Abstract
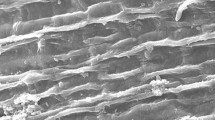
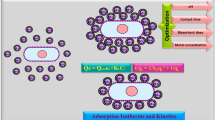
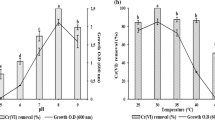
In this study, we investigated the modeling of chromium (Cr(VI)) removal using globally available plant biomass: Phragmites australis and Ziziphus spina-christi. Biosorption parameters were initial Cr(VI) concentration (50–800 mg L−1), contact time (1–180 min), adsorbent dose (0.25–2.0 g L−1), and pH (2–8) at agitation speed of 100 rpm. Based on the results of batch experiments and modeling, pseudo-second-order model was fitted to the experimental data where R2 = 0.99; besides, diffusion model played a significant role in the rate-determining step. Isotherm models were fitted in the order of Langmuir > Freundlich > Temkin models. Maximum adsorption capacities were recorded 21.32 mg g−1 and 15.55 mg g−1 for Phragmites australis and Ziziphus spina-christi, respectively. Insights into biosorption behavior were determined using Fourier-transform infrared spectra (FT-IR), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX). SEM–EDX revealed the chromium presence and its accumulation on both biosorbents after the biosorption process. Cr(VI) biosorption mechanism is illustrated and can be related to electrostatic interactions, reduction and chelation/complexation with the functional groups of both adsorbents.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altun T, Parlayıcı Ş, Pehlivan E (2016) Hexavalent chromium removal using agricultural waste “rye husk”. Desalin Water Treat 57(38):17748–17756
Barros A, da Silva M, Kleinübing S (2018) Evaluation of copper and lead biosorption on modified azolla pinnata (r. Br.). Environ Eng Manag J (EEMJ) 17(1):83–94
Chen H, Dou J, Xu H (2017) Removal of Cr(VI) ions by sewage sludge compost biomass from aqueous solutions: reduction to Cr(III) and biosorption. Appl Surf Sci 425:728–735
Chowdhury S, Mazumder MJ, Al-Attas O, Husain T (2016) Heavy metals in drinking water: occurrences, implications, and future needs in developing countries. Sci Total Environ 569:476–488
Dawodu FA, Akpan BM, Akpomie KG (2020) Sequestered capture and desorption of hexavalent chromium from solution and textile wastewater onto low cost Heinsia crinita seed coat biomass. Appl Water Sci 10(1):1–15
Derdour K, Bouchelta C, Naser-Eddine AK, Medjram MS, Magri P (2018) Removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions by using activated carbon supported iron catalysts as efficient adsorbents. World J Eng 15(1):3–13
Ding D-X, Liu X-T, Hu N, Li G-Y, Wang Y-D (2012) Removal and recovery of uranium from aqueous solution by tea waste. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 293(3):735–741
Duarte B, Silva V, Caçador I (2012) Hexavalent chromium reduction, uptake and oxidative biomarkers in halimione portulacoides. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 83:1–7
Fawzy M, Nasr M, Abdel-Gaber A, Fadly S (2016) Biosorption of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution using agricultural wastes, with artificial intelligence approach. Sep Sci Technol 51(3):416–426
Hlihor RM, Figueiredo H, Tavares T, Gavrilescu M (2017) Biosorption potential of dead and living arthrobacter viscosus biomass in the removal of Cr(VI): batch and column studies. Process Saf Environ Prot 108:44–56
Jobby R, Jha P, Yadav AK, Desai N (2018) Biosorption and biotransformation of hexavalent chromium [cr (vi)]: a comprehensive review. Chemosphere 207:255–266
Karri RR, Sahu J, Meikap B (2020) Improving efficacy of Cr(VI) adsorption process on sustainable adsorbent derived from waste biomass (sugarcane bagasse) with help of ant colony optimization. Ind Crops Prod 143:111927
Khalid R, Aslam Z, Abbas A, Ahmad W, Ramzan N, Shawabkeh R (2018) Adsorptive potential of acacia nilotica based adsorbent for chromium(VI) from an aqueous phase. Chin J Chem Eng 26(3):614–622
Kurniawan A, Sisnandy VOA, Trilestari K, Sunarso J, Indraswati N, Ismadji S (2011) Performance of durian shell waste as high capacity biosorbent for Cr(VI) removal from synthetic wastewater. Ecol Eng 37(6):940–947
Kushwaha S, Sudhakar PP (2013) Sorption of uranium from aqueous solutions using palm-shell-based adsorbents: a kinetic and equilibrium study. J Environ Radioact 126:115–124
Laxmi V, Kaushik G (2020) Toxicity of hexavalent chromium in environment, health threats, and its bioremediation and detoxification from tannery wastewater for environmental safety. In: Saxena G, Bharagava RN (eds) Bioremediation of industrial waste for environmental safety: volume I: industrial waste and its management. Springer, Singapore, pp 223–243
Mahmoud AED (2020a) Eco-friendly reduction of graphene oxide via agricultural byproducts or aquatic macrophytes. Mater Chem Phys 253:123336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2020.123336
Mahmoud AED (2020b) Graphene-based nanomaterials for the removal of organic pollutants: insights into linear versus nonlinear mathematical models. J Environ Manag 270:110911
Mahmoud AED, Fawzy M (2015) Statistical methodology for cadmium (cd2 +) removal from wastewater by different plant biomasses. J Bioremed Biodeg 6(304):2
Mahmoud AED, Fawzy M (2016) Bio-based methods for wastewater treatment: green sorbents. In: Ansari AA, Gill SS, GillG R, Lanza R, Newman L (eds) Phytoremediation: management of environmental contaminants, vol 3. Springer, Cham, pp 209–238
Mahmoud AED, Fawzy M, Radwan A (2016) Optimization of cadmium (cd2+) removal from aqueous solutions by novel biosorbent. Int J Phytorem 18(6):619–625
Mahmoud AED, Stolle A, Stelter M (2018a) Sustainable synthesis of high-surface-area graphite oxide via dry ball milling. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6(5):6358–6369. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b00147
Mahmoud AED, Stolle A, Stelter M, Braeutigam P (2018) Adsorption technique for organic pollutants using different carbon materials. In: Abstracts of papers of the American Chemical Society. Amer Chemical Soc 1155 16th st, NW, Washington, DC 20036 USA
Mahmoud AED, Franke M, Stelter M, Braeutigam P (2020) Mechanochemical versus chemical routes for graphitic precursors and their performance in micropollutants removal in water. Powder Technol 366:629–640. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2020.02.073
Mella B, Glanert AC, Gutterres M (2015) Removal of chromium from tanning wastewater and its reuse. Process Saf Environ Prot 95:195–201
Miretzky P, Cirelli AF (2010) Cr(VI) and Cr(III) removal from aqueous solution by raw and modified lignocellulosic materials: a review. J Hazard Mater 180(1–3):1–19
Mishra A, Dubey A, Shinghal S (2015) Biosorption of chromium(VI) from aqueous solutions using waste plant biomass. Int J Environ Sci Technol 12(4):1415–1426. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-014-0516-0
Mondal NK, Samanta A, Roy P, Das B (2019) Optimization study of adsorption parameters for removal of Cr(VI) using magnolia leaf biomass by response surface methodology. Sustain Water Resour Manag 5(4):1627–1639
Moussavi G, Barikbin B (2010) Biosorption of chromium(VI) from industrial wastewater onto pistachio hull waste biomass. Chem Eng J 162(3):893–900
Nasr M, Mahmoud AED, Fawzy M, Radwan A (2017) Artificial intelligence modeling of cadmium(II) biosorption using rice straw. Appl Water Sci 7(2):823–831
Niazi L, Lashanizadegan A, Sharififard H (2018) Chestnut oak shells activated carbon: preparation, characterization and application for Cr(VI) removal from dilute aqueous solutions. J Clean Prod 185:554–561
Oves M, Khan MS, Zaidi A (2013) Biosorption of heavy metals by Bacillus thuringiensis strain OSM29 originating from industrial effluent contaminated north Indian soil. Saudi J Biol Sci 20(2):121–129
Pholosi A, Naidoo EB, Ofomaja AE (2020a) Batch and continuous flow studies of Cr(VI) adsorption from synthetic and real wastewater by magnetic pine cone composite. Chem Eng Res Des 153:806–818. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2019.11.004
Pholosi A, Naidoo EB, Ofomaja AE (2020b) Intraparticle diffusion of Cr(VI) through biomass and magnetite coated biomass: a comparative kinetic and diffusion study. S Afr J Chem Eng 32:39–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajce.2020.01.005
Pillai SS, Mullassery MD, Fernandez NB, Girija N, Geetha P, Koshy M (2013) Biosorption of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution by chemically modified potato starch: equilibrium and kinetic studies. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 92:199–205
Prabhu SG, Srinikethan V, Hegde S (2020) Pelletization of pristine pteris vittata l Pinnae powder and its application as a biosorbent of CD(II) and Cr(VI). SN Appl Sci 2(1):1–9
Rathinam A, Maharshi B, Janardhanan SK, Jonnalagadda RR, Nair BU (2010) Biosorption of cadmium metal ion from simulated wastewaters using hypnea valentiae biomass: a kinetic and thermodynamic study. Biores Technol 101(5):1466–1470
Shahnaz T, Patra C, Sharma V, Selvaraju N (2020) A comparative study of raw, acid-modified and EDTA-complexed acacia auriculiformis biomass for the removal of hexavalent chromium. Chem Ecol 36(4):1–22
Shukla D, Vankar PS (2012) Efficient biosorption of chromium(VI) ion by dry araucaria leaves. Environ Sci Pollut Res 19(6):2321–2328
Ullah I, Nadeem R, Iqbal M, Manzoor Q (2013) Biosorption of chromium onto native and immobilized sugarcane bagasse waste biomass. Ecol Eng 60:99–107
Wang T, Sun H, Ren X, Li B, Mao H (2018) Adsorption of heavy metals from aqueous solution by UV-mutant Bacillus subtilis loaded on biochars derived from different stock materials. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 148:285–292
Xu M, McKay G (2017) Removal of heavy metals, lead, cadmium, and zinc, using adsorption processes by cost-effective adsorbents. In: Bonilla-Petriciolet A, Mendoza-Castillo DI, Reynel-Ávila HE (eds) Adsorption processes for water treatment and purification. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 109–138
Yang S, Jin P, Wang X, Zhang Q, Chen X (2016) Phosphate recovery through adsorption assisted precipitation using novel precipitation material developed from building waste: behavior and mechanism. Chem Eng J 292:246–254
Acknowledgements
The first and second authors would like to thank the team of “Green Technology Group,” Environmental Sciences Department and the research project entitled: Smart wireless sensor network to detect and purify water salinity and pollution for agriculture irrigation (SMARTWATIR), ERANETMED; Grant Number: 3.227. Furthermore, the support of Science, Technology, and Innovation Funding Authority (STDF-STIFA), Egypt, for the Project ID: 42961.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Jing Chen.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mahmoud, A.E.D., Fawzy, M., Hosny, G. et al. Equilibrium, kinetic, and diffusion models of chromium(VI) removal using Phragmites australis and Ziziphus spina-christi biomass. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 18, 2125–2136 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-020-02968-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-020-02968-7