Abstract
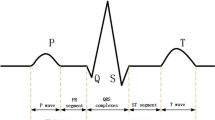
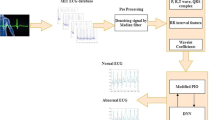
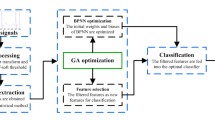
Recently Autosomal Recessive Single Gene (ARSG) diseases are highly effective to the children within the age of 5–10 years. One of the most ARSG disease is a Phenylketonuria (PKU). This single gene disease is associated with mutations in the gene that encodes the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH, Gene 612349). Through this mutation process, PAH of the gene affected patient can not properly manufacture PAH as a result the patients suffer from decreased muscle tone which shows abnormality in EMG signal. Here the extraction of the quality of the PKU affected EMG (PKU-EMG) signal is a keen interest, so it is highly necessary to remove the added ECG signal as well as the biological and instrumental noises. In the Present paper we proposed a method for detection and classification of the PKU affected EMG signal. Here Discrete Wavelet Transformation is implemented for extraction of the features of the PKU affected EMG signal. Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System (ANFIS) network is used for the classification of the signal. Modified Particle Swarm Optimization (MPSO) and Modified Genetic Algorithm (MGA) are used to train the ANFIS network. Simulation result shows that the proposed method gives better performance as compared to existing approaches. Also it gives better accuracy of 98.02% for the detection of PKU-EMG signal. The advantages of the proposed model is to use MGA and MPSO to train the parameters of ANFIS network for classification of ECG and EMG signal of PKU affected patients. The proposed method obtained the high SNR (18.13 ± 0.36 dB), SNR (0.52 ± 1.62 dB), RE (0.02 ± 0.32), MSE (0.64 ± 2.01), CC (0.99 ± 0.02), RMSE (0.75 ± 0.35) and MFRE (0.01 ± 0.02), RMSE (0.75 ± 0.35) and MFRE (0.01 ± 0.02). From authors knowledge, this is the first time a composite method is used for diagnosis of PKU affected patients. The accuracy (98.02%), sensitivity (100%) and specificity (98.59%) helps for proper clinical treatment. It can help for readers/researchers to improve the aforesaid performance for future prospective.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.R. Zurflüh, J. Zschocke, M. Lindner, F. Feillet, C. Chery, A. Burlina, R.C. Stevens, B. Thöny, N. Blau, Molecular genetics of tetrahydrobiopterin-responsive phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency. Hum. Mutat. 29, 167–175 (2008)
R. Koch, B. Burton, G. Hoganson, R. Peterson, W. Rhead, B. Rouse, R. Scott, J. Wolff, A.M. Stern, F. Guttler, M. Nelson, F. de la Cruz, J. Coldwell, R. Erbe, M.T. Geraghty, C. Shear, J. Thomas, C. Azen, Phenylketonuria in adulthood: a collaborative study. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 25, 333–346 (2002)
R. Matalon, P. Justice, M.N. Deanching, Phenylalanine hydroxylase in human placenta: novel system for study of phenylketonuria. (Letter). Lancet 309, 853–854 (1977). Note: Originally Volume I
S.L.C. Woo, Personal Communication. Houston, Tex. 1/11/1983
A.S. Lidsky, F.D. Ledley, A.G. DiLella, S.C.M. Kwok, S.P. Daiger, K.J.H. Robson, S.L.C. Woo, Extensive restriction site polymorphism at the human phenylalanine hydroxylase locus and application in prenatal diagnosis of phenylketonuria. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 37, 619–634 (1985)
A.G. DiLella, W.-M. Huang, S.L.C. Woo, Screening for phenylketonuria mutations by DNA amplification with the polymerase chain reaction. Lancet 331, 497–499 (1988). Note: Originally Volume I
S.J. Ramus, S.M. Forrest, R.G.H. Cotton, Illegitimate transcription of phenylalanine hydroxylase for detection of mutations in patients with phenylketonuria. Hum. Mutat. 1, 154–158 (1992)
V. Abadie, J. Jaruzelska, S. Lyonnet, P. Millasseau, M. Berthelon, F. Rey, A. Munnich, J. Rey, Illegitimate transcription of the phenylalanine hydroxylase gene in lymphocytes for identification of mutations in phenylketonuria. Hum. Molec. Genet. 2, 31–34 (1993)
L. Kalaydjieva, B. Dworniczak, V. Kucinskas, V. Yurgeliavicius, E. Kunert, J. Horst, Geographical distribution gradients of the major PKU mutations and the linked haplotypes. Hum. Genet. 86, 411–413 (1991)
S.M. Forrest, H.H. Dahl, D.W. Howells, I. Dianzani, R.G.H. Cotton, Mutation detection in phenylketonuria by using chemical cleavage of mismatch: importance of using probes from both normal and patient samples. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 49, 175–183 (1991). Note: Erratum: Am. J. Hum. Genet. 50: 659 only, 1992
A.J. Haig, J.B. Gelblum, J.J. Rechtien, A.J. Gitter, Technology assessment: the use of surface EMG in the diagnosis and treatment of nerve and muscle disorders. Muscle Nerve 9, 392–395 (1996)
D. Gross, A. Grassino, W.R.D. Ross, P.T. Macklem, Electromyogram pattern of diaphragmatic fatigue. Appl. Physiol. 46, 1–7 (1979)
R. Merletti, Politecnico di Torino. Int. Soc. Electrophysiol. Kinesiol. (ISEK) 9(1), 3–4 (1999)
J. Pan, W. Tompkins, A real-time QRS detection algorithm. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 32, 230–236 (1985)
S. Levine, J. Gillen, P. Weiser, M. Gillen, E. Kwatny, Description and validation of an ECG removal procedure for EMGdi power spectrum analysis. Appl. Physiol. 60, 1073–1081 (1986)
J.D.M. Drake, J.P. Callaghan, Elimination of electrocardiogram contamination from electromyogram signals: an evaluation of currently used removal techniques. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 16, 175–187 (2006)
P. Zhou, M. Lowery, R. Weir, T. Kuiken, Elimination of ECG artifacts from myoelectric prosthesis control signals developed by targeted muscle reinnervation, in 27th Conference on Engineering in Medicine and Biology, Shanghai, pp. 5276–5279 (2005)
H. Liang, Z. Lin, F. Yin, Removal of ECG contamination from diaphragmatic EMG by nonlinear filtering. Nonlinear Anal. 63, 745–753 (2005)
Y. Hu, J. Mak, H. Liu, K.D.K. Luk, ECG cancellation for surface electromyography measurement using independent component analysis, in International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, New Orleans, pp. 3235–3238 (2007)
C.K.S. Vijila, C.E.S. Kumar, Cancellation of ECG in electromyogram using back propagation network, in International Conference on Advances in Recent Technologies in Communication and Computing, Kottayam, Kerala, pp. 630–634 (2009)
C.K.S. Vijila, C.E.S. Kumar, Interference cancellation in EMG signal using ANFIS. Recent Trends in Eng. 2, 244–248 (2009)
M. Redfern, R. Hughes, D. Chaffin, High-pass filtering to remove electrocardiographic interference from torso EMG recordings. Clin. Biomech. 8, 44–48 (1993)
T.W. Schweitzer, J.W. Fitzgerald, J.A. Bowden, P. Lynne-Davies, Spectral analysis of human inspiratory diaphragmatic electromyograms. J. Appl. Physiol. Respir. Environ. Exerc. Physiol. 46(1), 152–165 (1979)
N.D. Panagiotacopulos, J.S. Lee, M.H. Pope, K. Friesen, Evaluation of EMG signals from rehabilitated patients with lower back pain using wavelets. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 8(4), 269–278 (1998)
C. Roberts, A. Bartolo, R. Dzwonczyk, E. Goldman, Analysis of diaphragm EMG signals: comparison of gating vs. subtraction for removal of ECG contamination. J. Appl. Physiol. 80(6), 1892–1902 (1996)
S. Levine, J. Gillen, P. Weiser, M. Gillen, E. Kwatny, Description and validation of an ECG removal procedure for EMGdi power spectrum analysis. J. Appl. Physiol. 60, 1073–1081 (1986)
G. Lu, J.-S. Brittain, P. Holland, J. Yianni, A.L. Green, J.F. Stein, T.Z. Aziz, S. Wang, RemovingECG noise from surface EMG signals using adaptive filtering. Neurosci. Lett. 462(1), 14–19 (2009)
J. Drake, J. Callaghan, Elimination of electrocardiogram contamination from electromyogram signals: an evaluation of currently used removal techniques. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 16(2), 175–187 (2006)
S. Sanei, T.K.M. Lee, V. Abolghasemi, A new adaptive line enhancer based on singular spectrum analysis. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 59(2), 428–434 (2012)
I. Christov, I. Daskalov, Filtering of electromyogram artifacts from the electrocardiogram. Med. Eng. Phys. 21(10), 731–736 (1999)
M. Nitzken, N. Bajaj, S. Aslan, Local wavelet-based filtering of electromyographic signals to eliminate the electrocardiographic-induced artifacts in patients with spinal cord injury. J. Biomed. Sci. Eng. 6(7B), 1–32 (2013)
B. Azzerboni, Neural-ICA and wavelet transform for artifacts removal in surface EMG, in Proceedings of the IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, vol. 4, pp. 3223–3228 (2004)
J.N.F. Mak, Y. Hu, K.D.K. Luk, An automated ECG-artifact removal method for trunk muscle surface EMG recordings. Med. Eng. Phys. 32(8), 840–848 (2010)
X. Ren, Z. Yan, Z. Wang, X. Hu, Noise reduction based on ICA decomposition and wavelet transform for the extraction of motor unit action potentials. J. Neurosci. Methods 158(2), 313–322 (2006)
N. Willigenburg, A. Daffertshofer, Removing ECG contamination from EMG recordings: a comparison of ICA-based and other filtering procedures. J. Eectromyogr. Kinesiol. 22(3), 485–493 (2012)
N.E. Huang, Z. Shen, S.R. Long, M.C. Wu, H.H. Shih, Q. Zheng, N.-C. Yen, C.C. Tung, H.H. Liu, The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 454(March (1971)), 903–995 (1998)
Z. Wu, N.E. Huang, Ensemble empirical mode decomposition: a noise-assisted data analysis method. Adv. Adapt. Data Anal. 1(01), 1–41 (2009)
N. Miljković, N. Popović, O. Djordjević, L. Konstantinović, T.B. Šekara, ECG artifact cancellation in surface EMG signals by fractional order calculus application. J. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 140, 256–264 (2017)
M. Niegowski, M. Zivanovic, Wavelet-based unsupervised learning method for electrocardiogram suppression in surface electromyograms. Med. Eng. Phys. 38, 248–256 (2016)
J. Barrios-Muriel, F. Romeroa, F.J. Alonsoa, K. Gianikellisb, A simple SSA-based de-noising technique to remove ECG interference in EMG signals. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 30, 117–126 (2016)
S. Abbaspour, M. Lindén, H. Gholamhosseini, ECG artifact removal from surface EMG signal using an automated method based on wavelet-ICA, in: Studies in Health Technology and Informatics, vol. 211. pHealth, pp. 91–97 (2015)
F.R. Hasmin et. al., Wavelet based motion artefact removal for ECG Signals, in IEEE EMBS International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Science (IECBES). IEEE, Langkawi (2012)
S. Mallat, A Wavelet Tour of Signal Processing, 2nd edn. (Academic Press, San Diego, 1999)
S. Abbaspour, A. Fallah, M. Linden, H. Gholamhosseini, A novel approach for removing ECG interferences from surface EMG signals using a combined ANFIS and wavelet. J. Electromyograph. Kinesiol. 26, 52–59 (2016)
J.S.R. Jang, ANFIS: adaptive network based fuzzy inference system. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 23(3), 665–683 (1993)
I. Mukherjee, P.K. Ray, A review of optimization techniques in metal cutting processes. Comput. Ind. Eng. 50(1–2), 15–34 (2006)
A.M. Zain et al., Application of GA to optimize cutting conditions for minimizing surface roughness in end milling machining process. Expert Syst. Appl. 37, 4650–4659 (2010)
F. Musharavati, A.S.M. Hamouda, Modified genetic algorithms for manufacturing process planning in multiple parts manufacturing lines. Expert Syst. Appl. 38, 10770–10779 (2011)
S. Abbaspour, H. Gholamhosseini, M. Linden, Evaluation of wavelet based methods in removing motion artifact from ECG signal, in 16th Nordic-Baltic Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Medical Physics. Sweden: Goutenburg, pp. 1–4 (2014)
M. Valipour, Global experience on irrigation management under different scenarios. J. Water Land Dev. 32(I–Iii), 95–102 (2017)
M. Valipour, A.A. Montazar, An evaluation of SWDC and WinSRFR models to optimize of infiltration parameters in furrow irrigation. American Journal of Scientific Research Issue 69, 128–142 (2012)
M. Valipour, Variations of land use and irrigation for next decades under different scenarios. Irriga, Botucatu, Edição Especial, Irrigação, pp. 262–288, 2016
M. Valipour, How much meteorological information is necessary to achieve reliable accuracy for rainfall estimations? Agriculture 6(53), 1–9 (2016)
M. Valipour, M.E. Banihabib, S.M.R. Behbahani, Comparison of the ARMA, ARIMA, and the autoregressive artificial neural network models in forecasting the monthly inflow of Dez dam reservoir. J. Hydrol. 476, 433–441 (2013)
D.P. Vieroa, M. Valipour, Modeling anisotropy in free-surface overland and shallow inundation flows. Adv. Water Resour. 104, 1–14 (2017)
J. Tealman, S. Van Huffel, A. Spaepen, Wavelet-independent component analysis to remove electrocardiography contamination in surface electromyography, in 29th International Conference on Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, United States (2007)
Y. Hu, J. Mak, H. Liu, K.D.K. Luk, ECG cancellation for surface electromyography measurement using independent component analysis, in International Symposium on Circuits and Systems. IEEE, New Orleans (2007)
J. Taelman, B. Mijovic, S. Van Huffel, S. Devuyst, T. Dutoit, ECG artifact removal from surface EMG signals by combining emperical mode decomposition and independent component analysis, in International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing. Rome, Italy (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohanty, M., Basu, M., Pattanayak, D.N. et al. A Simple Network to Remove Interference in Surface EMG Signal from Single Gene Affected Phenylketonuria Patients for Proper Diagnosis. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. B 99, 109–123 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40031-017-0301-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40031-017-0301-9