Abstract
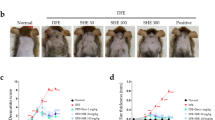
Effect of oral administration of methanolic extract from Scutellaria baicalensis root (SB) on the development of oxazolone-induced atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions in hairless mice was investigated. Mice were orally administered SB 250, 500 mg/kg/day, or dexamethasone 1 mg/kg/day for 33 days. Oral administration of SB inhibited the development of clinical symptoms, and reduced dermal mast cell infiltration, but did not show definite suppressive effect on elevation of serum total IgE level under experimental condition. Interleukin (IL)-6 level in serum and the mRNA expressions of IL-4, IL-13, IL-12, interfereon-γ, transforming growth factor-β, and fork head box P3 in draining lymph nodes were not significantly affected by SB administration, indicating SB could alleviate atopic dermatitis via the inhibition of mast cell infiltration.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akdis M, Blaser K, and Akdis CA (2005) T regulatory cells in allergy: Novel concepts in the pathogenesis, prevention, and treatment of allergic diseases. J Allergy Clin Immunol 116, 961–968.
Bae IH, Yun JW, Seo JA, Jung KM, Kim K, Noh M et al. (2010) Immunohistological comparison of cutaneous pathology of three representative murine atopic dermatitis models. J Dermatol Sci 59, 57–60.
Bieber T (2010) Atopic dermatitis. Ann Dermatol 22, 125–137.
Braun CM, Huang SK, Bashian GG, Kagey Sobotka A, Lichtenstein LM, and Essayan DM (1997) Corticosteroid modulation of human, antigenspecific Th1 and Th2 responses. J Allergy Clin Immunol 100, 400–407.
Carmi-Levy I, Homey B, and Soumelis V (2011) A modular view of cytokine networks in atopic dermatitis. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 4, 245–253.
Choi YH, Han EH, Chai OH, Kim YK, Kim KT, and Song CH (2010) Scutellaria baicalensis inhibits mast cell-mediated anaphylactic reactions. Korean J Phys Anthropol 23, 217–227.
Cookson W (2004) The immunogenetics of asthma and eczema: A new focus on the epithelium. Nat Rev Immunol 4, 978–988.
Hokazono H, Omori T, and Ono K (2010) Effects of single and combined administration of fermented barley extract and gamma-aminobutyric acid on the development of atopic dermatitis in NC/Nga mice. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 74, 135–139.
Ishihara K and Hirano T (2002) IL-6 in autoimmune disease and chronic inflammatory proliferative disease. Cytokine Growth F R 13, 357–368.
Isis M van Loon ND (1997) The golden root: Clinical applications of scutellaria baicalensis georgi flavonoids as modulators of the inflammatory response. Altern Med Rev 2, 472–480.
Kawakami T, Ando T, Kimura M, Wilson BS, and Kawakami Y (2009) Mast cells in atopic dermatitis. Curr Opin Immunol 21, 666–678.
Kim DS, Son EJ, Kim M, Heo YM, Nam JB, Ro JY et al. (2010a) Antiallergic herbal composition from Scutellaria baicalensis and Phyllostachys edulis. Planta Med 76, 678–682.
Kim DY, Jung JA, Kim TH, Seo SW, Jung SK, and Park CS (2009a) Oral administration of Uncariae rhynchophylla inhibits the development of DNFB-induced atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions via IFN-gamma down-regulation in NC/Nga mice. J Ethnopharmacol 122, 567–572.
Kim EH, Shim B, Kang S, Jeong G, Lee JS, Yu YB et al. (2009b) Antiinflammatory effects of Scutellaria baicalensis extract via suppression of immune modulators and MAP kinase signaling molecules. J Ethnopharmacol 126, 320–331.
Kim J, Lee I, Park S, and Choue R (2010b) Effects of Scutellariae radix and Aloe vera gel extracts on immunoglobulin E and cytokine levels in atopic dermatitis NC/Nga mice. J Ethnopharmacol 132, 529–532.
Kim MS, Hur YG, Kim WG, Park BW, Ahn KS, Kim JJ et al. (2011) Inhibitory effect of Platycodon grandiflorum on Th1 and Th2 immune responses in a murine model of 2,4-dinitrofluorobenzene-induced atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 106, 54–61.
Kim SH, Kim HJ, and Jung JY (2009c) Effects of baicalein on picryl chloride-induced contact dermatitis in BALB/c mice. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr 38, 160–165.
Kim YH and Park YS (2006) Effect of Scutellaria baicalensis water extract on antioxidative activity and epidermal thickness in DNCB-induced allergic contact dermatitis animal model. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr 35, 543–548.
Kindt TJ, Goldsby RA, and Osborne BA (2007) Immunology. pp. 380–386, W.H. Freeman and Company, New York, NY.
Kitagaki H, Fujisawa S, Watanabe K, Hayakawa K, and Shiohara T (1995) Immediate-type hypersensitivity response followed by a late reaction is induced by repeated epicutaneous application of contact sensitizing agents in mice. J Invest Dermatol 105, 749–755.
Kwon HK, Lee CG, So JS, Chae CS, Hwang JS, Sahoo A et al. (2010) Generation of regulatory dendritic cells and CD4+Foxp3+ T cells by probiotics administration suppresses immune disorders. Proc Natl Acad Sci 107, 2159–2164.
Lee HS, Kim SK, Han JB, Choi HM, Park JH, Kim EC et al. (2006) Inhibitory effects of Rumex japonicus Houtt. on the development of atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions in NC/Nga mice. Br J Dermatol 155, 33–38.
Lee JH, Jung KM, Bae IH, Cho S, Seo DB, Lee SJ et al. (2009) Antiinflammatory and barrier protecting effect of Lithospermum erythrorhizon extracts in chronic oxazolone-induced murine atopic dermatitis. J Dermatol Sci 56, 64–66.
Leung DY, Boguniewicz M, Howell MD, Nomura I, and Hamid QA (2004) New insights into atopic dermatitis. J Clin Invest 113, 651–657.
Li HB, Jiang Y, and Chen F (2004) Separation methods used for Scutellaria baicalensis active components. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 812, 277–290.
Liu FT, Goodarzi H, and Chen HY (2011) IgE, mast cells, and eosinophils in atopic dermatitis. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 41, 298–310.
Man M-Q, Hatano Y, Lee SH, Man M, Chang S, Feingold KR et al. (2008) Characterization of a hapten-induced, murine model with multiple features of atopic dermatitis: structural, immunologic, and biochemical changes following single versus multiple oxazolone challenges. J Invest Dermatol 128, 79–86.
Matsumoto M, Kotani M, Fujita A, Higa S, Kishimoto T, Suemura M et al. (2002) Oral administration of persimmon leaf extract ameliorates skin symptoms and transepidermal water loss in atopic dermatitis model mice, NC/Nga. Br J Dermatol 146, 221–227.
Matsuoka H, Maki N, Yoshida S, Arai M, Wang J, Oikawa Y, et al. (2003) A mouse model of the atopic eczema/dermatitis syndrome by repeated application of a crude extract of house-dust mite Dermatophagoides farinae. Allergy 58, 139–145.
Park EJ, Park KC, Eo H, Seo J, Son M, Kim KH et al. (2007) Suppression of spontaneous dermatitis in NC/Nga murine model by PG102 isolated from Actinidia arguta. J Invest Dermatol 127, 1154–1160.
Shiohara T, Hayakawa J, and Mizukawa Y (2004) Animal models for atopic dermatitis: Are they relevant to human disease? J Dermatol Sci 36, 1–9.
Szegedi A, Barth S, Nagy G, Szodoray P, Gl M, Sipka S et al. (2009) Regulatory T cells in atopic dermatitis: epidermal dendritic cell clusters may contribute to their local expansion. Br J Dermatol 160, 984–993.
Tomimori Y, Tanaka Y, Goto M, and Fukuda Y (2005) Repeated topical challenge with chemical antigen elicits sustained dermatitis in NC/Nga mice in specific-pathogen-free condition. J Invest Dermatol 124, 119–124.
Yano S, Umeda D, Yamashita S, Yamada K, and Tachibana H (2009) Dietary apigenin attenuates the development of atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions in NC/Nga mice. J Nutr Biochem 20, 876–881.
Yoon SB, Han HS, and Lee YJ (2011) Effect of Scutellariae radix extract on the proinflammatory mediators in Raw 264.7 cells induced by LPS. Korean J Herbology 26, 75–81.
Yun MY, Yang JH, Kim DK, Cheong KJ, Song HH, Kim DH et al. (2010) Therapeutic effects of baicalein on atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions of NC/Nga mice induced by dermatophagoides pteronyssinus. Int Immunopharmacol 10, 1142–1148.
Zheng H, Jeong YJ, Song J, and Ji GE (2011) Oral administration of ginsenoside Rh1 inhibits the development of atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions induced by oxazolone in hairless mice. Int Immunopharmacol 11, 511–518.
Ziegler SF (2006) FOXP3: Of mice and men. Annu Rev Immunol 24, 209–226.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, J., Zheng, H., Seo, H.J. et al. Effect of oral administration of Scutellaria Baicalensis root extract on atopic dermatitis-like skin lesion induced by oxazolone in hairless mice. J Korean Soc Appl Biol Chem 55, 175–181 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13765-012-1047-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13765-012-1047-3