Abstract
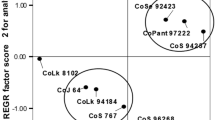
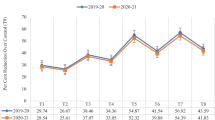
Sorghum shoot fly (Atherigona soccata Rondani), Stem borer (Chilo partellus Swinhoe), Head bug (Calocoris angustatus Lethiery) and midge (Contarinia sorghicola Coquillett) are the most important pests of sorghum in southern region of Tamil Nadu. The results on the field evaluation of popular varieties of sorghum over three years (post rainy or winter 2010–2012) revealed that DSV-4 and CSV-216R for shoot fly, DSV-4, Maulee, CSV-15, K-8, Phule Anuradha and M 35-1 for stem borer, Maulee and K-8 for midge were found to be more resistant and promising. In validation of IPM practices seed treatment with imidacloprid 70 WS @ 3 g/kg of seed + spray of metasystox @ 0.07 % or NSKE @ 5 % at 45 DAE, intercropping with cowpea (4:1)+ seed treatment with imidacloprid 70 WS @ 3 g/kg of seed were effective in reducing the attack of above pests. Intercropping with cowpea (4:1)+ imidacloprid 70 WS @ 3 g/kg of seed was the most effective and recorded the highest ICBR (1:25).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chapke RR, Mishra JS, Subbarayudu B, Hariprasanna K, Patil JV (2011) Sorghum cultivation in Rice Fallows: a Paradigm shift. Bulletin, Directorate of Sorghum research, Hyderabad, p 31
Chapke RR, Sunil Gomashe, Patil JV (2013) Transfer of sorghum entomology-success story. Bulletin, Publication No.4/2012-13/Extn. Directorate of Sorghum research, Hyderabad-30
GOI (2013) Agriculture statistics at a glance. Directorate of Economics and Statistics. Ministry of Agriculture, Government of India, New Delhi
Sharma HC (1985) Strategies for pest control in sorghum in India. Trop Pest Manag 31:167–185
Borad PK, Mittal VP (1983) Assessment of losses caused by pest complex of sorghum hybrid, CSH-5. In: Krishnamurthy Rao BH, Murthy KSRK (eds) Crop losses due to insect pests. Entomological Society of India, Rajendranagar, Hyderabad, pp 271–278
Gahukar RT, Jotwani MG (1980) Present status of field pests of sorghum and millets in India. Trop Pest Manag 26(2):138–151
Daware DG, Bhagwat VR, Ambilwade PP, Kamble RJ (2012) Evaluation of integrated pest management components for the control of sorghum shoot pests in rabi season. Indian J Entomol 74(1):58–61
Padmaja PG, Madhusudhana Seetharama N (2010) Sorghum shoot fly. Directorate of Sorghum research, Hyderabad, p 82
Anandhi P, Sankarapandian R (2013) IPM module for sorghum pest management. In: Patil JV, Chapke RR, Mishra JS, Umakanth AV, Hariprasanna K (eds) Sorghum cultivation—a compendium of improved technologies, vol I. Directorate of Sorghum research, Hyderabad, p 105
Singh BU, Rana BS (1986) Resistance in sorghum to the shoot fly, Atherigona soccata Rondani. Insect Sci Appl 7(5):577–587
Patel GM, Sukhani TR (1990) Biophysical characters associated with shoot fly resistance. Indian J Entomol 52(1):14–17
Sharma HC, Vidyasagar P, Nwanze KF (1993) Effect of host-plant resistance on economic injury levels for the sorghum midge, Contarinia sorghicola. Int J Pest Manag 39(4):435–444
Chikkarugi NM, Balikai RA (2011) Response of sorghum genotypes in shoot pest nursery to major pests. Res J Agric Sci 2(1):21–25
Subbarayudu B, Shyam Prasad G, Kalaisekar A, Bhagwat VR, Aruna C (2011) Evaluation of multiple resistances in sorghum genotypes against shoot fly, Atherigona soccata and stem borer, Chilo partellus. Indian J Entomol 73(1):26–29
Daware DG, Ambilwade PP, Kamble RJ, Bhosle BB (2011) Bio efficacy of insecticides against sorghum shoot fly Atherigona soccata (Rondani). Indian J Entomol 73(3):227–229
Jotwani MG (1983) Chemical control of cereal stem borer. Int J Trop Insect Sci 4(1–2):185–189
Anandhi P, Saravanan L, Ramtake PW, Elamathi S, Simon Sobita, Varma Savita (2012) Characterization of native Bacillus thuringiensis (Berliner) isolates from India. Natl Acad Sci Lett 35:243–247
Pawar VM, Kadam JR (1995) Entomological aspects of integrated pest management in important crops. Maharashtra State Level Conference on Integrated Pest Management, 26th May, 1995
Balikai RA (2003) Integrated pest management for shoot fly (Atherigona soccata Rondani) in rabi sorghum. Agric Sci Digest 23:291–293
Balikai RA, Bhagwat VR (2009) Evaluation of integrated pest management components for the management of shoot fly, shoot bug and aphid in rabi or winter sorghum. Karnataka J Agric Sci 22(3-spl. issue):532–534
Anandhi P, Saravanan L, Elamathi S, Ramtake PW, Savita V, Sobita S (2013) Native Bacillus thuringiensis Berliner isolates with a wide spectrum of activities against cruciferous pests from diverse habitats of India. Biol Agric Hortic 29(3):209–218
Sharma HC, Taneja SL, Leuschner K, Nwanze KF (1992) Techniques to screen sorghum for resistance to insect pests. Information bulletin no. 32 of ICRISAT, Patancheru
Gomez KA, Gomez AA (1984) Statistical procedures for agricultural research. John Wiley and Sons, New York, pp 7–20
Raina AK, Thindwa HZ, Othieno SM, Douglass LW (1984) Resistance in sorghum to sorghum shoot fly (Diptera: Muscidae) oviposition on selected cultivars. J Econ Ent 77(3):648–651
Khurana AD, Verma AN (1985) Some physical plant characters in relation to stem borer and shoot fly resistance in sorghum. Indian J Entomol 47:14–19
Kwesi Ampong-Nyarko KV, Reddy Seshu, Ruth A, Nyangor Saxena KN (1994) Reduction of insect pest attack on sorghum and cowpea by intercropping. Entomol Exp Appl 70(2):179–184
Rossetto CJ, Goncalves W, Diniz JLM (1975) Resistance of variety AF 28 to the sorghum midge, Contarinia sorghicola in the absence of the other varieties Resistencia da variedade AF 28 a mosca do sorgo, contarinia sorghicola, na ausencia de outras variedades. (In Pt.) Anais da Sociedade de Entomologic doBrasil 4:16–20
Franzmann BA (1993) Ovipositional antixenosis to Contarinia sorghicola (Coquillett) (Diptera: Cecidomyiidae) in grain sorghum midge (Diptera; Cecidomyiidae). J Econ Entomol 77:1033–1036
Sharma HC, Vidyasagar P (1994) Antixenosis component of resistance to sorghum midge, Contarinia sorghicola Coq. In Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench. Ann Appl Biol 124:495–507
Balikai RA, Balikai CD, Singh DI, Jirali DI (1998) Screening of Sorghum Genotypes against the Shoot fly, Atherigona soccata Rond. Karnataka J Agric Sci 11(1):208–211
Balikai RA, Biradar BD (2003) Field screening of sorghum entries against shoot fly, Atherigona soccata. Agric Sci Digest 23(4):282–284
Drinkwater TW, Groenewald LH (1994) Comparision of imidacloprid with furathiocarb seed dressing insecticides for the control of black maize beetle, Heteronychus arator Fabriceus (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae) in maize. Crop Prot 13:421–424
Drinkwater TW (1994) Comparision of imidacloprid with carbamate insecticides and the role of planting depth in the control of false wireworms, Somaticus species in maize. Crop Prot 13:341–345
Pons X, Albajes R (2002) Control of maize pests with imidacloprid seed dressing treatment in Catalonia under traditional crop conditions. Crop Prot 21:943–950
Omolo EO, Nyambo B, Simbi COJ, Ollimo P (1993) The role of host plant resistance and intercropping in integrated pest management (IPM) with specific reference to the Oyugis project. Int J Pest Manag 39(3):265–272
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Vice-Chancellor of Tamil Nadu Agricultural University for allowing them to carry out the field experiment at Agricultural Research station, Kovilpatti, Tamil Nadu Agricultural University, Tamil Nadu, India. The authors are also highly thankful to the Director, Directorate of Sorghum Research, Hyderabad under All India Co-Ordinated Sorghum Improvement Project (AICSIP) for providing the financial and technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anandhi, P., Bhagwat, V.R., Elamathi, S. et al. Evaluation of Indian Popular Varieties and Validation of Integrated Pest Management Strategies Against Major Pests of Sorghum. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., India, Sect. B Biol. Sci. 87, 261–266 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40011-015-0593-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40011-015-0593-y