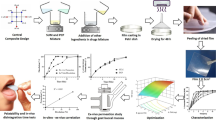
Abstract
Promethazine hydrochloride (PMZ-HCl) is a classical anti-motion sickness drug which has oral bioavailability (25 %) due to extensive hepatic first pass metabolism. To overcome this drawback, novel, fast dissolving sublingual film (FDSF) of drug was developed. FDSF was formulated using pullulan and propylene glycol (PG) by solvent casting method. Complete taste masking was successfully obtained with HP β-CD, aspartame and grape fruit flavour. Complex of drug was proved using Fourier transfer infrared spectroscopy, differential scanning calorimetry and X-ray diffraction studies. Optimization of concentration of pullulan and PG was done using 32 full factorial design. Batches were evaluated for the parameters like elongation, tensile strength, folding endurance and in vitro disintegration studies. In vitro dissolution indicated 100 % drug release within 7.5 min. Environmental scanning electron microscopy studies also showed uniform drug distribution and integrity of film. In vivo sublingual absorption in human indicated that 70 % of drug absorbed in 10 min. The stability studies indicated that label should state “Store at cool, dry place” at temperature 25 °C. So by formulating the taste masked FDSF of PMZ-HCl will give faster onset of action and avoid unnecessary drug intake leading to traveller friendly formulation.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aditya D, Mangal N (2008) Formulation and evaluation of fast dissolving films for delivery of triclosan to the oral cavity. AAPS PharmSciTech 9(2):349–355
Artusi M, Santi P, Colombo P, Junginger HE (2003) Buccal delivery of thiocolchicoside: in vitro and in vivo permeation studies. Int J Pharm 250(1):203–213
Ashok RP, Pradeep RV (2009) Preparation and evaluation of taste masked famotidine formulation using drug/β-cyclodextrin/polymer ternary complexation approach. AAPS PharmSciTech 10:544–550
Basani G, Subash V, Guru S, Madhusudan R (2010) Overview on fast dissolving films. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci 2(3):29–33
Chang RK, Guo X, Burnside BA, Couch RA (2000) Fast dissolving tablets. Pharm Tech 24:52–58
Choudhary DR, Patel VA, Chhalotiya UK, Patel HV, Kundawala AJ (2012) Natural polysaccharides as film former: a feasibility study for development of rapid dissolving films of ondansetron hydrochloride. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci 4(3):78–85
Cilurzo F, Cupone IE, Minghetti P, Burrati S, Gennari CG, Montanari L (2011) Diclofenac fast-dissolving film: suppression of bitterness by taste a sensing system. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 37(3):252–259
Dahiya M, Sumit SA (2009) A review on mouth dissolving films. Curr Drug Deliv 6:469–476
Dixit RP, Puthli SP (2009) Oral strip technology: overview and future potential. J Control Rel 139:94–107
El-Setouhy DA, Abd El-Malak NS (2010) Formulation of a novel tianeptine sodium orodispersible film. AAPS PharmSciTech 11(3):1018–1025
Ghosh TK, Pfister WR (2005) Drug delivery to oral cavity: molecules to market. CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group, Florida
Haware RV, Chaudhari PD, Parakh SR, Bauer-Brandl A (2008) Development of a melting tablet containing promethazine HCl against motion sickness. AAPS PharmSciTech 9(3):1006–1015
Kulkarni AS, Deokule HA, Mane MS, Ghadge DM (2010) Exploration of different polymers for use in the formulation of oral fast dissolving strips. J Curr Pharm Res 2(1):33–35
Mahesh A, Shastri N, Sadanandam M (2010) Development of taste masked fast disintegrating films of levocetirizine dihydrochloride for oral use. Curr Drug Deliv 7(1):21–27
Mishra R, Amin A (2009) Formulation development of taste masked rapidly dissolving films of cetirizine hydrochloride. Pharm Tech USA 33:48–56
Mishra R, Amin A (2011) Formulation and characterization of rapidly dissolving films of cetirizine hydrochloride using pullulan as a film forming agent. Indian J Pharm Edu Res 45:71–77
Narang NA, Sharma JH (2011) Sublingual mucosa as a route for systemic drug delivery. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci 3(2):18–22
Patel VF, Liu F, Brown MB (2011) Advances in oral transmucosal drug delivery. J Control Rel 153(2):106–116
Rajeswari C, Alka A, Javed A, Khar RK (2005) Cyclodextrins in drug delivery: an updated review. AAPS PharmSciTech 6(2):E329–E357
Rathbone MJ (1991) Human buccal absorption. A method for estimating the transfer kinetics of drugs across the human buccal membrane. Int J Pharm 69:103–108
Acknowledgments
These authors, J. N.Shah, K. Shah, T.A. Mehta, declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shah, J.N., Shah, K.N. & Mehta, T.A. Hydroxy propyl β-cyclodextrin complexation of promethazine hydrochloride for the formulation of fast dissolving sublingual film: in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Journal of Pharmaceutical Investigation 45, 91–99 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-014-0150-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-014-0150-3