Abstract
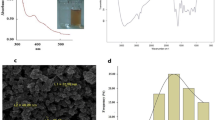
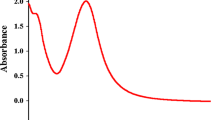
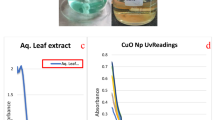
The major goal of this study was to fabricate ZnO nanoparticles (NPs) via chemical and biological routes to evaluate and compare their physiochemical behavior (size and morphology) and biological potentials. The synthesized NPs were confirmed via various spectroscopy and imagining techniques such as XRD, FT-IR, HPLC and SEM. The characterized NPs were then assessed for various in vitro biological applications. Furthermore, apoptotic potential was investigated using HepG2 cell lines by evaluating various signature markers of apoptosis including mitochondrial membrane potential, reactive oxygen/nitrogen (ROS/RNS) production, peroxidases and pro-apoptotic caspase 3 activation. Crystalline, hexagonal structured NPs with an average crystalline size distribution of 32 nm and 23 nm was obtained. Both green-mediated zinc oxide nanoparticles (G-ZnO NPs) and chemically derived NPs (C-ZnO NPs) exhibited high antioxidant, moderate enzyme inhibition, antibacterial and cytotoxicity potential. However, G-ZnO NPs exhibited excellent DPPH (80.1% ± 1.3%), TPC (97 ± 1.22 µgAAE/mg), TRP (94.5 ± 1.48 µgAAE/mg), lipase inhibition (82%), urease inhibition (81.3%), and α-amylase inhibition (18.9%) activity as compared to C-ZnO NPs. Both G-ZnO NPs and C-ZnO NPs showed good antimicrobial potential, however, effect of G-ZnO NPs was more potent than counter C-ZnO NPs. Results from apoptotic assays revealed that G-ZnO NPs showed excellent apoptotic potential in contrast to C-ZnO NPs. Overall results suggested that green route-mediated ZnO NPs exhibits excellent biological potential and could be used for future biomedical applications especially in antimicrobial and cancer therapeutics. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first ever study on Boerhavia diffusa linn-mediated biosynthesis of ZnO nanoparticles and evaluation of their biological activities.
Graphical abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali, M.A., Rehman, I., Iqbal, A., Din, S., Rao, A.Q., Latif, A., et al.: Nanotechnology, a new frontier in agriculture. Adv. Life Sci. 1(3), 129–138 (2014)
Rahman, K., Khan, S.U., Fahad, S., Chang, M.X., Abbas, A., Khan, W.U., et al.: Nano-biotechnology: a new approach to treat and prevent malaria. Int. J. Nanomed. 14, 1401–1410 (2019)
Sahu, T., Ratre, Y.K., Chauhan, S., Bhaskar, L.V.K.S., Nair, M.P., Verma, H.K.: Nanotechnology based drug delivery system: current strategies and emerging therapeutic potential for medical science. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 63, 102487 (2021)
Jun, Y.-w, Seo, J.-w, Cheon, J.: Nanoscaling laws of magnetic nanoparticles and their applicabilities in biomedical sciences. Acc. Chem. Res. 41(2), 179–189 (2008)
Bystrzejewska-Piotrowska, G., Golimowski, J., Urban, P.L.: Nanoparticles: their potential toxicity, waste and environmental management. Waste Manag. 29(9), 2587–2595 (2009)
Khezri, K., Saeedi, M., Dizaj, S.M.: Application of nanoparticles in percutaneous delivery of active ingredients in cosmetic preparations. Biomed. Pharmacother. 106, 1499–1505 (2018)
Demir, N.: Nanotechnology in cosmetics: opportunities and challenges. NanoEra 1(1), 19–23 (2021)
Iravani, S.: Green synthesis of metal nanoparticles using plants. Green Chem. 13(10), 2638–2650 (2011)
Tamilvanan, A., Balamurugan, K., Mohanraj, T., Selvakumar, P., Madhankumar, B.: Parameter optimization of copper nanoparticle synthesis by electrodeposition process using RSM and CS. Mater. Today Proc. 45, 751–756 (2021)
Amer, M.W., Awwad, A.M.: Green synthesis of copper nanoparticles by Citrus limon fruits extract, characterization and antibacterial activity. Chem Int. 7(1), 1–8 (2021)
Kim, J.-Y., Kim, M., Kim, H., Joo, J., Choi, J.-H.: Electrical and optical studies of organic light emitting devices using SWCNTs-polymer nanocomposites. Opt. Mater. 21(1–3), 147–151 (2003)
Thakkar, K.N., Mhatre, S.S., Parikh, R.Y.: Biological synthesis of metallic nanoparticles. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 6(2), 257–262 (2010)
Panigrahi, S., Kundu, S., Ghosh, S., Nath, S., Pal, T.: General method of synthesis for metal nanoparticles. J. Nanopart. Res. 6(4), 411–414 (2004)
Shamaila, S., Sajjad, A.K.L., Farooqi, S.A., Jabeen, N., Majeed, S., Farooq, I.: Advancements in nanoparticle fabrication by hazard free eco-friendly green routes. Appl. Mater. Today. 5, 150–199 (2016)
Kapoor, R.T., Salvadori, M.R., Rafatullah, M., Siddiqui, M.R., Khan, M.A., Alshareef, S.A.: Exploration of microbial factories for synthesis of nanoparticles—a sustainable approach for bioremediation of environmental contaminants. Front. Microbiol. 12, 1404 (2021)
El-Saadony, M.T., Alkhatib, F.M., Alzahrani, S.O., Shafi, M.E., Abdel-Hamid, S.E., Taha, T.F., et al.: Impact of mycogenic zinc nanoparticles on performance, behavior, immune response, and microbial load in Oreochromis niloticus. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 32, 101948 (2021)
Lengke, M.F., Fleet, M.E., Southam, G.: Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles by filamentous cyanobacteria from a silver (I) nitrate complex. Langmuir 23(5), 2694–2699 (2007)
Govindaraju, K., Shan, J., Levesque, K., Hussain, S.N., Powell, W.S., Eidelman, D.H.: Nitration of respiratory epithelial cells by myeloperoxidase depends on extracellular nitrite. Nitric Oxide 18(3), 184–194 (2008)
Hatamie, A., Khan, A., Golabi, M., Turner, A.P., Beni, V., Mak, W.C., et al.: Zinc oxide nanostructure-modified textile and its application to biosensing, photocatalysis, and as antibacterial material. Langmuir 31(39), 10913–10921 (2015)
Hanif, M., Lee, I., Akter, J., Islam, M., Zahid, A.A., Sapkota, K.P., et al.: Enhanced photocatalytic and antibacterial performance of ZnO nanoparticles prepared by an efficient thermolysis method. Catalysts 9(7), 608 (2019)
Singh, A., Gautam, P.K., Verma, A., Singh, V., Shivapriya, P.M., Shivalkar, S., et al.: Green synthesis of metallic nanoparticles as effective alternatives to treat antibiotics resistant bacterial infections: a review. Biotechnol. Rep. 25, e00427 (2020)
Bhuyan, T., Mishra, K., Khanuja, M., Prasad, R., Varma, A.: Biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles from Azadirachta indica for antibacterial and photocatalytic applications. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 32, 55–61 (2015)
Abbasi, B.H., Shah, M., Hashmi, S.S., Nazir, M., Naz, S., Ahmad, W., et al.: Green bio-assisted synthesis, characterization and biological evaluation of biocompatible ZnO NPs synthesized from different tissues of milk thistle (Silybum marianum). Nanomaterials 9(8), 1171 (2019)
Supraja, N., Prasad, T., Krishna, T.G., David, E.: Synthesis, characterization, and evaluation of the antimicrobial efficacy of Boswellia ovalifoliolata stem bark-extract-mediated zinc oxide nanoparticles. Appl. Nanosci. 6(4), 581–590 (2016)
Rad, S.S., Sani, A.M., Mohseni, S.: Biosynthesis, characterization and antimicrobial activities of zinc oxide nanoparticles from leaf extract of Mentha pulegium (L.). Microb. Pathog. 131, 239–245 (2019)
Rupa, E.J., Anandapadmanaban, G., Mathiyalagan, R., Yang, D.-C.: Synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles from immature fruits of Rubus coreanus and its catalytic activity for degradation of industrial dye. Optik 172, 1179–1186 (2018)
Nava, O., Soto-Robles, C., Gómez-Gutiérrez, C., Vilchis-Nestor, A., Castro-Beltrán, A., Olivas, A., et al.: Fruit peel extract mediated green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles. J. Mol. Struct. 1147, 1–6 (2017)
Siripireddy, B., Mandal, B.K.: Facile green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles by Eucalyptus globulus and their photocatalytic and antioxidant activity. Adv. Powder. Technol. 28(3), 785–797 (2017)
Han, D.: Sol–gel autocombustion synthesis of zinc oxide foam decorated with holes and its use as acetic acid gas sensor at sub-ppm level. Ceram. Int. 46(3), 3304–3310 (2020)
Jamdagni, P., Khatri, P., Rana, J.: Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using flower extract of Nyctanthes arbor-tristis and their antifungal activity. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 30(2), 168–175 (2018)
Singh, J., Kumar, S., Alok, A., Upadhyay, S.K., Rawat, M., Tsang, D.C., et al.: The potential of green synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles as nutrient source for plant growth. J. Clean. Prod. 214, 1061–1070 (2019)
Vijayakumar, S., Mahadevan, S., Arulmozhi, P., Sriram, S., Praseetha, P.: Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Atalantia monophylla leaf extracts: characterization and antimicrobial analysis. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 82, 39–45 (2018)
Sorbiun, M., Mehr, E.S., Ramazani, A., Fardood, S.T.: Green synthesis of zinc oxide and copper oxide nanoparticles using aqueous extract of oak fruit hull (jaft) and comparing their photocatalytic degradation of basic violet 3. Int. J. Environ. Res. 12(1), 29–37 (2018)
Abdullah, F., Bakar, N.A., Bakar, M.A.: Comparative study of chemically synthesized and low temperature bio-inspired Musa acuminata peel extract mediated zinc oxide nanoparticles for enhanced visible-photocatalytic degradation of organic contaminants in wastewater treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 406, 124779 (2021)
Kumar, P.V., Pammi, S., Kollu, P., Satyanarayana, K., Shameem, U.: Green synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using Boerhaavia diffusa plant extract and their anti bacterial activity. Ind. Crops Prod. 52, 562–566 (2014)
Mishra, S., Aeri, V., Gaur, P.K., Jachak, S.M.: Phytochemical, therapeutic, and ethnopharmacological overview for a traditionally important herb: Boerhavia diffusa Linn. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 1-19 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/808302
Nazir, S., Zaka, M., Adil, M., Abbasi, B.H., Hano, C.: Synthesis, characterisation and bactericidal effect of ZnO nanoparticles via chemical and bio-assisted (Silybum marianum in vitro plantlets and callus extract) methods: a comparative study. IET Nanobiotechnol. 12(5), 604–608 (2018)
McDougall, G.J., Kulkarni, N.N., Stewart, D.: Berry polyphenols inhibit pancreatic lipase activity in vitro. Food Chem. 115(1), 193–199 (2009)
Mahernia, S., Bagherzadeh, K., Mojab, F., Amanlou, M.: Urease inhibitory activities of some commonly consumed herbal medicines. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 14(3), 943 (2015)
Zahra, S.S., Ahmed, M., Qasim, M., Gul, B., Zia, M., Mirza, B., et al.: Polarity based characterization of biologically active extracts of Ajuga bracteosa Wall. ex Benth. and RP-HPLC analysis. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 17(1), 1–16 (2017)
Zaeem, A., Drouet, S., Anjum, S., Khurshid, R., Younas, M., Blondeau, J.P., et al.: Effects of biogenic zinc oxide nanoparticles on growth and oxidative stress response in flax seedlings vs. in vitro cultures: a comparative analysis. Biomolecules 10(6), 918 (2020)
Ahmed, M., Fatima, H., Qasim, M., Gul, B.: Polarity directed optimization of phytochemical and in vitro biological potential of an indigenous folklore: Quercus dilatata Lindl. ex Royle. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 17(1), 1–16 (2017)
Nazir, M., Tungmunnithum, D., Bose, S., Drouet, S., Garros, L., Giglioli-Guivarc’h, N., et al.: Differential production of phenylpropanoid metabolites in callus cultures of Ocimum basilicum L. with distinct in vitro antioxidant activities and in vivo protective effects against UV stress. J. Agric. Food Chem. 67(7), 1847–1859 (2019)
Hano, C., Addi, M., Fliniaux, O., Bensaddek, L., Duverger, E., Mesnard, F., et al.: Molecular characterization of cell death induced by a compatible interaction between Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. linii and flax (Linum usitatissimum) cells. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 46(5–6), 590–600 (2008)
Kaliraj, L., Ahn, J.C., Rupa, E.J., Abid, S., Lu, J., Yang, D.C.: Synthesis of panos extract mediated ZnO nano-flowers as photocatalyst for industrial dye degradation by UV illumination. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 199, 111588 (2019)
Hasan, M., Altaf, M., Zafar, A., Hassan, S.G., Ali, Z., Mustafa, G., Munawar, T., et al.: Bioinspired synthesis of zinc oxide nano-flowers: a surface enhanced antibacterial and harvesting efficiency. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 119, 111280 (2021)
Jan, H., Shah, M., Usman, H., Khan, A., Muhammad, Z., Hano, C., et al.: Biogenic synthesis and characterization of antimicrobial and anti-parasitic zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles using aqueous extracts of the Himalayan Columbine (Aquilegia pubiflora). Front. Mater. 7, 249 (2020)
Huang, J., Li, Q., Sun, D., Lu, Y., Su, Y., Yang, X., et al.: Biosynthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles by novel sundried Cinnamomum camphora leaf. Nanotechnology 18(10), 105104 (2007)
Henry, J., Mohanraj, K., Kannan, S., Barathan, S., Sivakumar, G.: Structural and optical properties of SnS nanoparticles and electron-beam-evaporated SnS thin films. J. Exp. Nanosci. 10(2), 78–85 (2015)
Wiley, B., Sun, Y., Mayers, B., Xia, Y.: Shape-controlled synthesis of metal nanostructures: the case of silver. Chem. Eur. J. 11(2), 454–463 (2005)
Naseer, M., Aslam, U., Khalid, B., Chen, B.: Green route to synthesize zinc oxide nanoparticles using leaf extracts of Cassia fistula and Melia azadarach and their antibacterial potential. Sci. Rep. 10(1), 1–10 (2020)
Rashad, M., Tekin, H., Zakaly, H.M., Pyshkina, M., Issa, S.A., Susoy, G.: Physical and nuclear shielding properties of newly synthesized magnesium oxide and zinc oxide nanoparticles. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 52(9), 2078–2084 (2020)
Huang, Y., Sun, Y., Wang, W.-W., Zhang, L.: Boeravinone B a natural rotenoid exerts anticancer activity via inducing internalization and degradation of inactivated EGFR and ErbB2 in human colon cancer cells. Am. J. Transl. Res. 10(12), 4183 (2018)
Shah, M., Nawaz, S., Jan, H., Uddin, N., Ali, A., Anjum, S., et al.: Synthesis of bio-mediated silver nanoparticles from Silybum marianum and their biological and clinical activities. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 112, 110889 (2020)
Singh, B.N., Rawat, A.K.S., Khan, W., Naqvi, A.H., Singh, B.R.: Biosynthesis of stable antioxidant ZnO nanoparticles by Pseudomonas aeruginosa rhamnolipids. PLoS ONE 9(9), e106937 (2014)
Das, D., Nath, B.C., Phukon, P., Dolui, S.K.: Synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles and evaluation of antioxidant and cytotoxic activity. Colloids. Surf. B Biointerfaces 111, 556–560 (2013)
Abinaya, C., Mayandi, J., Osborne, J., Frost, M., Ekstrum, C., Pearce, J.M.: Inhibition of growth of S. epidermidis by hydrothermally synthesized ZnO nanoplates. Mater. Res. Express. 4(7), 075401 (2017)
Mukherjee, M.: Human digestive and metabolic lipases—a brief review. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 22(5–6), 369–376 (2003)
Kusirisin, W., Srichairatanakool, S., Lerttrakarnnon, P., Lailerd, N., Suttajit, M., Jaikang, C., et al.: Antioxidative activity, polyphenolic content and anti-glycation effect of some Thai medicinal plants traditionally used in diabetic patients. Med. Chem. 5(2), 139–147 (2009)
Kumar, M., Sikri, N., Chahal, S., Sharma, J., Sharma, B., Yadav, P., Bhardwaj, M., et al.: Urease inhibitory kinetic studies of various extracts and pure compounds from Cinnamomum genus. Molecules 26(13), 3803 (2021)
Nisar, M., Khan, S.A., Qayum, M., Khan, A., Farooq, U., Jaafar, H.Z., et al.: Robust synthesis of ciprofloxacin-capped metallic nanoparticles and their urease inhibitory assay. Molecules 21(4), 411 (2016)
Mechchate, H., Es-Safi, I., Louba, A., Alqahtani, A.S., Nasr, F.A., Noman, O.M., Farooq, M., et al.: In vitro alpha-amylase and alpha-glucosidase inhibitory activity and in vivo antidiabetic activity of Withania frutescens L. foliar extract. Molecules 26(2), 293 (2021)
Singh, T.A., Sharma, A., Tejwan, N., Ghosh, N., Das, J., Sil, P.C.: A state of the art review on the synthesis, antibacterial, antioxidant, antidiabetic, and tissue regeneration activities of zinc oxide nanoparticles. Adv. Colloid. Interface Sci. 295, 102495 (2021)
Umrani, R.D., Paknikar, K.M.: Zinc oxide nanoparticles show antidiabetic activity in streptozotocin-induced Type 1 and 2 diabetic rats. Nanomedicine 9(1), 89–104 (2014)
Hayat, A., Haider, W., Raza, Y., Marty, J.L.: Colorimetric cholesterol sensor based on peroxidase like activity of zinc oxide nanoparticles incorporated carbon nanotubes. Talanta 143, 157–161 (2015)
Gu, B., Xu, C., Zhu, G., Liu, S., Chen, L., Wang, M., et al.: Layer by layer immobilized horseradish peroxidase on zinc oxide nanorods for biosensing. J. Phys. Chem. B. 113(18), 6553–6557 (2009)
Aula, S., Lakkireddy, S., Swamy, A., Kapley, A., Jamil, K., Tata, N.R., et al.: Biological interactions in vitro of zinc oxide nanoparticles of different characteristics. Mater. Res. Express. 1(3), 035041 (2014)
Ali, S.S., Morsy, R., El-Zawawy, N.A., Fareed, M.F., Bedaiwy, M.Y.: Synthesized zinc peroxide nanoparticles (ZnO2-NPs): a novel antimicrobial, anti-elastase, anti-keratinase, and anti-inflammatory approach toward polymicrobial burn wounds. Int. J. Nanomed. 12, 6059 (2017)
Jahan, I., Erci, F., Isildak, I.: Rapid green synthesis of non-cytotoxic silver nanoparticles using aqueous extracts of ‘Golden Delicious’ apple pulp and cumin seeds with antibacterial and antioxidant activity. SN Appl. Sci. 3(1), 1–14 (2021)
Khalil, A.T., Ovais, M., Ullah, I., Ali, M., Shinwari, Z.K., Khamlich, S., et al.: Sageretia thea (Osbeck.) mediated synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles and its biological applications. Nanomedicine 12(15), 1767–1789 (2017)
Manke, A., Wang, L., Rojanasakul, Y.: Mechanisms of nanoparticle-induced oxidative stress and toxicity. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 1–15 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/942916
Bexiga, M.G., Varela, J.A., Wang, F., Fenaroli, F., Salvati, A., Lynch, I., et al.: Cationic nanoparticles induce caspase 3-, 7-and 9-mediated cytotoxicity in a human astrocytoma cell line. Nanotoxicology 5(4), 557–567 (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HA conceptualize, prepared, and compile the manuscript. Resources were provided by BHA, NGG and MZ. JSA helped in conceptualization the experiment and assisted in biological assays. SD, JP and CL done all the cell viability assay while BM and JI assisted during the whole experiment. AA and MN help in final editing of the article and supervision of research was done by BHA. CH, AA, SD and HB performed activities, CH and NGG reviewed the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The current study was ethically approved by Quaid-i-azam University, Islamabad, Bioethical committee.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ashraf, H., Meer, B., Iqbal, J. et al. Comparative evaluation of chemically and green synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles: their in vitro antioxidant, antimicrobial, cytotoxic and anticancer potential towards HepG2 cell line. J Nanostruct Chem 13, 243–261 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40097-021-00460-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40097-021-00460-3