Abstract
The efficient removal of the antibiotic ciprofloxacin (CIP) from aqueous samples using magnetic nanosorbents prepared using three sulfated polysaccharides, κ-, ι- and λ-carrageenan and an alkoxysilane agent containing a reactive epoxide ring is described. The prepared nanosorbents were characterized in detail using FTIR spectroscopy, solid-state 29Si and 13C NMR spectroscopy and elemental microanalysis. The synthesis method was more effective for incorporating higher amounts of κ-carrageenan in the siliceous shells. Although being less sulfated, κ-carrageenan is cheaper than the other carrageenan tested. The CIP adsorption was a cooperative process, well described by the Dubinin–Radushkevich isotherm, with maximum adsorption capacities of 878, 969 and 865 mg/g for κ-, ι- and λ-carrageenan sorbents, respectively. Overall, the produced magnetic nanosorbents are among the best magnetic systems with high adsorptive efficiency for CIP. It is suggested that protonated CIP molecules are exchanged with ester sulfate counterions of carrageenan at the particles’ surface as the main pathway for CIP adsorption. The adsorption process was exothermic and entropically favorable for the three sorbents. However, at 298 K, the adsorption was spontaneous for κ-carrageenan-based sorbents and non-spontaneous for ι- and λ-carrageenan particles. The magnetic sorbents could be reused and maintained their ability towards CIP removal up to four cycles. The removal efficiency in wastewater was enhanced with the sorbent dose.
Graphical abstract

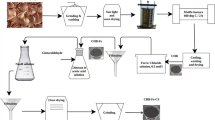
Magnetic carrageenan nanosorbents were prepared using three carrageenan polysaccharides (κ-, ι-, and λ-carrageenan). The resulting magnetic particles removed the antibiotic ciprofloxacin efficiently from ultra-pure water and wastewater samples. Magnetic features enabled the fast magnetic separation of the nanosorbents from water.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sabri, N.A., van Holst, S., Schmitt, H., et al.: Fate of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes during conventional and additional treatment technologies in wastewater treatment plants. Sci. Total Environ. 741, 140199 (2020)
Tavengwa, N.T., Moyo, B., Musarurwa, H., et al.: Challenges and future directions in the analysis of emerging pollutants in aqueous environments. In: Dalu, T., Tavengwa, N.T. (eds.) Emerging Freshwater Pollutants, pp. 373–379. Elsevier (2022)
Sanganyado, E., Kajau, T.A.: The fate of emerging pollutants in aquatic systems: an overview. In: Dalu, T., Tavengwa, N.T. (eds.) Emerging Freshwater Pollutants, pp. 119–135. Elsevier (2022)
Burke, V., Richter, D., Greskowiak, J., et al.: Occurrence of antibiotics in surface and groundwater of a drinking water catchment area in germany. Water Environ. Res. 88, 652–659 (2016)
Boy-Roura, M., Mas-Pla, J., Petrovic, M., et al.: Towards the understanding of antibiotic occurrence and transport in groundwater: findings from the Baix Fluvià alluvial aquifer (NE Catalonia, Spain). Sci. Total Environ. 612, 1387–1406 (2018)
Gu, D., Feng, Q., Guo, C., et al.: Occurrence and risk assessment of antibiotics in manure, soil, wastewater, groundwater from livestock and poultry farms in Xuzhou, China. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 103, 590–596 (2019)
Van Doorslaer, X., Dewulf, J., Van Langenhove, H., Demeestere, K.: Fluoroquinolone antibiotics: an emerging class of environmental micropollutants. Sci. Total Environ. 500, 250–269 (2014)
Rasheed, T., Bilal, M., Nabeel, F., et al.: Environmentally-related contaminants of high concern: potential sources and analytical modalities for detection, quantification, and treatment. Environ. Int. 122, 52–66 (2019)
Sivagami, K., Vignesh, V.J., Srinivasan, R., et al.: Antibiotic usage, residues and resistance genes from food animals to human and environment: an Indian scenario. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 8, 102221 (2020)
Ahmadzadeh, S., Asadipour, A., Pournamdari, M., et al.: Removal of ciprofloxacin from hospital wastewater using electrocoagulation technique by aluminum electrode: optimization and modelling through response surface methodology. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 109, 538–547 (2017)
El-Shafey, E.-S.I., Al-Lawati, H., Al-Sumri, A.S.: Ciprofloxacin adsorption from aqueous solution onto chemically prepared carbon from date palm leaflets. J. Environ. Sci. 24, 1579–1586 (2012)
Igwegbe, C.A., Oba, S.N., Aniagor, C.O., et al.: Adsorption of ciprofloxacin from water: a comprehensive review. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 93, 57–77 (2021)
Zhang, X., Tang, Y., Zhang, F., Lee, C.-S.: A novel aluminum-graphite dual-ion battery. Adv. Energy Mater. 6, 1502588 (2016)
Wang, M., Jiang, C., Zhang, S., et al.: Reversible calcium alloying enables a practical room-temperature rechargeable calcium-ion battery with a high discharge voltage. Nat. Chem. 10, 667–672 (2018)
Mu, S., Liu, Q., Kidkhunthod, P., et al.: Molecular grafting towards high-fraction active nanodots implanted in N-doped carbon for sodium dual-ion batteries. Natl. Sci. Rev. 8, 1–12 (2020)
Chen, X., Wang, D., Wang, T., et al.: Enhanced photoresponsivity of a GaAs nanowire metal-semiconductor-metal photodetector by adjusting the fermi level. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 11, 33188–33193 (2019)
Li, H., Tang, J., Kang, Y., et al.: Optical properties of quasi-type-II structure in GaAs/GaAsSb/GaAs coaxial single quantum-well nanowires. Appl. Phys. Lett. 113, 233104 (2018)
Tang, X., Wu, J., Wu, W., et al.: Competitive-type pressure-dependent immunosensor for highly sensitive detection of diacetoxyscirpenol in wheat via monoclonal antibody. Anal. Chem. 92, 3563–3571 (2020)
Zhu, W., Deng, M., Chen, D., et al.: Dual-phase CsPbCl3–Cs4PbCl6 perovskite films for self-powered, visible-blind UV photodetectors with fast response. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 12, 32961–32969 (2020)
Xu, P., Cao, J., Yin, C., et al.: Quantum chemical study on the adsorption of megazol drug on the pristine BC3 nanosheet. Supramol. Chem. 33, 63–69 (2021)
Zhao, C., Xi, M., Huo, J., et al.: Electro-reduction of N2 on nanostructured materials and the design strategies of advanced catalysts based on descriptors. Mater. Today Phys. 22, 100609 (2022)
Girardi, C., Greve, J., Lamshöft, M., et al.: Biodegradation of ciprofloxacin in water and soil and its effects on the microbial communities. J. Hazard. Mater. 198, 22–30 (2011)
Wei, X., Chen, J., Xie, Q., et al.: Distinct photolytic mechanisms and products for different dissociation species of ciprofloxacin. Environ. Sci. Technol. 47, 4284–4290 (2013)
Couto, C.F., Santos, A.V., Amaral, M.C.S., et al.: Assessing potential of nanofiltration, reverse osmosis and membrane distillation drinking water treatment for pharmaceutically active compounds (PhACs) removal. J. Water Process Eng. 33, 101029 (2020)
Mu, Y., Huang, C., Li, H., Chen, L., et al.: Electrochemical degradation of ciprofloxacin with a Sb-doped SnO2 electrode: performance, influencing factors and degradation pathways. RSC Adv. 9, 29796–29804 (2019)
Fallah, Z., Zare, E.N., Ghomi, M., et al.: Toxicity and remediation of pharmaceuticals and pesticides using metal oxides and carbon nanomaterials. Chemosphere 275, 130055 (2021)
Biswal, B.K., Balasubramanian, R.: Adsorptive removal of sulfonamides, tetracyclines and quinolones from wastewater and water using carbon-based materials: Recent developments and future directions. J. Clean. Prod. 349, 131421 (2022)
Ahmad, I., Siddiqui, W.A., Ahmad, T.: Synthesis and characterization of molecularly imprinted magnetite nanomaterials as a novel adsorbent for the removal of heavy metals from aqueous solution. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 8, 4239–4252 (2019)
Soares, S.F., Fernandes, T., Trindade, T., Daniel-da-Silva, A.L.: Recent advances on magnetic biosorbents and their applications for water treatment. Environ. Chem. Lett. 18, 151–164 (2020)
Zare, E.N., Mudhoo, A., Khan, M.A., et al.: Water decontamination using bio-based, chemically functionalized, doped, and ionic liquid-enhanced adsorbents: review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 19, 3075–3114 (2021)
Theamwong, N., Intarabumrung, W., Sangon, S., et al.: Activated carbons from waste Cassia bakeriana seed pods as high-performance adsorbents for toxic anionic dye and ciprofloxacin antibiotic remediation. Bioresour. Technol. 341, 125832 (2021)
Wang, X., Wang, Y., Zhao, C., et al.: Ciprofloxacin removal by ultrasound-enhanced carbon nanotubes/permanganate process: in situ generation of free reactive manganese species via electron transfer. Water Res. 202, 117393 (2021)
Huang, X., Tian, J., Li, Y., et al.: Preparation of a three-dimensional porous graphene oxide–kaolinite–poly(vinyl alcohol) composite for efficient adsorption and removal of ciprofloxacin. Langmuir 36, 10895–10904 (2020)
Hu, Y., Pan, C., Zheng, X., et al.: Removal of ciprofloxacin with aluminum-pillared kaolin sodium alginate beads (CA-Al-KABs): kinetics, isotherms, and BBD model. Water (Basel) 12, 905 (2020)
Falyouna, O., Maamoun, I., Bensaida, K., et al.: Encapsulation of iron nanoparticles with magnesium hydroxide shell for remarkable removal of ciprofloxacin from contaminated water. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 605, 813–827 (2022)
Laabd, M., Brahmi, Y., el Ibrahimi, B., et al.: A novel mesoporous Hydroxyapatite@Montmorillonite hybrid composite for high-performance removal of emerging Ciprofloxacin antibiotic from water: Integrated experimental and Monte Carlo computational assessment. J. Mol. Liq. 338, 116705 (2021)
Yang, Y., Zhong, Z., Li, J., et al.: Efficient with low-cost removal and adsorption mechanisms of norfloxacin, ciprofloxacin and ofloxacin on modified thermal kaolin: experimental and theoretical studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 430, 128500 (2022)
Jiang, W.-T., Chang, P.-H., Wang, Y.-S., et al.: Removal of ciprofloxacin from water by birnessite. J. Hazard. Mater. 250, 362–369 (2013)
Soares, S.F., Rocha, M.J., Ferro, M., et al.: Magnetic nanosorbents with siliceous hybrid shells of alginic acid and carrageenan for removal of ciprofloxacin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 139, 827–841 (2019)
Yaashikaa, P.R., Senthil Kumar, P., Karishma, S.: Review on biopolymers and composites—evolving material as adsorbents in removal of environmental pollutants. Environ. Res. 212, 113114 (2022)
Dang, B.-T., Bui, X.-T., Tran, D.P.H., et al.: Current application of algae derivatives for bioplastic production: a review. Bioresour. Technol. 347, 126698 (2022)
Guo, Z., Wei, Y., Zhang, Y., et al.: Carrageenan oligosaccharides: a comprehensive review of preparation, isolation, purification, structure, biological activities and applications. Algal Res. 61, 102593 (2022)
Zia, K.M., Tabasum, S., Nasif, M., et al.: A review on synthesis, properties and applications of natural polymer based carrageenan blends and composites. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 96, 282–301 (2017)
Papageorgiou, M., Nanaki, S., Kyzas, G., et al.: Novel isocyanate-modified carrageenan polymer materials: preparation, characterization and application adsorbent materials of pharmaceuticals. Polymers (Basel). 9, 595 (2017)
Soares, S.F., Simões, T.R., António, M., et al.: Hybrid nanoadsorbents for the magnetically assisted removal of metoprolol from water. Chem. Eng. J. 302, 560–569 (2016)
Sharma, G., Khosla, A., Kumar, A., et al.: A comprehensive review on the removal of noxious pollutants using carrageenan based advanced adsorbents. Chemosphere 289, 133100 (2022)
Mohd Yusop, H., Mohd Ismail, A.I.H., Wan Ismail, W.N.: Preparation and characterization of new sol–gel hybrid inulin–TEOS adsorbent. Polymers (Basel). 13, 1295 (2021)
Benvenuti, J., Giraldi Fisch, A., Zimnoch Dos Santos, J.H., Gutterres, M.: Hybrid sol–gel silica adsorbent material based on grape stalk applied to cationic dye removal. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy. 39, 1–10 (2020)
Samiey, B., Cheng, C.-H., Wu, J.: Organic-inorganic hybrid polymers as adsorbents for removal of heavy metal ions from solutions: a review. Materials. 7, 673–726 (2014)
Soares, S.F., Fateixa, S., Trindade, T., Daniel-da-Silva, A.L.: A versatile synthetic route towards gelatin-silica hybrids and magnetic composite colloidal nanoparticles. Adv. Compos. Hybrid. Mater. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-021-00386-y
Huang, Y., Keller, A.A.: Magnetic nanoparticle adsorbents for emerging organic contaminants. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 1, 731–736 (2013)
Kharissova, O.V., Dias, H.V.R., Kharisov, B.I.: Magnetic adsorbents based on micro- and nano-structured materials. RSC Adv. 5, 6695–6719 (2015)
Malek, N.N.A., Jawad, A.H., Ismail, K., et al.: Fly ash modified magnetic chitosan-polyvinyl alcohol blend for reactive orange 16 dye removal: adsorption parametric optimization. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 189, 464–476 (2021)
Reghioua, A., Barkat, D., Jawad, A.H., et al.: Parametric optimization by Box-Behnken design for synthesis of magnetic chitosan-benzil/ZnO/Fe3O4 nanocomposite and textile dye removal. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 9, 105166 (2021)
Soares, S.F., Fernandes, T., Sacramento, M., et al.: Magnetic quaternary chitosan hybrid nanoparticles for the efficient uptake of diclofenac from water. Carbohydr. Polym. 203, 35–44 (2019)
Oliveira-Silva, R., Pinto da Costa, J., Vitorino, R., Daniel-da-Silva, A.L.: Magnetic chelating nanoprobes for enrichment and selective recovery of metalloproteases from human saliva. J. Mater. Chem. B. 3, 238–249 (2015)
Stöber, W., Fink, A., Bohn, E.: Controlled growth of monodisperse silica spheres in the micron size range. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 26, 62–69 (1968)
Soares, S.F., Amorim, C.O., Amaral, J.S., et al.: On the efficient removal, regeneration and reuse of quaternary chitosan magnetite nanosorbents for glyphosate herbicide in water. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 9, 105189 (2021)
Gómez-Ordóñez, E., Rupérez, P.: FTIR-ATR spectroscopy as a tool for polysaccharide identification in edible brown and red seaweeds. Food Hydrocoll. 25, 1514–1520 (2011)
Prado-Fernández, J., Rodrı́guez-Vázquez, J.A., Tojo, E., Andrade, J.M.: Quantitation of κ-, ι- and λ-carrageenans by mid-infrared spectroscopy and PLS regression. Anal. Chim. Acta. 480, 23–37 (2003)
Pereira, L., Amado, A.M., Critchley, A.T., et al.: Identification of selected seaweed polysaccharides (phycocolloids) by vibrational spectroscopy (FTIR-ATR and FT-Raman). Food Hydrocoll. 23, 1903–1909 (2009)
Pereira, L., Gheda, S.F., Ribeiro-Claro, P.J.A.: Analysis by vibrational spectroscopy of seaweed polysaccharides with potential use in food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries. Int. J. Carbohydr. Chem. 2013, 1–7 (2013)
Soares, S.F., Fernandes, T., Trindade, T., Daniel-da-Silva, A.L.: Trimethyl chitosan/siloxane-hybrid coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles for the uptake of sulfamethoxazole from water. Molecules 24, 1958 (2019)
Wang, N., Teng, H., Li, L., et al.: Synthesis of phosphated k-carrageenan and its application for flame-retardant waterborne epoxy. Polymers (Basel). 10, 1268 (2018)
Soares, S.F., Trindade, T., Daniel-da-Silva, A.L.: Carrageenan-silica hybrid nanoparticles prepared by a non-emulsion method. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2015, 4588–4594 (2015)
Ouyang, Z.-W., Chen, E.-C., Wu, T.-M.: Thermal stability and magnetic properties of polyvinylidene fluoride/magnetite nanocomposites. Materials 8, 4553–4564 (2015)
Mahdavinia, G.R., Massoudi, A., Baghban, A., Shokri, E.: Study of adsorption of cationic dye on magnetic kappa-carrageenan/PVA nanocomposite hydrogels. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2, 1578–1587 (2014)
Long, J., Wu, Z., Li, X., et al.: New method for the immobilization of pullulanase onto hybrid magnetic (Fe3O4–κ-carrageenan) nanoparticles by electrostatic coupling with pullulanase/chitosan complex. J. Agric. Food Chem. 63, 3534–3542 (2015)
Kulal, P., Badalamoole, V.: Hybrid nanocomposite of kappa-carrageenan and magnetite as adsorbent material for water purification. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 165, 542–553 (2020)
Silva, R.R., Salvi, D.T.B., Santos, M.V., et al.: Multifunctional organic–inorganic hybrids based on cellulose acetate and 3-glycidoxypropyltrimethoxysilane. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 81, 114–126 (2017)
Vueva, Y., Connell, L.S., Chayanun, S., et al.: Silica/alginate hybrid biomaterials and assessment of their covalent coupling. Appl. Mater. Today. 11, 1–12 (2018)
van de Velde, F., Pereira, L., Rollema, H.S.: The revised NMR chemical shift data of carrageenans. Carbohydr. Res. 339, 2309–2313 (2004)
Turquois, T., Acquistapace, S., Vera, F.A., Welti, D.H.: Composition of carrageenan blends inferred from 13C-NMR and infrared spectroscopic analysis. Carbohydr. Polym. 31, 269–278 (1996)
Silva, F.R.F., Dore, C.M.P.G., Marques, C.T., et al.: Anticoagulant activity, paw edema and pleurisy induced carrageenan: action of major types of commercial carrageenans. Carbohydr. Polym. 79, 26–33 (2010)
Babonneau, F., Baccile, N., Laurent, G., et al.: Solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance: A valuable tool to explore organic-inorganic interfaces in silica-based hybrid materials. C. R. Chim. 13, 58–68 (2010)
Barberena-Fernández, A.M., Carmona-Quiroga, P.M., Blanco-Varela, M.T.: Interaction of TEOS with cementitious materials: Chemical and physical effects. Cem. Concr. Compos. 55, 145–152 (2015)
Chen, L., Yuan, T., Ni, R., et al.: Multivariate optimization of ciprofloxacin removal by polyvinylpyrrolidone stabilized NZVI/Cu bimetallic particles. Chem. Eng. J. 365, 183–192 (2019)
Schefer, L., Adamcik, J., Mezzenga, R.: Unravelling secondary structure changes on individual anionic polysaccharide chains by atomic force microscopy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 53, 5376–5379 (2014)
Khan, N.A., Najam, T., Shah, S.S.A., et al.: Development of Mn-PBA on GO sheets for adsorptive removal of ciprofloxacin from water: kinetics, isothermal, thermodynamic and mechanistic studies. Mater. Chem. Phys. 245, 122737 (2020)
Lagergren, S.: Zur theorie der sogenannten adsorption gelöster stoffe. Springer-Verlag (1907)
Ho, Y.S., McKay, G.: Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem. 34, 451–465 (1999)
Chien, S.H., Clayton, W.R.: Application of Elovich equation to the kinetics of phosphate release and sorption in soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 44, 265 (1980)
Bui, T.X., Choi, H.: Adsorptive removal of selected pharmaceuticals by mesoporous silica SBA-15. J. Hazard. Mater. 168, 602–608 (2009)
Sotelo, J.L., Rodríguez, A.R., Mateos, M.M., et al.: Adsorption of pharmaceutical compounds and an endocrine disruptor from aqueous solutions by carbon materials. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B 47, 640–652 (2012)
Wu, F.-C., Tseng, R.-L., Juang, R.-S.: Characteristics of Elovich equation used for the analysis of adsorption kinetics in dye-chitosan systems. Chem. Eng. J. 150, 366–373 (2009)
Langmuir, I.: The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 40, 1361–1403 (1918)
Freundlich, H.Z.: Concerning adsorption in solutions. Z. Phys. Chem. 57, 444–448 (1906)
Dubinin, M.M., Radushkevich, L.V.: Equation of the characteristic curve of activated charcoal. Proc. Acad. Sci. USSR Sect. C Phys. Chem. 55, 331–333 (1947)
Togue Kamga, F.: Modeling adsorption mechanism of paraquat onto Ayous (Triplochiton scleroxylon) wood sawdust. Appl. Water Sci. 9, 1 (2019)
Ayawei, N., Ebelegi, A.N., Wankasi, D.: Modelling and interpretation of adsorption isotherms. J. Chem. 2017, 3039817 (2017)
Çelebi, O., Üzüm, Ç., Shahwan, T., Erten, H.N.: A radiotracer study of the adsorption behavior of aqueous Ba2+ ions on nanoparticles of zero-valent iron. J. Hazard. Mater. 148, 761–767 (2007)
Mutavdžić Pavlović, D., Ćurković, L., Grčić, I., et al.: Isotherm, kinetic, and thermodynamic study of ciprofloxacin sorption on sediments. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 24, 10091–10106 (2017)
Awe, A.A., Opeolu, B.O., Fatoki, O.S., et al.: Preparation and characterisation of activated carbon from Vitisvinifera leaf litter and its adsorption performance for aqueous phenanthrene. Appl. Biol. Chem. 63, 12 (2020)
Nazraz, M., Yamini, Y., Asiabi, H.: Chitosan-based sorbent for efficient removal and extraction of ciprofloxacin and norfloxacin from aqueous solutions. Mikrochim. Acta. 186, 459 (2019)
Wang, Y.X., Ngo, H.H., Guo, W.S.: Preparation of a specific bamboo based activated carbon and its application for ciprofloxacin removal. Sci. Total Environ. 533, 32–39 (2015)
Zhang, B., Han, X., Gu, P., et al.: Response surface methodology approach for optimization of ciprofloxacin adsorption using activated carbon derived from the residue of desilicated rice husk. J. Mol. Liq. 238, 316–325 (2017)
Huang, L., Wang, M., Shi, C., et al.: Adsorption of tetracycline and ciprofloxacin on activated carbon prepared from lignin with H3PO4 activation. Desalin. Water Treat. 52, 2678–2687 (2014)
Privar, Y., Shashura, D., Pestov, A., et al.: Metal-chelate sorbents based on carboxyalkylchitosans: Ciprofloxacin uptake by Cu(II) and Al(III)-chelated cryogels of N-(2-carboxyethyl)chitosan. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 131, 806–811 (2019)
Zhuang, Y., Yu, F., Ma, J., Chen, J.: Enhanced adsorption removal of antibiotics from aqueous solutions by modified alginate/graphene double network porous hydrogel. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 507, 250–259 (2017)
Li, L., Zhao, J., Sun, Y., et al.: Ionically cross-linked sodium alginate/ĸ-carrageenan double-network gel beads with low-swelling, enhanced mechanical properties, and excellent adsorption performance. Chem. Eng. J. 372, 1091–1103 (2019)
Wang, F., Yang, B., Wang, H., et al.: Removal of ciprofloxacin from aqueous solution by a magnetic chitosan grafted graphene oxide composite. J. Mol. Liq. 222, 188–194 (2016)
Zhou, Y., Cao, S., Xi, C., et al.: A novel Fe3O4/graphene oxide/citrus peel-derived bio-char based nanocomposite with enhanced adsorption affinity and sensitivity of ciprofloxacin and sparfloxacin. Bioresour. Technol. 292, 121951 (2019)
Álvarez-Torrellas, S., Peres, J.A., Gil-Álvarez, V., et al.: Effective adsorption of non-biodegradable pharmaceuticals from hospital wastewater with different carbon materials. Chem. Eng. J. 320, 319–329 (2017)
Yu, F., Cui, T., Yang, C., et al.: κ-Carrageenan/Sodium alginate double-network hydrogel with enhanced mechanical properties, anti-swelling, and adsorption capacity. Chemosphere 237, 124417 (2019)
Rasoulzadeh, H., Mohseni-Bandpei, A., Hosseini, M., Safari, M.: Mechanistic investigation of ciprofloxacin recovery by magnetite–imprinted chitosan nanocomposite: Isotherm, kinetic, thermodynamic and reusability studies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 133, 712–721 (2019)
Zhao, P., Yu, F., Wang, R., et al.: Sodium alginate/graphene oxide hydrogel beads as permeable reactive barrier material for the remediation of ciprofloxacin-contaminated groundwater. Chemosphere 200, 612–620 (2018)
Saha, P., Chowdhury, S.: Insight into adsorption thermodynamics. In: Tadashi, M. (ed.) Thermodynamics, pp. 349–364. InTech, Vienna (2011)
Husein, D.Z.: Adsorption and removal of mercury ions from aqueous solution using raw and chemically modified Egyptian mandarin peel. Desalin. Water Treat. 51, 6761–6769 (2013)
Liu, S.: Cooperative adsorption on solid surfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 450, 224–238 (2015)
Maheshwari, M., Vyas, R.K., Sharma, M.: Kinetics, equilibrium and thermodynamics of ciprofloxacin hydrochloride removal by adsorption on coal fly ash and activated alumina. Desalin. Water Treat. 51, 7241–7254 (2013)
Soares, S.F., Simões, T.R., Trindade, T., Daniel-da-Silva, A.L.: Highly efficient removal of dye from water using magnetic carrageenan/silica hybrid nano-adsorbents. Water Air Soil Poll. 228, 87 (2017)
Nemati Sani, O., Navaei fezabady, A.A., Yazdani, M., Taghavi, M.: Catalytic ozonation of ciprofloxacin using γ-Al2O3 nanoparticles in synthetic and real wastewaters. J. Water Process Eng. 32, 100894 (2019)
Das, S., Barui, A., Adak, A.: Montmorillonite impregnated electrospun cellulose acetate nanofiber sorptive membrane for ciprofloxacin removal from wastewater. J. Water Process Eng. 37, 101497 (2020)
Wang, C.-J., Li, Z., Jiang, W.T., et al.: Cation exchange interaction between antibiotic ciprofloxacin and montmorillonite. J. Hazard. Mater. 183, 309–314 (2010)
Wang, Y., Nie, Q., Huang, B., et al.: Removal of ciprofloxacin as an emerging pollutant: a novel application for bauxite residue reuse. J. Clean. Prod. 253, 120049 (2020)
Wang, W., Cheng, J., Jin, J., et al.: Effect of humic acid on ciprofloxacin removal by magnetic multifunctional resins. Sci. Rep. 6, 30331 (2016)
Ma, S., Si, Y., Wang, F., et al.: Interaction processes of ciprofloxacin with graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide in the presence of montmorillonite in simulated gastrointestinal fluids. Sci. Rep. 7, 2588 (2017)
Inglezakis, V.J., Poulopoulos, S.G., Kazemian, H.: Insights into the S-shaped sorption isotherms and their dimensionless forms. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 272, 166–176 (2018)
Li, J., Beuerman, R., Verma, C.: The effect of molecular shape on oligomerization of hydrophobic drugs: molecular simulations of ciprofloxacin and nutlin. J. Chem. Phys. 148, 104902 (2018)
Pavli, M., Baumgartner, S., Kos, P., Kogej, K.: Doxazosin–carrageenan interactions: a novel approach for studying drug–polymer interactions and relation to controlled drug release. Int. J. Pharm. 421, 110–119 (2011)
Liu, X., Lu, S., Liu, Y., et al.: Adsorption of sulfamethoxazole (SMZ) and ciprofloxacin (CIP) by humic acid (HA): characteristics and mechanism. RSC Adv. 7, 50449–50458 (2017)
Zhang, H., Khanal, S.K., Jia, Y., et al.: Fundamental insights into ciprofloxacin adsorption by sulfate-reducing bacteria sludge: Mechanisms and thermodynamics. Chem. Eng. J. 378, 122103 (2019)
Acknowledgements
This work was developed within the scope of the project CICECO-Aveiro Institute of Materials, UIDB/50011/2020, UIDP/50011/2020 & LA/P/0006/2020, financed by national funds through the FCT/MEC (PIDDAC). The authors thank the RNME (National Electronic Microscopy Network) for microscopy facilities. S. F. Soares thanks the Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia (FCT) for the PhD Grant SFRH/BD/121366/2016. J. Nogueira thanks the Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia (FCT) for the PhD Grant SFRH/BD/146249/2019. A. L. D.-d.-S. acknowledges FCT for the research contract under the Program' Investigador FCT' 2014 and for funding from the project IF/00405/2014.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soares, S.F., Nogueira, J., Trindade, T. et al. Towards efficient ciprofloxacin adsorption using magnetic hybrid nanoparticles prepared with κ-, ι-, and λ-carrageenan. J Nanostruct Chem 13, 283–302 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40097-022-00498-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40097-022-00498-x