Abstract
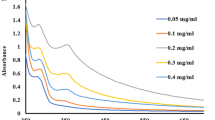
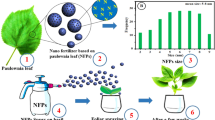
Nanofertilizers have gained more interest in the agricultural sector for enhancing the crop production. In addition, bionanofertilizers are eco-friendly when compared to the chemical fertilizers. Two diazotrophic Azospirillum strains were isolated and characterized from soil samples in the present study. Then, Azospirillum-capped ZnO NPs (As-ZnO NPs) was green synthesized and characterized by bio-physical techniques. UV–Vis spectrum exhibited an absorbance peak at 386 nm. The presence of diffraction peak in XRD indicates the pure crystalline form of As-ZnO NPs. The various functional molecules involved in the bioreduction of Zn+ to ZnO were noticed through FTIR spectroscopy. SEM micrograph confirmed the presence of spherical nanostructures with a mean size of 20.6 nm. A significant increase in the seed germination rate (95%) and leaf area index (LAI) (45.6%) was observed in strain 2-mediated ZnO NPs at 30 days after treatment (DAT). Similarly, following treatment with strain 2-mediated ZnO NPs (T4), the number of roots, root length, shoot length, fresh weight and dry weight were 8.4, 9.6 cm, 21.4 cm, 2.05 g, and 0.915 g, respectively. Treatment with strain 2-mediated ZnO NPs (T4), the chlorophyll A, B and AB, and carotenoid contents were 4.445, 10.36 and 10.98, and 11.08 mg g−1, respectively. The results showed that As-ZnO NPs were potential nanofertilizer and could be used in agriculture for sustainable food production. In addition, the developed nanofertilizers are eco-friendly and do not harm the environment when compared to chemical fertilizers.







Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Available.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Hulakoti, N.I., Taranath, T.C.: Biosynthesis of nanoparticles using microbes: a review. Colloids Surf. Biol. Interfaces. 121, 474–483 (2014)
Cassán, F., Díaz-Zorita, M.: Azospirillum sp. in current agriculture: from the laboratory to the field. Soil Biol. Biochem. 103, 117–130 (2016)
Sharma, A., Patni, B., Shankhdhar, D., Shankhdhar, S.C.: Zinc—an indispensable micronutrient. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants. 19(1), 11–20 (2013)
Youssef, M.M.A., Eissa, M.F.M.: Biofertilizers and their role in management of plant parasitic nematodes: a review. E3 J. Biotechnol. Pharm. Res. 5, 1–6 (2014)
Maikozhundan, B., Vinodhini, J.: Nanopesticidal effects of Pongamia pinnata leaf extract coated zinc oxide nanoparticle against the Pulse beetle Callosobruchus maculatus. Mater. Today Commun. 14, 106–115 (2018)
Malaikozhundan, B., Vaseeharan, B., Vijayakumar, S., Merlin, P.T.: Bacillus thuringiensis coated zinc oxide nanoparticle and its biopesticidal effects on the Pulse beetle, Callosobruchus maculatus. J. Photochem. Photobiol. 174, 306–314 (2017)
Ahmad, F., Ahmad, I., Khan, M.S.: Screening of free-living rhizospheric bacteria for their multiple plant growth promoting activities. Microbiol. Res. 163, 173–181 (2008)
Sharma, S. D., Kumar, P., Raj, H., Bhardwaj, S. K.: Isolation of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and Azotobacter chroococcum from local litchi orchards and evaluation of their activity in the air-layers system. Sci. Hortic. 123, 117–123 (2009)
Malaikozhundan, B., Vinodhini, J., Rajamohamed Kalanjiam, M., Vinotha, V., Palanisamy, S., Vijayakumar, S., Vaseeharan, B., Mariyappan, A.: High synergistic antibacterial, antibiofilm, antidiabetic and antimetabolic activity of Withania somnifera leaf extract-assisted zinc oxide nanoparticle. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2020(43), 1533–1547 (2020)
Malaikozhundan, B., Vaseeharan, B., Vijayakumar, S., Sudhakaran, R., Gobi, N., Shanthini, G.: Antibacterial and antibiofilm assessment of Momordica charantia fruit extract coated silver nanoparticle. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 8, 189–196 (2016)
Rajiv, P., Vanathi, P.: Effect of Parthenium based vermicompost and zinc oxide nanoparticles on growth and yield of Arachis hypogaea L. in zinc deficient soil. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 13, 251–257 (2018)
Megali, L., Glauser, G., Rasmann, S.: Fertilization with beneficial microorganisms decreases tomato defenses against insect pests. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 34, 649–656 (2014)
Bergey, D.H., Holt, J.G.: Bergey's Manual of Determinative Bacteriology. 9th Edn, Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, Maryland (1994)
Sahoo, R.K., Ansari, M.W., Pradhan, M., Dangar, T.K., Mohanty, S., Tuteja, N.: Phenotypic and molecular characterization of efficient native Azospirillum strains from rice fields for crop improvement. Protoplasma 251, 943–953 (2014)
Sinha, R.K., Valani, D., Chauhan, K., Agarwal, S.: Embarking on a second green revolution for sustainable agriculture by vermiculture biotechnology using earthworms: reviving the dreams of Sir Charles Darwin. Int. J. Agric. Health Saf. 1, 50–64 (2014)
Gupta, G., Parihar, S.S., Ahirwar, N.K., Snehi, S.K., Singh, V.: Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR): current and future prospects for development of sustainable agriculture. J. Microb. Biochem. Technol. 7, 96–102 (2015)
Chauhan, H.S., Bagyaraj, D.J., Selvakumar, G., Sundaram, S.P.: Novel plant growth promoting rhizobacteria—prospects and potential. Appl. Soil Ecol. 95, 38–53 (2015)
Andrews, D., Nann, T., Lipson, R.H.: Comprehensive nanoscience and nanotechnology. Academic Press, Cambridge (2019)
Pestovsky, Y.S., Martínez-Antonio, A.: The use of nanoparticles and nanoformulations in agriculture. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 17, 8699–8730 (2017)
Peters, R., Brandhoff, P., Weigel, S., Marvin, H., Bouwmeester, H., Aschberger, K., et al.: Inventory of nanotechnology applications in the agricultural, feed and food sector, p. 11. EFSA Supporting Publications, Parma (2014)
Adisa, I.O., Pullagurala, V.L.R., Peralta-Videa, J.R., Dimkpa, C.O., Elmer, W.H., Gardea-Torresdey, J.L., et al.: Recent advances in nano-enabled fertilizers and pesticides: a critical review of mechanisms of action. Environ. Sci. Nano 6, 2002–2030 (2019)
Shang, Y., Hasan, M.K., Ahammed, G.J., Li, M., Yin, H., Zhou, J.: Applications of nanotechnology in plant growth and crop protection: a review. Molecules 24, 2558–2580 (2019)
Kupryashina, M.A., Vetchinkina, E.P., Burov, A.M., Ponomareva, E.G., Nikitina, V.E.: Biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles by Azospirillum brasilense. Microbiology 82(6), 833–840 (2013)
Shamsuzzaman, A., Mashrai, H., Khanam, R.N., Aljawfi, R.N.: Biological synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using C. albicans and studying their catalytic performance in the synthesis of steroidal pyrazolines. Arab. J. Chem. 10(2), S1530–S1536 (2013)
Kalia, A., Sharma, S.P., Kaur, H.: Nanoscale fertilizers: harnessing boons for enhanced nutrient use efficiency and crop productivity. In: Abd-Elsalam, K.A., Prasad, R. (eds.) Nanobiotechnology applications in plant protection nanotechnology in the life sciences, vol. 2, pp. 191–208. Springer, Cham (2019)
Jyothi, T.V., Hebsur, N.S.: Effect of nanofertilizers on growth and yield of selected cereals—a review. Agric. Rev. 38, 112–120 (2017)
Kalia, A., Sharma, S.P.: Nanomaterials and vegetable crops: realizing the concept of sustainable production. In: Pudake, R.N., Chauhan, N., Kole, C. (eds.) Nanoscience for sustainable agriculture, pp. 323–353. Springer, Cham (2019)
Kah, M., Kookana, R.S., Gogos, A., Bucheli, T.D.: A critical evaluation of nanopesticides and nanofertilizers against their conventional analogues. Nat. Nanotechnol. 13, 677–684 (2018)
Yusefi-Tanha, E., Fallah, S., Rostamnejadi, A., Pokhrel, L.R.: Particle size and concentration dependent toxicity of copper oxide nanoparticles (CuONPs) on seed yield and antioxidant defense system in soil grown soybean (Glycine max cv. Kowsar). Sci. Total Environ. 715, 136994 (2020)
Mahil, E.I.T., Kumar, B.A.: Foliar application of nanofertilizers in agricultural crops—ā review. J. Farm Sci. 32(3), 239–249 (2019)
Du, W., Yang, J., Peng, Q., Liang, X., Mao, H.: Comparison study of zinc nanoparticles and zinc sulphate on wheat growth: from toxicity and zinc biofortification. Chemosphere 227, 109–116 (2019)
Munir, T., Rizwan, M., Kashif, M., Shahzad, A., Ali, S., Amin, N., Zahid, R., Alam, M.F.E., Imran, M.: Effect of zinc oxide nanoparticles on the growth and Zn uptake in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) by seed priming method. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biosyst. 13, 315–323 (2018)
Salama, D.M., Osman, S.A., Abd El-Aziz, M.E., Elwahed, M.S.A.A., Shaaban, E.A.: Effect of zinc oxide nanoparticles on the growth, genomic DNA, production and the quality of common dry bean (Phaseolus vulgaris). Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 18, 1–8 (2019)
Prasad, R., Bhattacharyya, A., Nguyen, Q.D.: Nanotechnology in sustainable agriculture: recent developments, challenges, and perspectives. Front. Microbiol. 8, 1014 (2017)
El-Ramady, H.R., Alshaal, T.A., Shehata, S.A., Domokos-Szabolcsy, E., Elhawat, N., Prokisch, J., Fari, M., Marton, L.: Plant nutrition: from liquid medium to micro-farm. In: Ozier-Lafontaine, H., Lesueur-Jannoyer, M. (eds.) Sustainable agriculture reviews 14 (agroecology and global change), sustainable agriculture reviews, vol. 14, pp. 449–508. Springer, Cham (2014)
Solanki, P., Bhargava, A., Chhipa, H., Jain, N., Panwar, J.: Nano-fertilizers and their smart delivery system in agriculture. In: Nanoscience in food and agriculture, pp. 81–101. Springer, Berlin (2016)
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Professor and Head, Department of Biology, The Gandhigram Rural Institute (Deemed to be University), Gandhigram for his support to perform this research. The authors gratefully acknowledge the Department of Chemistry, The Gandhigram Rural Institute (Deemed to be University), Gandhigram for their support in SEM analysis.
Funding
No funding sources.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
NM: conceptualization, design, methodology, and writing original draft, SA: investigation, methodology, data curation, and formal analysis, BM: writing—review and editing, statistics, TB: methodology, software, review and editing. All the authors approved the final version of this manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All the co-authors have given consent for publication in the journal.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manivannan, N., Aswathy, S., Malaikozhundan, B. et al. Nano-zinc oxide synthesized using diazotrophic Azospirillum improves the growth of mung bean, Vigna radiata. Int Nano Lett 11, 405–415 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40089-021-00351-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40089-021-00351-z