Abstract
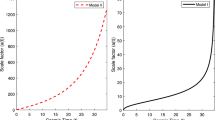
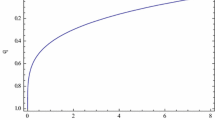
The present study deals with spatially homogeneous and anisotropic axially symmetric Bianchi type-I cosmological model with time variable G and Λ in the presence of bulk viscous fluid. The coefficient of bulk viscosity ζ is considered as a quadratic function of Hubble parameter H (i.e. ζ = ζ 0 + ζ 1 H + ζ 2 H 2, where ζ 0, ζ 1 and ζ 2 are constants). The Einstein’s field equations are solved explicitly by using a law of variation for the Hubble parameter, which gives a constant value of deceleration parameter. The law generates power law and exponential form of average scale factor in terms of cosmic time. The physical and kinematical properties of the models are discussed.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Perlmutter S, Gabi S, Goobar A, Groom DE, Hook IM, Kim AG, Kim MY, Lee JC, Pain R, Pannypackr CR, Small IA, Ellis RS, McMahon RG, Boyle BJ, Bunclark PS, Carter D, Irwin MJ, Glazebrook K, Newberg HJM, Filippenko AV, Mathesson T, Dopita M, Couch WJ (1997) Measurements of the cosmological parameters Ω and Λ from the first seven supernovae at z ≥ 0.35. Astrophys J 483:565–585
Perlmutter S, Aldering G, Della Valle M, Deustua S, Ellis RS, Fabbro S, Fruchter A, Goldhaber G, Groom DE, Hook IM, Kim AG, Kim MY, Knop RA, Lidman C, McMahon RG, Nugent P, Pain R, Panagia N, Pennypacker CR, Ruiz-Lapuente P, Schaefer B, Walton N (1998) Discovery of supernova explosion at half the age of the universe. Nature 391:51–54
Perlmutter S, Aldering G, Goldhaber G, Knop RA, Nugent P, Castro PG, Deustua S, Fabbro S, Goobar A, Groom DE, Hook IM, Kim AG, Kim MY, Lee JC, Nunes NJ, Pain R, Pannypacekr CR, Quimby R, Lidman C, Ellis RS, Irwin M, McMahon RG, Ruiz-Lapuente P, Walton N, Schaefer B, Boyle BJ, Filippenko AV, Matheson T, Fruchter AS, Panagia N, Newberg HJM, Couch WJ, the supernova cosmology project (1999) Measurements of Omega and Lambda from 42 high-redshift supernovae. Astrophys J 517:565–585
Riess AG, Filippenko Challis P, Clocchiatti A, Diercks A, Garnavich PM, Gilliland RL, Hogan CJ, Jha S, Kirshner RP, Leibundgut B, Philips MM, Reiss D, Schmidt BP, Schommer RA, Smith RC, Spyromilio J, Stubbs C, Suntzeff NB, Tonry J (1998) Observational evidence from supernovae for an accelerating universe and a cosmological constant. Astron J 116:1009–1038
Dolgov AD (1983) In: Gibbons GW, Hawking SW, Siklos STC (eds) The very early universe. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, p 449
Chen W, Wu YS (1990) Implication of a cosmological constant varying as R −2. Phys Rev D 41:695–698
Pavon D (1991) Non equilibrium fluctions in cosmic vacuum decay. Phys Rev D 43:375–378
Carvalho JC, Lima JAS, Waga I (1992) Cosmological consequences of a time dependent Λ-term. Phys Rev D 46:2404–2407
Lima JAS, Maia JMF (1994) Deflationary cosmology with decaying vacuum energy density. Phys Rev D 49:5597
Lima JAS, Trodden M (1996) Decaying vacuum energy and deflationary cosmology in open and closed universes. Phys Rev D 53:4280–4286
Arbab AI, Abdel-Rahaman AMM (1994) Nonsingular cosmology with a time dependent cosmological term. Phys Rev D 50:7725–7728
Vishwakarma RG (2001) Study of the magnitude–redshift relation for type 1a supernova in a model resulting from a Ricci-symmetry. Gen Relat Gravit 33:1973–1984
Dirac PAM (1937) The cosmological constant. Nature 139:323
Canuto VM, Narlikar JV (1980) Cosmological tests of the Hoyle–Narlikar conformal gravity. Astrophys J 236:6–23
Abdussattar, Vishwakarma RG (1997) Some FRW models with variable G andΛ. Class Quantum Gravity 14:945–953
Arbab AI (1998) Viscous big bang cosmology with variable G andΛ. Astro-ph/9810213
Arbab AI (1997) Cosmological models with variable cosmological and gravitational constants and bulk viscous models. Gen Relat Gravit 29:61–74
Beesham A (1986) Comment on the paper, the cosmological constant Λ as a possible link to Einstein theory of gravity, the problem of hadronic and creation. Nuovo Cimento B 96:17–20
Kalligas D, Wesson PS, Everitt CWF (1992) Flat FRW models with variable G andΛ. Gen Relat Gravit 24:351–357
Vishwakarma RG (2005) A model to explain varying Λ, G and σ 2 simultaneously. Gen Relat Gravit 37:1305–1311
Bali R, Tinker S (2009) Bianchi type-III bulk viscous barotropic fluid cosmological models with variable G and Λ. Chin Phys Lett 26:029802–029804
Pradhan A, Yadav L, Yadav AK (2005) Generation of Bianchi type-V cosmological models with varying Λ term. Czech J Phys 55:503–518
Saha B (2005) Bianchi type-I universe with viscous fluid. Mod Phys Lett A 20:2127–2144
Singh CP, Beesham A (2010) Anisotropic Bianchi type-V perfect fluid space-time with variable G andΛ. Int J Mod Phys A 25:3824–3825
Singh JP, Pradhan A, Singh AK (2008) Bianchi type-I cosmological models with variable G and Λ term in general relativity. Astrophys Space Sci 314:83–88
Yadav AK, Pradhan A, Singh AK (2012) Bulk viscous Bianchi type-I universe with variable G andΛ. Astrophys Space Sci 337:379–385
Misner CW (1967) Transport processes in the primordial fireball. Nature 214:40–41
Misner CW (1968) The isotropy of the universe. Astrophys J 151:431–457
Weinberg S (1971) Entropy generation and the survival of proto galaxies in an expanding universe. Astrophys J 168:175–194
Murphy GL (1973) Big bang without singularities. Phys Rev D 8:423–4233
Padmanabhan T, Chitre SM (1987) Viscous universe. Phys Lett A 120:433–436
Belinskii VA, Khalatnikov IM (1976) Effect of viscosity on nature of cosmological evolution. Sov Phys JETP 42:205–210
Singh CP (2009) Imperfect fluid cosmology with heat flow. Gravit Cosmol 15:381–390
Meng Xin-he, Ma Zhi-yuan (2012) Rip/singularity free cosmological models with bulk viscosity. Eur Phys J C 72:2053–2057
Collins CB, Stewart JM (1971) Qualitative cosmology. Mon Notices R Astron Soc 153:419–434
Coley AA, Tupper BOJ (1984) Imperfect fluid cosmology with thermodynamics: some exact solutions. Astrophys J 280:26–33
Santos NO, Dias RS, Banerjee A (1985) Isotropic homogeneous universe with bulk viscous fluid. J Math Phys 26:876–882
Banerjee A, Duttachaudhary SB, Sanyal AK (1986) Bianchi type-II cosmological model with viscous fluid. Gen Relat Gravit 18:461–477
Banerjee A, Sanyal AK (1986) Homogeneous anisotropic cosmological models with viscous fluid and magnetic field. Gen Relat Gravit 12:1251–11262
Johri VB, Sudarshan R (1988) Friedmann universes with bulk viscosity. Phys Lett A 132:316–320
Pavon D, Zimdahl W (1993) Dark matter and dissipation. Phys Lett A 179:261–265
Reddy DRK, Rao MVS (2006) Axially symmetric string cosmological model in Brans–Dicke theory of gravitation. Astrophys Space Sci 305:183–186
Reddy DRK, Rao MVS, Kelkar I (2006) Axially symmetric radiating model in Brans–Dicke cosmology. Astrophys Space Sci 306:1–3
Reddy DRK, Naidu RL, Rao VUM (2006) Axially symmetric cosmic strings in a scalar tensor theory. Astrophys Space Sci 306:185–188
Reddy DRK, Naidu RL, Adhav KS (2007) A cosmological model with a negative constant deceleration parameter in scale covariant theory of gravitation. Astrophys Space Sci 307:365–367
Berman MS (1983) A special law of Hubble’s parameter. Nuovo Cimento B 74:182–186
Berman MS, Gomide F (1988) Cosmological models with constant deceleration parameter. Gen Relat Gravit 20:191–198
Saha B (2006) Anisotropic cosmological models with perfect fluid and a Λterm. Astrophys Space Sci 302:83–91
Maharaj SD, Naidoo R (1993) Solutions to the field equations and deceleration parameter. Astrophys Space Sci 208:261–276
Kumar S (2011) Some FRW models of accelerating universe of dark energy. Astrophys Space Sci 332:449–454
Pradhan A, Amirhaschi H, Saha B (2011) Bianchi type-I anisotropic dark energy models with constant deceleration parameter. Int J Theor Phys 50:2923–2938
Amirhaschi H, Pradhan A, Saha B (2011) Variable equation of state for Bianchi type VI 0 dark energy models. Astrophys Space Sci 333:295–303
Baghel PS, Singh JP (2012) Bianchi type V universe with bulk viscous matter and time varying gravitational and cosmological constants. Research in Astron Astrophys 11:1457–1466
Vishwakarma RG (2000) A study of angular size redshift relation for the models in which lambda decays as the energy density. Class Quant Grav 17:3833–3842
Starobinskii AA (1981) Can the effective gravitational constant become negative? Sov Astron Lett 7:36–38
Acknowledgments
Authors acknowledge the financial support of UGC, New Delhi and the department of Mathematics, Gauhati University for giving facilities for research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Das, K., Ali, N. Axially Symmetric Bianchi Type-I Bulk Viscous Cosmological Model with Time Varying Gravitational and Cosmological Constants. Natl. Acad. Sci. Lett. 37, 173–179 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40009-013-0222-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40009-013-0222-3