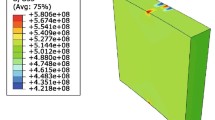
Abstract
Fiber reinforced polymer composite materials with their higher specific strength, moduli and tailorability characteristics will result in reduction of weight of the structure. The composite pressure vessels with integrated end domes develop hoop stresses that are twice longitudinal stresses and when isotropic materials like metals are used for development of the hardware and the material is not fully utilized in the longitudinal/meridional direction resulting in over weight components. The determination of a proper winding angles and thickness is very important to decrease manufacturing difficulties and to increase structural efficiency. In the present study a methodology is developed to understand structural characteristics of filament wound pressure vessels with integrated end domes. Progressive ply wise failure analysis of composite pressure vessel with geodesic end domes is carried out to determine matrix crack failure, burst pressure values at various positions of the shell. A three dimensional finite element analysis is computed to predict the deformations and stresses in the composite pressure vessel. The proposed method could save the time to design filament wound structures, to check whether the ply design is safe for the given input conditions and also can be adapted to non-geodesic structures. The results can be utilized to understand structural characteristics of filament wound pressure vessels with integrated end domes. This approach can be adopted for various applications like solid rocket motor casings, automobile fuel storage tanks and chemical storage tanks. Based on the predictions a composite pressure vessel is designed and developed. Hydraulic test is performed on the composite pressure vessel till the burst pressure.




















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Vf :
-
Volume fraction
- Sr:
-
Strength ratio
- σfH :
-
Fiber strength in helical
- FRP:
-
Fiber reinforced polymer
- β:
-
Slope of the meridional contour
- a:
-
Axial distance
- CLT:
-
Classical lamination theory
- σfφ :
-
Fiber strength in hoop direction
- ϕ:
-
Helical winding angle
- r:
-
Local radius
References
C.C. Liang, H.-W. Chen, C.-H. Wang, Optimum design of dome contour for filament wound composite pressure vessels based on a shape factor. Compos Struct. 58, 469–480 (2002)
C.-U. Kim, I.-H. Kang, C.-S. Hong, C.-G. Kim, Optimal design of filament wound structures under internal pressure based on the semi-geodesic path algorithm. Compos. Struct. 67, 443–452 (2005)
A. Beakou, A. Mohamed, Influence of variable scattering on the optimum winding angle of cylindrical laminated composites. Compos. Struct. 53, 287–293 (2001)
M.Z. Kabir, Finite element analysis of composite pressure vessels with a load sharing metallic liner. Compos. Struct. 49, 247–255 (2000)
A. Nagesh, Finite-element analysis of composite pressure vessels with progressive degradation. Def. Sci. J. 53(1), 75–86 (2003)
S.T. Peters, W.D. Humphrey, R.F. Foral, Filament winding composite structure fabrication (SAMPE, Covina, 1990)
N. Katirci, Design of fiber-reinforced composite pressure vessels, M.S. Thesis, Middle East Technical University, Turkey, 1998
V.A. Bunakov, V.D. Protasov, Composite pressure vessels, structures and design, hand book of composites, vol. 2 (Elsevier, Oxford, 1989), pp. 464–529
U. Icardi, A. Longo, S. Locatto, Assessment of recent theories for predicting failure of composite laminates. Appl. Mech. Rev. 2, 76–86 (2007)
D.L. Logan, Finite element method (Brooks/Cole, Pacific Grove, 2000)
Acknowledgement
The authors are thankful to DRDO for facilitating the research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Madhavi, M., Venkat, R. Predicting Structural Behavior of Filament Wound Composite Pressure Vessel Using Three Dimensional Shell Analysis. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. C 95, 41–50 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40032-014-0094-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40032-014-0094-4