Abstract
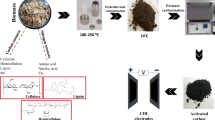
Permeable carbon atoms or aerogels support novel electrode materials. It is essential to improve the wetting surface area of carbon electrode for higher Capacitive Deionization (CDI) potency. To enhance the wettability of CDI electrodes, poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) binder (a water-soluble polymer) was used to fabricate the carbon electrodes, followed by the cross-linking of PVA with Glutaric Acid (GA). Morphological characteristics of modified electrodes were ascertained by Scanning Electron Microscopy. The primary purpose of this work is to investigate the desalting performance of PVA-bonded carbon electrodes by arranging a modified electrode with activated carbon powder and to observe its efficiency at a varied initial concentration of salt (400–1000 ppm). This makes CDI a feasible and economical means for the desalination of brackish water. The energy consumption during experiments was low, i.e., 2–5 kWh/m3 of desalted wastewater.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. F. Service, Desalination freshens up. Science 313, 1088 (2006)
A.S. Yasin, I.M.A. Mohamed, M.T. Amen, N.A.M. Barakat, C.H. Park, C.S. Kim, Incorporating zirconia nanoparticles into activated carbon as electrode material for capacitive deionization. J. Alloys Compd. 772, 1079 (2019)
W. Suwaileh, D. Johnson, N. Hilal, Brackish water desalination for agriculture: assessing the performance of inorganic fertilizer draw solutions. Desalination 456, 53 (2019)
R. Semiat, Energy issues in desalination processes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 42(22), 8193 (2008)
Y. Tanaka, Development of a computer simulation program of batch ion-exchange membrane electrodialysis for saline water desalination. Desalination 320, 118 (2013)
D.E. Sachit, J.N. Veenstra, Analysis of reverse osmosis membrane performance during desalination of simulated brackish surface waters. J. Memb. Sci. 453, 136 (2014)
G. Naidu, S. Jeong, Y. Choi, E. Jang, T.M. Hwang, S. Vigneswaran, Application of vacuum membrane distillation for small scale drinking water production. Desalination 354, 53 (2014)
S. Zhao, L. Zou, D. Mulcahy, Brackish water desalination by a hybrid forward osmosis-nanofiltration system using divalent draw solute. Desalination 284, 175 (2012)
X. Sun, H. Lu, J. Wang, Brackish water desalination using electro-deionization reversal. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 104, 262 (2016)
D. Liu, X. Ning, Y. Hong, Y. Li, Q. Bian, J. Zhang, Covalent triazine-based frameworks as electrodes for high-performance membrane capacitive deionization. Electrochim. Acta 296, 327 (2019)
D. He, C.E. Wong, W. Tang, P. Kovalsky, T. David Waite, Faradaic reactions in water desalination by batch-mode capacitive deionization. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 3(5), 222 (2016)
Z. Sun et al., Capacitive deionization of chloride ions by activated carbon using a three-dimensional electrode reactor. Sep. Purif. Technol. 191, 424 (2018)
Y. Gao et al., Electrosorption behavior of cations with carbon nanotubes and carbon nanofibres composite film electrodes. Thin Solid Films 517(5), 1616 (2009)
Y. Bian, P. Liang, X. Yang, Y. Jiang, C. Zhang, X. Huang, Using activated carbon fiber separators to enhance the desalination rate of membrane capacitive deionization. Desalination 381, 95 (2016)
R. Kumar et al., Carbon aerogels through organo-inorganic co-assembly and their application in water desalination by capacitive deionization. Carbon 99, 375 (2016)
S. Porada, R. Zhao, A. Van Der Wal, V. Presser, P.M. Biesheuvel, Review on the science and technology of water desalination by capacitive deionization. Prog. Mater Sci. 58(8), 1388 (2013)
W. Tang et al., Various cell architectures of capacitive deionization: recent advances and future trends. Water Res. 150, 225 (2019)
K. Singh, S. Porada, H.D. de Gier, P.M. Biesheuvel, L.C.P.M. de Smet, Timeline on the application of intercalation materials in Capacitive Deionization. Desalination 455, 115 (2019)
B.H. Park, Y.J. Kim, J.S. Park, J. Choi, Capacitive deionization using a carbon electrode prepared with water-soluble poly(vinyl alcohol) binder. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 17(4), 717 (2011)
J.Y. Choi, J.H. Choi, A carbon electrode fabricated using a poly(vinylidene fluoride) binder controlled the Faradaic reaction of carbon powder. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 16(3), 401–405 (2010)
A. Siekierka, M. Bryjak, Novel anion exchange membrane for concentration of lithium salt in hybrid capacitive deionization. Desalination 452, 279 (2019)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the research Grant provided by National Institute of Technology, Raipur (C.G.)-India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, A.S., Ghime, D. & Ghosh, P. Poly(Vinyl Alcohol)-Bonded Carbon Electrodes for Desalination of Brackish Water Using Capacitive Deionization. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. E 101, 125–131 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40034-020-00165-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40034-020-00165-2