Abstract
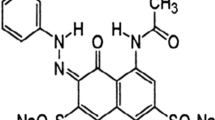
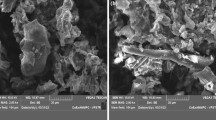
In the present study, removal of synozol ds red dye from waste water using treated Turbinaria vulgaris (T. vulgaris) was investigated. The biosorbent morphology, functional groups presence before biosorption and shifting of groups after the biosorption were analyzed by Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR). Response Surface Methodology (RSM) was used for the optimization of the selected parameters like pH (3–8), initial dye (20–100 mg L−1) and biosorbent dosage (0.1–0.5 g). The variables, impact on the removal of synozol ds red was analyzed from 3D graphs. The findings were well suited by Langmuir isotherm and pseudo-second-order models and the maximum biosorbent coverage was 30.3 mg g−1. Intraparticle and liquid film diffusion were rate limiting steps in the removal of synozol ds red. Therefore, treated T.vulgaris could be utilized as potential biosorbent for elimination of coloring agents from textile industrial effluents.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. Thiyagarajan, P. Saravanan, S. Shiyamaladevi, P. Saranya, N. Nagendra Gandhi, S. Renganathan, Biosorption of reactive red 2 using positively charged Metapenaeus monoceros shells. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jscs.2013.05.004
D. Sidra Ilyas, A. Bukhari, A. Rehman, Decolorization of synozol red 6HBN by yeast, Candida tropicalis 4S, isolated from industrial wastewater. Pakistan J. Zool 47, 1181–1185 (2015)
X. Chen, Z. Wu, D. Liu, Z. Gao, Preparation of ZnO photocatalyst for the efficient and rapid photocatalytic degradation of azo dyes. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 12, 1 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-017-1904-4
A.N. Soon, B.H. Hameed, Heterogeneous catalytic treatment of synthetic dyes in aqueous media using Fenton and photo-assisted Fenton process. Desalination 269, 1–16 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2010.11.002
V.R. Pereira, A.M. Isloor, U.K. Bhat, A.F. Ismail, A. Obaid, H.K. Fun, Preparation and performance studies of polysulfone-sulfated nano-titania (S-TiO2) nanofiltration membranes for dye removal. RSC Adv. 5, 53874–53885 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA07994B
M.X. Zhu, L. Lee, H.H. Wang, Z. Wang, Removal of an anionic dye by adsorption/precipitation processes using alkaline white mud. J. Hazard. Mater. 149, 735–741 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.04.037
S. Kuppusamy, K. Venkateswarlu, P. Thavamani, Y.B. Lee, R. Naidu, M. Megharaj, Quercusrobur a corn peel as a novel coagulating adsorbent for cationic dye removal from aquatic ecosystems. Ecol. Eng. 101, 3–8 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2017.01.014
J. Ooi, L.Y. Lee, B.Y.Z. Hiew, S. Thangalazhy-Gopakumar, S.S. Lim, S. Gan, Assessment of fish scales waste as a low cost and eco-friendly adsorbent for removal of an azo dye: Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Bioresour. Technol. 245, 656–664 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.08.153
T. Ahmad, M. Danish, M. Rafatullah, A. Ghazali, O. Sulaiman, R. Hashim, M. Nasir, M. Ibrahim, The use of date palm as a potential adsorbent for wastewater treatment: a review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 19, 1464–1484 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-011-0709-8
A.S. Sartape, A.M. Mandhare, V.V. Jadhav, P.D. Raut, M.A. Anuse, S.S. Kolekar, Removal of malachite green dye from aqueous solution with adsorption technique using Limoniaacidissima (wood apple) shell as low cost adsorbent. Arab. J. Chem. 10, S3229–S3238 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2013.12.019
I. Anastopoulosa, G.Z. Kyzas, Agricultural peels for dye adsorption: a review of recent literature. J. Mol. Liq. 200, 381–389 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2014.11.006
V. Karthik, K. Saravanan, C. Patra, B. Ushadevi, S. Vairam, N. Selvaraju, Biosorption of acid yellow 12 from simulated wastewater by non-viable T. harzianum: kinetics, isotherm and thermodynamic studies. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 16, 6895–6906 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-2073-4
Y.A.R. Moreira, L.V.S. Santos, Studies on dye biosorption enhancement by chemically modified Fucus vesiculosus, Spirulina maxima and Chlorella pyrenoidosa algae. J. Clean. Prod. 240, 118197 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118197
J.Y. Chin, L.M. Chng, S.S. Leong, S.P. Yeap, N.H.M. Yasin, P.Y. Toh, Removal of synthetic Dye by Chlorella vulgaris microalgae as natural adsorbent. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 45(9), 7385–7395 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04557-9
X. Zhang, J. Zhou, Y. Fan, J. Liu, Adsorption of dyes from water by Prunella vulgaris stem and subsequent fungal decolorization. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 37(9), 1445–1452 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-020-0601-7
S.S. Moghaddam, M.R.A. Moghaddam, M. Arami, Coagulation/ flocculation process for dye removal using sludge from water treatment plant: optimization through response surface methodology. J. Hazard. Mater. (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.10.058
S. Chatterjee, A. Kumar, S. Basu, S. Dutta, Application of response surface methodology for Methylene Blue dye removal from aqueous solution using low-cost adsorbent. Chem. Eng. J. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1177/0263617416675625
A. Witek-Krowiak, K. Chojnacka, D. Podstawczyk, A. Dawiec, K. Pokomeda, Application of response surface methodology and artificial neural network methods in modelling and optimization of biosorption process. Biores. Technol. 160, 150–160 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.01.021
S. Boddu, J.B. Dulla, V.N. Alugunulla, A.A. Khan, An assessment on removal performance of arsenic with treated Turbinaria vulgaris as an adsorbent: characterization, optimization, isotherm, and kinetics study. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 39, 2 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/ep.13313
R.K. Gautam, A. Mudhoo, G. Lofrano, M.C. Chattopadhyaya, Biomass-derived biosorbents for metal ions sequestration: adsorbent modification and activation methods and adsorbent regeneration. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2, 239–259 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2013.12.019
M. Asgher, H.N. Bhatti, Mechanistic and kinetic evaluation of biosorption of reactive azo dyes by free, immobilized and chemically treated Citrus sinensis waste biomass. Ecol. Eng. 36, 1660–1665 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2010.07.003
A.L. Kumar Suranjit Prasad, R. Jaishree Paul, V. Subramanian, R. Prasad, Biosorption of arsenite (As+3) and arsenate (As+5) from aqueous solution by Arthrobacter sp. biomass. Environ. Technol. 34, 2701–2708 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2013.786137
B. Sumalatha, A. Venkata Narayana, D. John Babu, P. Rajasekhar Reddy, K. Anoar Ali, Estimation of biosorption characteristics of chromium (VI) from aqueous and real tannery effluents by treated T. vulgaris: experimental assessment and statistical modelling. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2020.1789617
J.B. Dulla, B. Sumalatha, P. King, P.K. Yekula, Investigation on biosorption of Cd (II) onto Gelidiellaacerosa (brown algae): optimization (using RSM& ANN) and mechanistic studies. Desalination Water Treat. 107, 195–206 (2018). https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2018.22145
J.B. Dulla, M.R. Tamana, S. Boddu, K. Pulipati, K. Srirama, Biosorption of copper (II) onto spent biomass of Gelidiella acerosa (brown marine algae): optimization and kinetic studies. Appl. Water Sci. 10, 1–10 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-019-1125-3
R. Maurya, T. Ghosh, C. Paliwal, A. Shrivastav, K. Chokshi, I. Pancha, S. Mishra, Biosorption of methylene blue by de-oiled algal biomass: equilibrium, kinetics and artificial neural network modelling. PLoS ONE 9(10), e109545 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone
A. Dheetcha, S. Mishra, Biosequestering potential of Spirulina platensis for uranium. Curr Microbiol 57, 508–514 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-008-9277-7
R. Mahesh, M. Gadekar, M. Ahammed, Modelling dye removal by adsorption onto water treatment residuals using combined response surface methodology-artificial neural network approach. J. Environ. Manag. 231, 241–248 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.10.017
J. Sharma, A.S. Chadha, V. Pruthi, P. Anand, J. Bhatia, B.S. Kaith, Sequestration of dyes from artificially prepared textile effluent using RSM-CCD optimized hybrid backbone based adsorbent-kinetic and equilibrium studies. J. Environ. Manag. 190, 176–187 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.12.065
C.A. Igwegbe, L. Mohmmadi, S. Ahmadi, A. Rahdar, D. Khadkhodaiy, R. Dehghani, S. Rahdar, Modeling of adsorption of Methylene blue dye on Ho-CaWO4 nanoparticles using response surface methodology (RSM) and artificial neural network (ANN) techniques. Methods X 6, 1779–1797 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mex.2019.07.016
B. Sumalatha, Y. Prasanna Kumar, K. Kiran Kumar, D. John Babu, A. Venkata Narayana, K. Maria Das, T.C. Venkateswarulu, Removal of Indigo Carmine from aqueous solution by using activated carbon. Res. J. Pharm. Biol. Chem. Sci. 5, 912–922 (2014)
S. Banerjee, M.C. Chattopadhyaya, Adsorption characteristics for the removal of a toxic dye, tartrazine from aqueous solutions by a low-cost agricultural by-product. Arab. J. Chem. 10, S1629-S1638 (2017)
F. Deniz, R.A. Kepekci, Biosorption of dye from synthetic wastewater using alga enriched in phenolic compounds. Environ. Prog. Sustainable Energy 35, 737–742 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/ep.12286
H. Mittal, S.M. Alhassan, S.S. Ray, Efficient organic dye removal from wastewater by magnetic carbonaceous adsorbent prepared from corn starch. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 6, 7119–7131 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JECE.2018.11.010
J.S. Piccin, M. Guterres, N.P.G. Salau, G.L. Dotto, Mass transfer models for the adsorption of Acid Red 357 and Acid Black 210 by tannery solid wastes. Adsorp. Sci. Technol. 35, 300–316 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1177/0263617416675624
Funding
There is no external fundings received for the present research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare they have no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boddu, S., Dulla, J.B., Alugunulla, V.N. et al. Enhanced Sequestration of Synozol ds Red onto Treated Turbinria Vulgaris from Waste Water: Statistical Optimization. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. D 102, 355–365 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40033-021-00271-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40033-021-00271-4