Abstract
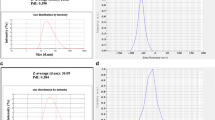
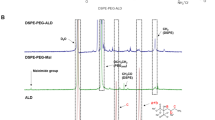
Zoledronic acid (ZOL) is one of the most potent nitrogen containing bisphosphonates (N-BP) which are used for cancer-induced skeletal disease by inhibiting osteoclast-mediated bone resorption. It acts by inhibiting the farnesyldiphosphate synthase which is one of several key enzymes in the mevalonate pathway consequently leading to osteoclast apoptosis. From recent studies, direct anti-cancer effects of bisphosphonates, particularly ZOL, was demonstrated in breast cancers. The synergic anti-cancer effects of ZOL treated with other anti-cancer agents in breast cancer cells were also reported. However, pharmacokinetic properties of ZOL have limited its cytotoxic activities because almost 60 % of injected ZOL are disposed into bone and 40 % of the dose cleared rapidly from blood, so that not enough dose of ZOL delivered to the cancer cells. For this reason, we introduced transferrin-conjugated long-circulating liposomes as targeted delivery system for enhancing the anti-cancer effect of ZOL. Transferrin receptors have been explored as a target to deliver therapeutics into cancer cells due to their increased expression on malignant cells. Liposomes were prepared by a reverse-phase evaporation vesicle method with aqueous ZOL solution. Transferrins were attached to the neutral liposomes via free thiols (–SH) to the PDP-end of the pyridylthiopropionoylamino-PEG-distearoyl-phosphatidyethanolamine (PDP-PEG-DSPE). Liposomes were characterized by measuring size distribution and zeta potential. The mean diameter of liposomes was 190 nm, and the encapsulation efficiency of ZOL was about 10 %, which was determined by HPLC analysis. Based on the 50 % inhibitory concentration (IC50) of ZOL against breast cancer cell MDA-MB-231, increased anti-cancer effect of transferrin-conjugated liposomal ZOL was evaluated compared to free ZOL and non-conjugated liposomal ZOL. In conclusion, transferrin-conjugated liposome can enhance the anti-cancer effect of ZOL and it is suggested that ZOL can be used as an anti-cancer agent with this formulation in breast cancer patients.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aft R (2011) Bisphosphonates in breast cancer: antitumor effects. Clin Adv Hematol Oncol 9(4):292–299
Asikoglu M, Durak FG (2009) The rabbit biodistribution of a therapeutic dose of zoledronic acid labeled with Tc-99m. Appl Radiat Isotopes 67(9):1616–1621
Bartlett GR (1959) Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem 234(3):466–468
Bligh EG, Dyer WJ (1959) A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol 37(8):911–917
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Caraglia M, Marra M, Naviglio S, Botti G, Addeo R, Abbruzzese A (2010) Zoledronic acid: an unending tale for an antiresorptive agent. Expert Opin Pharmacother 11(1):141–154
Chen T, Berenson J, Vescio R, Swift R, Gilchick A, Goodin S, LoRusso P, Ma P, Ravera C, Deckert F, Schran H, Seaman J, Skerjanec A (2002) Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of zoledronic acid in cancer patients with bone metastases. J Clin Pharmacol 42(11):1228–1236
Chern CS, Chiu HC, Yang YS (2006) Interactions between nonionic Triton X surfactants and cholesterol-containing phosphatidylcholine liposomes. J Colloid Interface Sci 302(1):335–340
Clyburn RD, Reid P, Evans CA, Lefley DV, Holen I (2010) Increased anti-tumour effects of doxorubicin and zoledronic acid in prostate cancer cells in vitro: supporting the benefits of combination therapy. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 65(5):969–978
Coleman RE, Winter MC, Cameron D, Bell R, Dodwell D, Keane MM, Gil M, Ritchie D, Passos-Coelho JL, Wheatley D, Burkinshaw R, Marshall SJ, Thorpe H (2010) The effects of adding zoledronic acid to neoadjuvant chemotherapy on tumour response: exploratory evidence for direct anti-tumour activity in breast cancer. Br J Cancer 102(7):1099–1105
Coleman RE, Marshall H, Cameron D, Dodwell D, Burkinshaw R, Keane M, Gil M, Houston SJ, Grieve RJ, Barrett-Lee PJ, Ritchie D, Pugh J, Gaunt C, Rea U, Peterson J, Davies C, Hiley V, Gregory W, Bell R (2011) Breast-cancer adjuvant therapy with zoledronic acid. N Engl J Med 365(15):1396–1405
De Luca A, Lamura L, Gallo M, Daniele G, D’Alessio A, Giordano P, Maiello MR, Pergameno M, Perrone F, Normanno N (2011) Pharmacokinetic evaluation of zoledronic acid. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 7(7):911–918
Drake MT, Clarke BL, Khosla S (2008) Bisphosphonates: mechanism of action and role in clinical practice. Mayo Clin Proc 83(9):1032–1045
Epstein-Barash H, Gutman D, Markovsky E, Mishan-Eisenberg G, Koroukhov N, Szebeni J, Golomb G (2010) Physicochemical parameters affecting liposomal bisphosphonates bioactivity for restenosis therapy: internalization, cell inhibition, activation of cytokines and complement, and mechanism of cell death. J Control Release 146(2):182–195
Faulk WP, Hsi BL, Stevens PJ (1980) Transferrin and transferrin receptors in carcinoma of the breast. Lancet 2(8191):390–392
Forsea AM, Muller C, Riebeling C, Orfanos CE, Geilen CC (2004) Nitrogen-containing bisphosphonates inhibit cell cycle progression in human melanoma cells. Br J Cancer 91(4):803–810
Fox KR (2010) Adding zoledronic acid to endocrine therapy in the adjuvant treatment of hormone-sensitive breast cancer in premenopausal women: a new care standard or a provocative idea? Curr Oncol Rep 12(1):1–3
Gnant M (2011) Anticancer activity of bisphosphonates in breast cancer. Anticancer Agents Med Chem 12:114–122
Goffinet M, Thoulouzan M, Pradines A, Lajoie-Mazenc I, Weinbaum C, Faye JC, Seronie-Vivien S (2006) Zoledronic acid treatment impairs protein geranyl-geranylation for biological effects in prostatic cells. BMC Cancer 6:60
Goni FM, Urbaneja MA, Arrondo JL, Alonso A, Durrani AA, Chapman D (1986) The interaction of phosphatidylcholine bilayers with Triton X-100. Eur J Biochem 160(3):659–665
Haidar A, Jonler M, Folkmar TB, Lund L (2009) Bisphosphonate (zoledronic acid)-induced osteonecrosis of the jaw. Scand J Urol Nephrol 43(6):442–444
Holen I, Coleman RE (2010) Anti-tumour activity of bisphosphonates in preclinical models of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res 12(6):214
Hong M, Zhu S, Jiang Y, Tang G, Sun C, Fang C, Shi B, Pei Y (2010) Novel anti-tumor strategy: PEG-hydroxycamptothecin conjugate loaded transferrin-PEG-nanoparticles. J Control Release 141(1):22–29
Inoue T, Cavanaugh PG, Steck PA, Brunner N, Nicolson GL (1993) Differences in transferrin response and numbers of transferrin receptors in rat and human mammary carcinoma lines of different metastatic potentials. J Cell Physiol 156(1):212–217
Ishida O, Maruyama K, Tanahashi H, Iwatsuru M, Sasaki K, Eriguchi M, Yanagie H (2001) Liposomes bearing polyethyleneglycol-coupled transferrin with intracellular targeting property to the solid tumors in vivo. Pharm Res 18(7):1042–1048
Jagdev SP, Coleman RE, Shipman CM, Rostami HA, Croucher PI (2001) The bisphosphonate, zoledronic acid, induces apoptosis of breast cancer cells: evidence for synergy with paclitaxel. Br J Cancer 84(8):1126–1134
Jiang Y, Zhang XQ, Xu ZR (2004) Analysis of zoledronic acid and its related substances by ion-pair RP-LC. Chromatographia 60(7–8):405–409
Lee MV, Fong EM, Singer FR, Guenette RS (2001) Bisphosphonate treatment inhibits the growth of prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res 61(6):2602–2608
Li X, Ding L, Xu Y, Wang Y, Ping Q (2009) Targeted delivery of doxorubicin using stealth liposomes modified with transferrin. Int J Pharm 373(1–2):116–123
Liu D, Mori A, Huang L (1992) Role of liposome size and RES blockade in controlling biodistribution and tumor uptake of GM1-containing liposomes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1104(1):95–101
Luckman SP, Hughes DE, Coxon FP, Graham R, Russell G, Rogers MJ (1998) Nitrogen-containing bisphosphonates inhibit the mevalonate pathway and prevent post-translational prenylation of GTP-binding proteins, including Ras. J Bone Miner Res 13(4):581–589
Maeda H (2001) The enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect in tumor vasculature: the key role of tumor-selective macromolecular drug targeting. Adv Enzyme Regul 41:189–207
Maruyama K (2011) Intracellular targeting delivery of liposomal drugs to solid tumors based on EPR effects. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 63(3):161–169
Matsumura Y, Maeda H (1986) A new concept for macromolecular therapeutics in cancer chemotherapy: mechanism of tumoritropic accumulation of proteins and the antitumor agent smancs. Cancer Res 46(12 Pt 1):6387–6392
Mehrotra B, Ruggiero S (2006) Bisphosphonate complications including osteonecrosis of the jaw. Hematol Am Soc Hematol Educ Program 356–360:515
Neville-Webbe HL, Coleman RE, Holen I (2010) Combined effects of the bisphosphonate, zoledronic acid and the aromatase inhibitor letrozole on breast cancer cells in vitro: evidence of synergistic interaction. Br J Cancer 102(6):1010–1017
Ottewell PD, Brown HK, Jones M, Rogers TL, Cross SS, Brown NJ, Coleman RE, Holen I (2012) Combination therapy inhibits development and progression of mammary tumours in immunocompetent mice. Breast Cancer Res Treat 133:523–536
Rao BM, Srinivasu MK, Rani ChP, kumar SS, Kumar PR, Chandrasekhar KB, Veerender M (2005) A validated stability indicating ion-pair RP-LC method for zoledronic acid. J Pharm Biomed Anal 39(3–4):781–790
Senaratne SG, Colston KW (2002) Direct effects of bisphosphonates on breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res 4(1):18–23
Senaratne SG, Pirianov G, Mansi JL, Arnett TR, Colston KW (2000) Bisphosphonates induce apoptosis in human breast cancer cell lines. Br J Cancer 82(8):1459–1468
Shindelman JE, Ortmeyer AE, Sussman HH (1981) Demonstration of the transferrin receptor in human breast cancer tissue. Potential marker for identifying dividing cells. Int J Cancer 27(3):329–334
Szoka F Jr, Papahadjopoulos D (1978) Procedure for preparation of liposomes with large internal aqueous space and high capture by reverse-phase evaporation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 75(9):4194–4198
Tassone P, Tagliaferri P, Viscomi C, Palmieri C, Caraglia M, D’Alessandro A, Galea E, Goel A, Abbruzzese A, Boland CR, Venuta S (2003) Zoledronic acid induces antiproliferative and apoptotic effects in human pancreatic cancer cells in vitro. Br J Cancer 88(12):1971–1978
Walker RA, Day SJ (1986) Transferrin receptor expression in non-malignant and malignant human breast tissue. J Pathol 148(3):217–224
Weiss HM, Pfaar U, Schweitzer A, Wiegand H, Skerjanec A, Schran H (2008) Biodistribution and plasma protein binding of zoledronic acid. Drug Metab Dispos 36(10):2043–2049
Winter MC, Holen I, Coleman RE (2008) Exploring the anti-tumour activity of bisphosphonates in early breast cancer. Cancer Treat Rev 34(5):453–475
Yamada J, Tsuno NH, Kitayama J, Tsuchiya T, Yoneyama S, Asakage M, Okaji Y, Shuno Y, Nishikawa T, Tanaka J, Takahashi K, Nagawa H (2009) Anti-angiogenic property of zoledronic acid by inhibition of endothelial progenitor cell differentiation. J Surg Res 151(1):115–120
Zeisberger SM, Odermatt B, Marty C, Zehnder-Fjallman AH, Ballmer-Hofer K, Schwendener RA (2006) Clodronate-liposome-mediated depletion of tumour-associated macrophages: a new and highly effective antiangiogenic therapy approach. Br J Cancer 95(3):272–281
Zhao M, Tominaga Y, Ohuchida K, Mizumoto K, Cui L, Kozono S, Fujita H, Maeyama R, Toma H, Tanaka M (2012) Significance of combination therapy of zoledronic acid and gemcitabine on pancreatic cancer. Cancer Sci 103:58–66
Conflict of interest
All authors (M Choi, DH Shin and JS Kim) declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, M., Shin, D.H. & Kim, JS. Repositioning of zoledronic acid for breast cancer using transferrin-conjugated liposome. Journal of Pharmaceutical Investigation 43, 461–469 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-013-0091-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-013-0091-2