher GB, Christian JT (2003) Reliability and statistics in geotechnical engineering. Wiley, West Sussex
Wang W-C, Chau K-W, Cheng C-T, Qiu L (2009) A comparison of performance of several artificial intelligence methods for forecasting monthly discharge time series. J Hydrol 374:294–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2009.06.019
Nayak PC, Sudheer KP, Rangan DM, Ramasastri KS (2005) Short-term flood forecasting with a neurofuzzy model. Water Resour Res. https://doi.org/10.1029/2004WR003562
Gokceoglu C, Zorlu K (2004) A fuzzy model to predict the uniaxial compressive strength and the modulus of elasticity of a problematic rock. Eng Appl Artif Intell 17:61–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2003.11.006
Ceryan N, Okkan U, Kesimal A (2013) Prediction of unconfined compressive strength of carbonate rocks using artificial neural networks. Environ Earth Sci 68:807–819. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-012-1783-z
Yagiz S, Sezer EA, Gokceoglu C (2012) Artificial neural networks and nonlinear regression techniques to assess the influence of slake durability cycles on the prediction of uniaxial compressive strength and modulus of elasticity for carbonate rocks. Int J Numer Anal Methods Geomech. https://doi.org/10.1002/nag.1066
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, V., Samui, P., Himanshu, N. et al. Reliability-Based Slope Stability Analysis of Durgawati Earthen Dam Considering Steady and Transient State Seepage Conditions Using MARS and RVM. Indian Geotech J 49, 650–666 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40098-019-00373-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40098-019-00373-7