Abstract
Purpose
Lornoxicam is a drug that is used for various diseases related to inflammation and pain. In the clinical application of lornoxicam, studies on individualized pharmacotherapy and modeling considering interindividual pharmacokinetic variability have rarely been reported. In this study, a population pharmacokinetic modeling study was performed with a search for effective covariates that could explain the interindividual pharmacokinetic variability of lornoxicam.
Methods
Based on the bioequivalence results of 28 healthy Korean males and the identification of various genetic and physicochemical parameters of the participants, a population pharmacokinetic modeling of lornoxicam was performed by a non-linear mixed-effects modeling method using Phoenix NLME.
Results
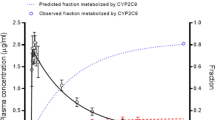
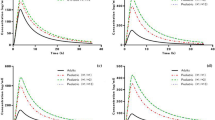
The pharmacokinetics of lornoxicam in the population were well explained by the one-compartment basic model with first-order absorption/elimination and lag-time reflected in the absorption phase. The covariates investigated to account for interindividual pharmacokinetic variability were extended to the established basic model. Creatinine clearance (CrCl), which is used as a general indicator of renal function, was positively correlated with the clearance of lornoxicam, and this was identified as a valid covariate in the population pharmacokinetic model of lornoxicam. According to the genetic polymorphism of CYP2C9, a significant difference was confirmed in the clearance of lornoxicam, which was also a valid covariate in the model.
Conclusion
Considering that the metabolism of lornoxicam is mainly by the CYP2C9 enzyme and a significant proportion of the metabolite is excreted in the urine through the kidneys, it was appropriate to explore the CYP2C9 genotype and CrCl levels as covariates in the population pharmacokinetic model of lornoxicam. Through the results of this study, individualized and effective lornoxicam therapy taking into account the genotype and degree of renal function of individuals will be possible in the future.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Naamani N, Maarouf O, Wilt J, D’Ovidio F, Sonett J, Arcasoy S, Nickolas T, Lederer D, Kawut S (2008) 25: the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease (MDRD) formula predicts kidney failure after lung transplantation. J Heart Lung Transplant 27:S69
Ankier S, Brimelow A, Crome P, Johnston A, Warrington S, Turner P, Ferber H (1988) Chlortenoxicam pharmacokinetics in young and elderly human volunteers. Postgrad Med J 64:752–754
Bae J-W, Choi C-I, Kim M-J, Oh D-H, Keum S-K, Park J-I, Kim B-H, Bang H-K, Oh S-G, Kang B-S (2011) Frequency of CYP2C9 alleles in Koreans and their effects on losartan pharmacokinetics. Acta Pharmacol Sin 32:1303–1308
Balfour JA, Fitton A, Barradell LB (1996) Lornoxicam. Drugs 51:639–657
Bareggi SR, Gambaro V, Valenti M, Benvenuti C (1997) Absorption of oral lornoxicam in healthy volunteers using a granular formulation in comparison with standard tablets. Arzneimittelforschung 47:755–757
Bonnabry P, Leemann T, Dayer P (1996) Role of human liver microsomal CYP2C9 in the biotransformation of lornoxicam. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 49:305–308
Canada (2020) Showing metabocard for Lornoxicam (HMDB0015666)
Choi CI, Kim MJ, Jang CG, Park YS, Bae JW, Lee SY (2011) Effects of the CYP2C9* 1/* 13 genotype on the pharmacokinetics of lornoxicam. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 109:476–480
Dittrich P, Radhofer-Welte S, Magometschnigg D, Kukovetz W, Mayerhofer S, Ferber H (1990) The effect of concomitantly administered antacids on the bioavailability of lornoxicam, a novel highly potent NSAID. Drugs Exp Clin Res 16:57–62
El Edelbi R, Lindemalm S, Eksborg S (2012) Estimation of body surface area in various childhood ages–validation of the Mosteller formula. Acta Paediatr 101:540–544
FDA (2018) Bioanalytical Method Validation Gudiance for Industry, US Department of Health and Human Services, Food and Drug Administration, Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER), Center for Veterinary Medicine (CVM), Rockville, MD, USA
Guo Y, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Chen X, Si D, Zhong D, Fawcett JP, Zhou H (2005) Role of CYP2C9 and its variants (CYP2C9* 3 and CYP2C9* 13) in the metabolism of lornoxicam in humans. Drug Metab Dispos 33:749–753
Hermsen ED, Maiefski MM, Florescu MC, Qiu F, Rupp ME (2009) Comparison of the modification of diet in renal disease and Cockcroft-Gault equations for dosing antimicrobials. Pharmacother J Hum Pharmacol Drug Ther 29:649–655
Hitzenberger G, Radhofer-Welte S, Takacs F, Rosenow D (1990) Pharmacokinetics of lornoxicam in man. Postgrad Med J 66:S22–S27
Hotta M, Li Y, Anme T, Ushijima H (2005) Risk factors for low Kaup index among children in rural ethnic minority areas of Yunnan, China. Pediatr Int 47:147–153
Iida I, Miyata A, Arai M, Hirota M, Akimoto M, Higuchi S, Kobayashi K, Chiba K (2004) Catalytic roles of CYP2C9 and its variants (CYP2C9* 2 and CYP2C9* 3) in lornoxicam 5′-hydroxylation. Drug Metab Dispos 32:7–9
Jang J-H, Jeong S-H, Cho H-Y, Lee Y-B (2019) Population pharmacokinetics of Cis-, Trans-, and total cefprozil in healthy male Koreans. Pharmaceutics 11:531–545
Jeong S-H, Jang J-H, Cho H-Y, Lee Y-B (2020) Population pharmacokinetic analysis of tiropramide in healthy Korean subjects. Pharmaceutics 12:374
Jeong S-H, Jang J-H, Cho H-Y, Lee Y-B (2021) Population pharmacokinetic analysis of cefaclor in healthy Korean subjects. Pharmaceutics 13:754–773
Jonker JW, Schinkel AH (2004) Pharmacological and physiological functions of the polyspecific organic cation transporters: OCT1, 2, and 3 (SLC22A1-3). J Pharmacol Exp Ther 308:2–9
Kang H-A, Cho H-Y, Lee Y-B (2006) Bioequivalence of Lornocam Tablet to Xefo® Tablet (Lornoxicam 4 mg). J Pharm Investig 36:67–73
Kim S-M, Lee S-N, Yoon H, Kang H-A, Cho H-Y, Lee I-K, Lee Y-B (2009) Haplotype analysis and single nucleotide polymorphism frequency of organic cation transporter gene (OCT1 and 2) in Korean subjects. J Pharm Investig 39:345–351
Kuan Y, Hossain M, Surman J, El Nahas AM, Haylor J (2005) GFR prediction using the MDRD and Cockcroft and Gault equations in patients with end-stage renal disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant 20:2394–2401
Kuehl P, Zhang J, Lin Y, Lamba J, Assem M, Schuetz J, Watkins PB, Daly A, Wrighton SA, Hall SD (2001) Sequence diversity in CYP3A promoters and characterization of the genetic basis of polymorphic CYP3A5 expression. Nat Genet 27:383–391
Leabman MK, Huang CC, Kawamoto M, Johns SJ, Stryke D, Ferrin TE, DeYoung J, Taylor T, Clark AG, Herskowitz I (2002) Polymorphisms in a human kidney xenobiotic transporter, OCT2, exhibit altered function. Pharmacogenet Genom 12:395–405
Liang Y, Shi Q, Zhou Y-w (2006) Pharmacokinetics and bioequivalence of lornoxicam tablet in healthy volunteers. Chin J Clin Pharmacol 22:336
Lim Y-J, Cha E-Y, Jung H-E, Ghim J-L, Lee S-J, Kim E-Y, Shin J-G (2014) Genetic polymorphisms of CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP3A4, and CYP3A5 in Vietnamese-Koreans. Transl Clin Pharmacol 22:70–77
Liou Y-H, Lin C-T, Wu Y-J, Wu LS-H (2006) The high prevalence of the poor and ultrarapid metabolite alleles of CYP2D6, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP3A4, and CYP3A5 in Taiwanese population. J Hum Genet 51:857–863
Liu Y-L, Zhang W, Tan Z-R, Ouyang D-S, Luo C-h, Liu Z-Q, Qiu Y, Chen Y, He Y-J, Zhou G (2006) Effect of the CYP2C9* 3 allele on lornoxicam metabolism. Clin Chim Acta 364:287–291
Liu Q, Zhong L-L, Zhao H, Du H-W, Hong Q-Q, S-y H, Tang D (2010) Pharmacokinetics and bioequivalence of 2 kinds of lornoxicam preparations in healthy volunteers. China Pharm 2010:30
Olkkola KT, Brunetto AV, Mattila MJ (1994) Pharmacokinetics of oxicam nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents. Clin Pharmacokinet 26:107–120
Prasad Byrav D, Medhi B, Prakash A, Patyar S, Wadhwa S (2009) Lornoxicam: a newer NSAID. IJPMR 20:27–31
Radhofer-Welte S, Rabasseda X (2000) Lornoxicam, a new potent NSAID with an improved tolerability profile. Drugs Today 36:55–76
Ravic M, Johnston A, Turner P, Takacs F, Rosenow D (1991) The effect of repeated oral doses of lornoxicam on antipyrine elimination in normal human volunteers. Hum Exp Toxicol 10:375–377
Shu Y, Leabman MK, Feng B, Mangravite LM, Huang CC, Stryke D, Kawamoto M, Johns SJ, DeYoung J, Carlson E (2003) Evolutionary conservation predicts function of variants of the human organic cation transporter, OCT1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:5902–5907
Skjodt NM, Davies NM (1998) Clinical pharmacokinetics of lornoxicam. Clin Pharmacokinet 34:421–428
Turner P, Johnston A (1990) Clinical pharmacokinetic studies with lornoxicam. Postgrad Med J 66:S28–S29
Van Schaik RH, Van Der Heiden IP, Van Den Anker JN, Lindemans J (2002) CYP3A5 variant allele frequencies in Dutch Caucasians. Clin Chem 48:1668–1671
Yoo HD, Cho HY, Lee YB (2010) Population pharmacokinetic analysis of cilostazol in healthy subjects with genetic polymorphisms of CYP3A5, CYP2C19 and ABCB1. Br J Clin Pharmacol 69:27–37
Zaid AN, Mousa A, Jaradat N, Bustami R (2017) Lornoxicam immediate-release tablets: formulation and bioequivalence study in healthy mediterranean volunteers using a validated LC-MS/MS method. Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev 6:564–569
Zhang Y, Zhong D, Si D, Guo Y, Chen X, Zhou H (2005) Lornoxicam pharmacokinetics in relation to cytochrome P450 2C9 genotype. Br J Clin Pharmacol 59:14–17
Zhou W-J, Huang M, Wang M, Hua W-Y, Zhang Q-Y (2012) Bioequivalence study of lornoxicam tablets in healthy volunteers by LC–MS/MS method. Chin J Hosp Pharm 5
Acknowledgements
This research did not receive any specific Grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors (S.H. Jeong, J.H. Jang, and Y.B. Lee) have no conflicts of interest relevant to this study to disclose.
Ethical approval
The study protocol was reviewed and approved by the Institutional Review Board of the Institute of Bioequivalence and Bridging Study, Chonnam National University, Gwangju, Republic of Korea. The bioequivalence study permit numbers were 819; 08.22.2005. Clinical studies were conducted in accordance with the Rules of Good Clinical Practice and the revised Declaration of Helsinki for biomedical research with human subjects.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jeong, SH., Jang, JH. & Lee, YB. Population pharmacokinetic analysis of lornoxicam in healthy Korean males considering creatinine clearance and CYP2C9 genetic polymorphism. J. Pharm. Investig. 52, 109–127 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-021-00550-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-021-00550-y